Honors Chemistry Name_________________________________
... neutral atom in long form and short form. Write the electron configuration of an ion in long and short form. Relate the position of an atom on the periodic table and its predicted electron configuration. Identify the number of valence electrons in a given atom or ion. Explain the similaritie ...
... neutral atom in long form and short form. Write the electron configuration of an ion in long and short form. Relate the position of an atom on the periodic table and its predicted electron configuration. Identify the number of valence electrons in a given atom or ion. Explain the similaritie ...
worksheet 7b answers - Iowa State University
... Iowa State University 1) Effective Nuclear Charge: the net positive charge experienced by an electron in a many-electron atom. What is the equation? Zeff = Z – S Z = atoms number (# of protons or electrons) S = Shielding/Screening electrons Same n: 0.35 n-1: 0.85 n-2,3+: 1 ...
... Iowa State University 1) Effective Nuclear Charge: the net positive charge experienced by an electron in a many-electron atom. What is the equation? Zeff = Z – S Z = atoms number (# of protons or electrons) S = Shielding/Screening electrons Same n: 0.35 n-1: 0.85 n-2,3+: 1 ...
1. Millikan did his experiments with the balance of
... Mo3+ is paramagnetic because in the d orbital there are unpaired electrons. b.) The condensed ground-state electron configuration of Au+ : [Xe] 6s2, 4f14,5d8 Au+ is paramagnetic because in the d orbital there are unpaired electrons. c.) The condensed ground-state electron configuration of Mn2+ : [Ar ...
... Mo3+ is paramagnetic because in the d orbital there are unpaired electrons. b.) The condensed ground-state electron configuration of Au+ : [Xe] 6s2, 4f14,5d8 Au+ is paramagnetic because in the d orbital there are unpaired electrons. c.) The condensed ground-state electron configuration of Mn2+ : [Ar ...
November 18
... and how much energy does it have? To find frequency, use first formula, c=lambda x frequency Frequency = 3x 108 m/s / 700 x 10-9 meters = 4.29 x 1014 Hz To find Energy, plug it into the second formula: E = hf = (6.6 x 10-34) x (4.29 x 1014 Hz) = 2.82 x 10-19 Joules What is Fire? Excited electrons wh ...
... and how much energy does it have? To find frequency, use first formula, c=lambda x frequency Frequency = 3x 108 m/s / 700 x 10-9 meters = 4.29 x 1014 Hz To find Energy, plug it into the second formula: E = hf = (6.6 x 10-34) x (4.29 x 1014 Hz) = 2.82 x 10-19 Joules What is Fire? Excited electrons wh ...
Introduction to Chemistry
... To show that light has both wave and particulate properties. To describe how diffraction experiments were used to demonstrate the dual nature of all matter. To show that the line spectrum of hydrogen demonstrates the quanitzed nature of the energy of its electron. To describe the development of the ...
... To show that light has both wave and particulate properties. To describe how diffraction experiments were used to demonstrate the dual nature of all matter. To show that the line spectrum of hydrogen demonstrates the quanitzed nature of the energy of its electron. To describe the development of the ...
WORKSHEET 36: ATOMIC PROPERTIES
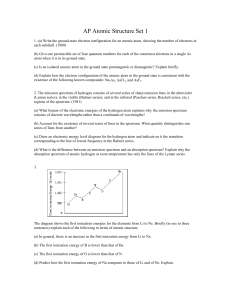
... 17. How would you expect the magnitude of the energy released in a similar process (5 th shell 1st shell transition) in question 16 to vary for a He+ ion? Explain your answer. _____________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________ ...
... 17. How would you expect the magnitude of the energy released in a similar process (5 th shell 1st shell transition) in question 16 to vary for a He+ ion? Explain your answer. _____________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________ ...
المحاضرة الثانية اساسيات الكم
... (i) Stationary states exist in which the energy of the electron is constant; such states ...
... (i) Stationary states exist in which the energy of the electron is constant; such states ...
Exam 3 Review - Iowa State University
... d. Na>Mg>Si>P>Ar e. Ar>P>Si>Mg>Na 8. Which of the following has the smallest ionization energy. a. Mg b. Se c. Ba d. Po 9. Which has the largest 2nd Ionization energy between K and Ca? a. K b. Ca c. Both K and Ca have the same second Ionization energy d. It’s impossible to tell 10. In terms of elect ...
... d. Na>Mg>Si>P>Ar e. Ar>P>Si>Mg>Na 8. Which of the following has the smallest ionization energy. a. Mg b. Se c. Ba d. Po 9. Which has the largest 2nd Ionization energy between K and Ca? a. K b. Ca c. Both K and Ca have the same second Ionization energy d. It’s impossible to tell 10. In terms of elect ...
Ch1-8 Brown and LeMay Review
... CrO42SO42OH7. Calculate the molar concentration of OH- when 40.0 mL of 0.25 M KOH is added to 60.0 mL of 0.15 M Ba(OH)2 ? Assume the volumes are additive. Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle Hund’s Rule Wave nature of light Pauli Exclusion Principle Shielding effect A) Can be used to predict that a gas ...
... CrO42SO42OH7. Calculate the molar concentration of OH- when 40.0 mL of 0.25 M KOH is added to 60.0 mL of 0.15 M Ba(OH)2 ? Assume the volumes are additive. Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle Hund’s Rule Wave nature of light Pauli Exclusion Principle Shielding effect A) Can be used to predict that a gas ...
Chap 2 Solns
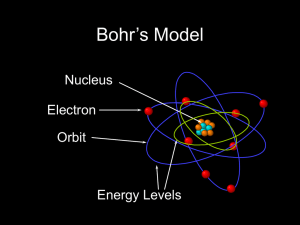
... 2.4 (a) Two important quantum-mechanical concepts associated with the Bohr model of the atom are (1) that electrons are particles moving in discrete orbitals, and (2) electron energy is quantized into shells. (b) Two important refinements resulting from the wave-mechanical atomic model are (1) that ...
... 2.4 (a) Two important quantum-mechanical concepts associated with the Bohr model of the atom are (1) that electrons are particles moving in discrete orbitals, and (2) electron energy is quantized into shells. (b) Two important refinements resulting from the wave-mechanical atomic model are (1) that ...
09 Exam 1 Key
... 7. (8) Fill in the blanks with a word from the following list of possibilities. ...
... 7. (8) Fill in the blanks with a word from the following list of possibilities. ...
Ionization

Ionization is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons to form ions, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. Ionization can result from the loss of an electron after collisions with sub atomic particles, collisions with other atoms, molecules and ions, or through the interaction with light. Heterolytic bond cleavage and heterolytic substitution reactions can result in the formation of ion pairs. Ionization can occur through radioactive decay by the internal conversion process, in which an excited nucleus transfers its energy to one of the inner-shell electrons causing it to be ejected.