Powerpoint handout
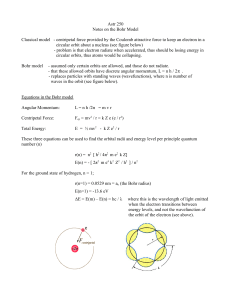
... proposing that electrons in atoms could have only certain energies, and that light was given off when an electron underwent a transition from a higher energy level to a lower one. ...
... proposing that electrons in atoms could have only certain energies, and that light was given off when an electron underwent a transition from a higher energy level to a lower one. ...
Rutherford–Bohr model
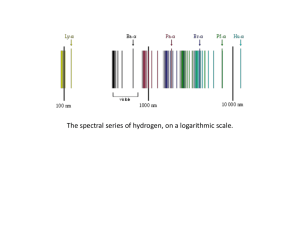
... The four visible hydrogen emission spectrum lines in the Balmer series. H-alpha is the red line at the right. ...
... The four visible hydrogen emission spectrum lines in the Balmer series. H-alpha is the red line at the right. ...
AP Chemistry Chapter 6 Outline for Concepts to Know 6.1 Wave
... 6.3 Line Spectra and the Bohr Model Emission spectrum of hydrogen (see p. 225) is due to energy transitions of the single electron of hydrogen being excited to higher energy levels and then falling back down, emitting specific wavelengths of light. Line spectra for other elements are generally m ...
... 6.3 Line Spectra and the Bohr Model Emission spectrum of hydrogen (see p. 225) is due to energy transitions of the single electron of hydrogen being excited to higher energy levels and then falling back down, emitting specific wavelengths of light. Line spectra for other elements are generally m ...
Chemistry 1 Concept 5 “Electrons in Atoms” Study Guide
... 18. The spin quantum number indicates that the number of possible spin states for an electron in an orbital is __________ 19. The angular momentum quantum number indicates the ________________________ 20. What is the energy of a photon whose frequency is 5.0 x 1020 Hz? ______________ 21. What state ...
... 18. The spin quantum number indicates that the number of possible spin states for an electron in an orbital is __________ 19. The angular momentum quantum number indicates the ________________________ 20. What is the energy of a photon whose frequency is 5.0 x 1020 Hz? ______________ 21. What state ...
Periodic Trends/Patterns
... Effective Nuclear Charge: The s, p, d, and f orbitals within a given shell have slightly different energies. The difference in energies between subshells result in electron–electron repulsion which shields outer electrons from the nucleus. The net nuclear charge felt by an electron is called the eff ...
... Effective Nuclear Charge: The s, p, d, and f orbitals within a given shell have slightly different energies. The difference in energies between subshells result in electron–electron repulsion which shields outer electrons from the nucleus. The net nuclear charge felt by an electron is called the eff ...
Homework 4 Answer Key
... spherical polar coordinate system used for an atom is simply r. An average from many measurements is the expectation value,. Since our 2s wave function is normalized,
we have in general
r
...
... spherical polar coordinate system used for an atom is simply r. An average from many measurements is the expectation value,
Chapter 4-Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms
... 1. What is the best basis for describing the energy interaction between protons and electrons in this model? ...
... 1. What is the best basis for describing the energy interaction between protons and electrons in this model? ...
Atomic Structure and Periodicity
... atoms of a transition element The ground-state configuration of a negative ion of a halogen The ground-state configuration of a common ion of an alkaline earth element ...
... atoms of a transition element The ground-state configuration of a negative ion of a halogen The ground-state configuration of a common ion of an alkaline earth element ...
21Sc , 48 22Ti , 50 22Ti , 50
... 9. A 3.6 g sample of lithium contains ________ atoms. 10. How many elements are in the fifth period of the periodic table? 11. What is the correct formula for an ionic compound that contains magnesium ions and fluoride ions? 12. What is the correct name for NH4ClO4? 13. What is the correct name for ...
... 9. A 3.6 g sample of lithium contains ________ atoms. 10. How many elements are in the fifth period of the periodic table? 11. What is the correct formula for an ionic compound that contains magnesium ions and fluoride ions? 12. What is the correct name for NH4ClO4? 13. What is the correct name for ...
CH1710 HW#7 (2017)-Quanta, electron config
... 1. An FM station broadcasts classical music at 93.5 MHz (megahertz or 106 Hz). Find the wavelength (in m, nm and Å) of these radio waves. ...
... 1. An FM station broadcasts classical music at 93.5 MHz (megahertz or 106 Hz). Find the wavelength (in m, nm and Å) of these radio waves. ...
Exam 2 Review - Iowa State University
... 12. Consider the sine waves representing light or electromagnetic radiation. Which one corresponds to photons with the largest energy? ...
... 12. Consider the sine waves representing light or electromagnetic radiation. Which one corresponds to photons with the largest energy? ...
(Bohr Model And X-Rays) Part-1
... • An electron resolves around the nucleus only in those orbits for which the angular momentum is some integral multiple of L= ...
... • An electron resolves around the nucleus only in those orbits for which the angular momentum is some integral multiple of L= ...
Ionization

Ionization is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons to form ions, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. Ionization can result from the loss of an electron after collisions with sub atomic particles, collisions with other atoms, molecules and ions, or through the interaction with light. Heterolytic bond cleavage and heterolytic substitution reactions can result in the formation of ion pairs. Ionization can occur through radioactive decay by the internal conversion process, in which an excited nucleus transfers its energy to one of the inner-shell electrons causing it to be ejected.