* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download (Bohr Model And X-Rays) Part-1
Hidden variable theory wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
James Franck wikipedia , lookup
Bohr–Einstein debates wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
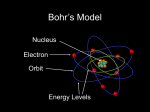
Modern Physics (Bohr Model And X-Rays) Part-1 Neils Bohr gave forward his model of atom with answeres most of the flaws that Rutherford model had. This model introduced quantization principal and this model is regarded as first quantum mechanical model. We will explore in detail, this structure of atom. We will also look into X - ray formation which is a converse process of photoclectric effect and will examine Moreley's law in pantium. THE BOHR THEORY OF HYDROGE ATOM (AND HYDROGEN LIKE ATOM): Bohr gave following postulates for electron in hydrogen atom :• An electron in an atom could resolve in certain stable orbits without the emission of radiant energy. • An electron resolves around the nucleus only in those orbits for which the angular momentum is some integral multiple of L= , where n . Thus angular of electron is QUANTAIZED. principal quantum number. • An electron might a transition from one of its specified non-radiating orbits to another of lower energy. When it does so, a single photon is amitted having energy equal to the energy difference between the initial and final slater. The frequency of emitted photon is given by h = Ei - Ef Dumb Question:- Are these equations valid for all atoms ? Ans:- No, equations are valid only for single electron system, i.e. systems where only one electron is present. Ideally this equation applies only to Hydrogen atom, Singly ionized helium He+, and doubly ionized Lithium Li+ +. In Bohr's model, radius of nth orbit is given by rn = = if values of constant are evaluate then, and speed of electron is given by Vn rn = 0.529 n2/z where n z and Vn = 2.19 X 106 m/sec. Principal quantum number/shell number. atomic number of nucleus involved. Why ? from Bohr's postulate, angular momentum of electron in nth orbit is L = mechanics L = mvnrn mvnrn = also from ............................................... (1) for electron to resolve in its orbit, Electrostatic force is providing the required centripetal force. Solving (1) & (2) simultaneously yields the required result.