CHM 50- Class activity
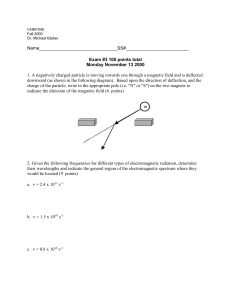
... The retina of a human eye can detect light when radiant energy incident on it is at least 4.0 x 10-17 J. For light of 5.85 nm wavelength , how many photons does this energy correspond to? ...
... The retina of a human eye can detect light when radiant energy incident on it is at least 4.0 x 10-17 J. For light of 5.85 nm wavelength , how many photons does this energy correspond to? ...
Trends in the Periodic Table
... movement of the subatomic particles, specifically electrons? • A: Temperature does not have enough energy to affect subatomic particle movement, only molecule movement. ...
... movement of the subatomic particles, specifically electrons? • A: Temperature does not have enough energy to affect subatomic particle movement, only molecule movement. ...
CHM 101
... a. Draw the energy vs reaction progress graph on the axes above paying attention to all values. Label a point that represents all products and one that represents all reactants. ...
... a. Draw the energy vs reaction progress graph on the axes above paying attention to all values. Label a point that represents all products and one that represents all reactants. ...
The Periodic Table
... Reason: electrons added in the same principal quantum level do not completely shield the increasing nuclear charge caused by the added protons. The electrons in the same principal quantum level are generally more strongly bound when moving left to right across the periodic table (NOTE: This trend is ...
... Reason: electrons added in the same principal quantum level do not completely shield the increasing nuclear charge caused by the added protons. The electrons in the same principal quantum level are generally more strongly bound when moving left to right across the periodic table (NOTE: This trend is ...
Modern physics 2330
... Q1 Indicate (√ ) for true statement and (× ) for false statement. 1- ( ) A black body is defined as an object that absorbs all the electromagnetic radiation falling on it and consequently appears black. 2- ( ) In certain situations light exhibits wave properties like diffraction and Compton Effect. ...
... Q1 Indicate (√ ) for true statement and (× ) for false statement. 1- ( ) A black body is defined as an object that absorbs all the electromagnetic radiation falling on it and consequently appears black. 2- ( ) In certain situations light exhibits wave properties like diffraction and Compton Effect. ...
Atoms, electrons, nuclei J.J. Thomson discovered the electron (1897
... beam of Hydrogen atoms used in the experiment was split into two parts, proving the quantized nature of magnetic momentum, but based on the azimuthal and magnetic quantum numbers Hydrogen atom should have zero angular momentum in the ground state (we expect that the magnetic momentum will also be ze ...
... beam of Hydrogen atoms used in the experiment was split into two parts, proving the quantized nature of magnetic momentum, but based on the azimuthal and magnetic quantum numbers Hydrogen atom should have zero angular momentum in the ground state (we expect that the magnetic momentum will also be ze ...
Excitation of Quantum Jumps by Collisions
... Muonic atoms are objects of the nuclear physics research. ...
... Muonic atoms are objects of the nuclear physics research. ...
P114 PROBLEM SET 9 Spring 2014
... [4] A hydrogen atom is in its tenth excited state according to the Bohr model (n=11). (a) What is the radius of the Bohr orbit? (b) What is the angular momentum of the electron? (c) What is the electron’s kinetic energy? (d) What is the electron’s potential energy? (e) What is the electron’s total e ...
... [4] A hydrogen atom is in its tenth excited state according to the Bohr model (n=11). (a) What is the radius of the Bohr orbit? (b) What is the angular momentum of the electron? (c) What is the electron’s kinetic energy? (d) What is the electron’s potential energy? (e) What is the electron’s total e ...
Sugárkémiai áttekintés Schiller Róbert
... One must know the activity of the source, then Delementary must be integrated over source and irradiated space. ...
... One must know the activity of the source, then Delementary must be integrated over source and irradiated space. ...
CHM1045 - Michael Blaber
... E = h * (the relationship between energy and frequency for electromagnetic radiation En = -RH / n2 or En = -B / n2 (the relationship between the energy of an electron in Bohr's model of the hydrogen atom, and the orbit number of the electron) Elevel = RH * (1/ni2 - 1/nf2) or En = B * (1/ni2 - 1/n ...
... E = h * (the relationship between energy and frequency for electromagnetic radiation En = -RH / n2 or En = -B / n2 (the relationship between the energy of an electron in Bohr's model of the hydrogen atom, and the orbit number of the electron) Elevel = RH * (1/ni2 - 1/nf2) or En = B * (1/ni2 - 1/n ...
e - Purdue Physics - Purdue University
... 3.40 eV - 1.51 eV=1.89 eV of energy, the energy of the red-color photon. •The 656 nm emission line from H has a frequency f=4.57×1014 Hz. A photon of this color has an energy of hf= 3.03×10−19 J (1.89 eV). ...
... 3.40 eV - 1.51 eV=1.89 eV of energy, the energy of the red-color photon. •The 656 nm emission line from H has a frequency f=4.57×1014 Hz. A photon of this color has an energy of hf= 3.03×10−19 J (1.89 eV). ...
Introduction_to_Geochemistry_Pre-Lecture_Quiz
... (a) The diameter of an atom is less than the diameter of its nucleus. (b) The relative atomic mass of an atom is the mass of an atom relative to an atom of 12C. (c) p-orbitals can contain a maximum of 10 electrons. (d) The first ionisation energy of an element is the energy input (in kg mol-1) requi ...
... (a) The diameter of an atom is less than the diameter of its nucleus. (b) The relative atomic mass of an atom is the mass of an atom relative to an atom of 12C. (c) p-orbitals can contain a maximum of 10 electrons. (d) The first ionisation energy of an element is the energy input (in kg mol-1) requi ...
Chemistry I Honors – Semester Exam Review – Fall 2000
... Hydrogen atoms have specific energy levels. Therefore, the atoms can only gain or lose certain amounts of energy. When atoms lose energy, they emit photons which correspond to the lines in the emission spectrum. The more energy lost, the more energy the photon has. Bohr’s model stated that electrons ...
... Hydrogen atoms have specific energy levels. Therefore, the atoms can only gain or lose certain amounts of energy. When atoms lose energy, they emit photons which correspond to the lines in the emission spectrum. The more energy lost, the more energy the photon has. Bohr’s model stated that electrons ...
Problem set #1 - U.C.C. Physics Department
... the lines along which ψ(x, y, t) = 1. Calculate the repeat distance of the wave along the x-direction, the y-direction, and its direction of motion. 2) Bohr’s atomic model Recall that Bohr derived Rydberg’s constant by assuming (1) that the electrons move around the nucleus in discrete orbits; and ( ...
... the lines along which ψ(x, y, t) = 1. Calculate the repeat distance of the wave along the x-direction, the y-direction, and its direction of motion. 2) Bohr’s atomic model Recall that Bohr derived Rydberg’s constant by assuming (1) that the electrons move around the nucleus in discrete orbits; and ( ...
Ionization

Ionization is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons to form ions, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. Ionization can result from the loss of an electron after collisions with sub atomic particles, collisions with other atoms, molecules and ions, or through the interaction with light. Heterolytic bond cleavage and heterolytic substitution reactions can result in the formation of ion pairs. Ionization can occur through radioactive decay by the internal conversion process, in which an excited nucleus transfers its energy to one of the inner-shell electrons causing it to be ejected.