Chapter 7 Student Learning Map
... How is the wave-particle duality explanation used to explain light and electrons? What is the relationship between the speed, frequency, and wavelength of ...
... How is the wave-particle duality explanation used to explain light and electrons? What is the relationship between the speed, frequency, and wavelength of ...
Chem 115 POGIL Worksheet - Week 10 Periodic Trends Why? The
... Size decreases across a period. Electrons are added to the same shell and do not shield one another very effectively from the increasing nuclear charge. This causes all orbitals (including the outermost size-determining orbitals) to contract as Z increases. Transition elements contract up to the mid ...
... Size decreases across a period. Electrons are added to the same shell and do not shield one another very effectively from the increasing nuclear charge. This causes all orbitals (including the outermost size-determining orbitals) to contract as Z increases. Transition elements contract up to the mid ...
CHEMISTRY 113 EXAM 3(A)
... A. reflection of light by metal surface B. ejection of electrons by a metal when struck by light C. acceleration of electrons in vacuum by the electric field D. effect of the electric field on the emission of light 3. The frequency of electromagnetic radiation required to promote an electron from n= ...
... A. reflection of light by metal surface B. ejection of electrons by a metal when struck by light C. acceleration of electrons in vacuum by the electric field D. effect of the electric field on the emission of light 3. The frequency of electromagnetic radiation required to promote an electron from n= ...
Midterm Review File
... 25. If an atom has an electron configuration of 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p2, how many valence electrons does it have? ...
... 25. If an atom has an electron configuration of 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p2, how many valence electrons does it have? ...
Midterm review
... 1. Total number of valence electrons is sum of valence electrons of each atom minus the overall charge 2. Arrange the atoms in a structure and distribute the electrons so that each atom has 8 electrons around it (exceptions, H has 2, B can have 6 and third row and lower atoms can have more than 8). ...
... 1. Total number of valence electrons is sum of valence electrons of each atom minus the overall charge 2. Arrange the atoms in a structure and distribute the electrons so that each atom has 8 electrons around it (exceptions, H has 2, B can have 6 and third row and lower atoms can have more than 8). ...
Louie de Broglie
... Heisenberg concluded that it is impossible to make any measurement on an object without disturbing it – at least a little. Electrons are detected by photons and because a photon and an electron have the same energy, any attempt to locate an electron with a photon will knock the electron off course ...
... Heisenberg concluded that it is impossible to make any measurement on an object without disturbing it – at least a little. Electrons are detected by photons and because a photon and an electron have the same energy, any attempt to locate an electron with a photon will knock the electron off course ...
PowerPoint-Präsentation
... K. Krajewska, J.Z. Kaminski, K. Wodkiewicz, Opt. Commun., to be published ...
... K. Krajewska, J.Z. Kaminski, K. Wodkiewicz, Opt. Commun., to be published ...
3.3 Review Name________________________________ Period_______Date_____________________
... 21. Label an excited state of this atom. 22. Draw an arrow to show the direction an electron moves when it absorbs energy. ...
... 21. Label an excited state of this atom. 22. Draw an arrow to show the direction an electron moves when it absorbs energy. ...
Document
... 21. Label an excited state of this atom. 22. Draw an arrow to show the direction an electron moves when it absorbs energy. ...
... 21. Label an excited state of this atom. 22. Draw an arrow to show the direction an electron moves when it absorbs energy. ...
ap chemistry review – multiple choice
... (c) Ionization Energy (d) Kinetic Energy (e) Lattice Energy 1. The energy required to convert a ground-state atom in the gas phase to a positive gaseous ion. 2. The energy change that occurs in the conversion of an ionic solid to widely spaced gaseous ions. 3. The energy in a chemical or physical ch ...
... (c) Ionization Energy (d) Kinetic Energy (e) Lattice Energy 1. The energy required to convert a ground-state atom in the gas phase to a positive gaseous ion. 2. The energy change that occurs in the conversion of an ionic solid to widely spaced gaseous ions. 3. The energy in a chemical or physical ch ...
Slide 1
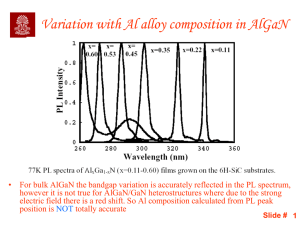
... • For bulk AlGaN the bandgap variation is accurately reflected in the PL spectrum, however it is not true for AlGaN/GaN heterostructures where due to the strong electric field there is a red shift. So Al composition calculated from PL peak position is NOT totally accurate ...
... • For bulk AlGaN the bandgap variation is accurately reflected in the PL spectrum, however it is not true for AlGaN/GaN heterostructures where due to the strong electric field there is a red shift. So Al composition calculated from PL peak position is NOT totally accurate ...
Exam #2
... Planck’s successful explanation of the black-body radiation spectrum introduced the hypothesis that radiation is emitted not continuously but in discrete quanta. Rutherford’s experiment on the scattering of alpha particles showed that the mass of the nucleus is concentrated in a very small volume. T ...
... Planck’s successful explanation of the black-body radiation spectrum introduced the hypothesis that radiation is emitted not continuously but in discrete quanta. Rutherford’s experiment on the scattering of alpha particles showed that the mass of the nucleus is concentrated in a very small volume. T ...
Regents questions
... you think are important in explaining this difference? Give it some thought – Describe the relationship between the trends in metallic character and trends in ionization ...
... you think are important in explaining this difference? Give it some thought – Describe the relationship between the trends in metallic character and trends in ionization ...
Atomic Structure
... A. Qualitative Questions: 1. The Bohr model of the atom was the first quantum mechanical model of the atom. a. Bohr postulated that a hydrogen atom could only exist without radiating in one of a set of stationary states. Explain what is meant by this postulate. b. Bohr related his postulate to the c ...
... A. Qualitative Questions: 1. The Bohr model of the atom was the first quantum mechanical model of the atom. a. Bohr postulated that a hydrogen atom could only exist without radiating in one of a set of stationary states. Explain what is meant by this postulate. b. Bohr related his postulate to the c ...
Slide 1
... The end of classical physics: photons, electrons, atoms Last time: Discovery of the electron: Charge quantization photo-electric effect: light behaves as a particle Discovery of the nucleus: Rutherford scattering experiment Today: Atomic spectra: emission and absorption. Evidence for atomic ener ...
... The end of classical physics: photons, electrons, atoms Last time: Discovery of the electron: Charge quantization photo-electric effect: light behaves as a particle Discovery of the nucleus: Rutherford scattering experiment Today: Atomic spectra: emission and absorption. Evidence for atomic ener ...
Ionization

Ionization is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons to form ions, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. Ionization can result from the loss of an electron after collisions with sub atomic particles, collisions with other atoms, molecules and ions, or through the interaction with light. Heterolytic bond cleavage and heterolytic substitution reactions can result in the formation of ion pairs. Ionization can occur through radioactive decay by the internal conversion process, in which an excited nucleus transfers its energy to one of the inner-shell electrons causing it to be ejected.