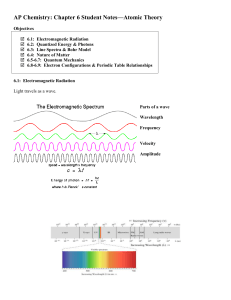
ELECTRONS IN ATOMS
... on the exact path an electron follows around the nucleus. 7. Is the following sentence true or false? The quantum mechanical model of the atom estimates the probability of finding an electron in a certain position. true ______________________ ...
... on the exact path an electron follows around the nucleus. 7. Is the following sentence true or false? The quantum mechanical model of the atom estimates the probability of finding an electron in a certain position. true ______________________ ...
Lec-23_Strachan
... When light is incident on a system of atoms, both stimulated absorption and stimulated emission are equally probable Generally, a net absorption occurs since most atoms are in the ground state If you can cause more atoms to be in excited states, a net emission of photons can result This situation is ...
... When light is incident on a system of atoms, both stimulated absorption and stimulated emission are equally probable Generally, a net absorption occurs since most atoms are in the ground state If you can cause more atoms to be in excited states, a net emission of photons can result This situation is ...
Quantum numbers
... and has a wave function That represents the x, y and z coordinates of the electron. A specific wave function is often called an orbital. ...
... and has a wave function That represents the x, y and z coordinates of the electron. A specific wave function is often called an orbital. ...
a non-perturbative approach for quantum field theory
... Obtain the eigenvalues (electron mass) and eigenstates (electron wavefunctions) for ground state (physical electron) and several low-lying excited states (excited electrons) Evaluate other observables (anomalous magnetic moment, parton distribution function) from electron wavefunction (vector-matrix ...
... Obtain the eigenvalues (electron mass) and eigenstates (electron wavefunctions) for ground state (physical electron) and several low-lying excited states (excited electrons) Evaluate other observables (anomalous magnetic moment, parton distribution function) from electron wavefunction (vector-matrix ...
Corso di Fisica Moderna
... With the use of spectroscopy in the late 19th century, it was found that the radiaAon from hydrogen, as well as other atoms, was emiNed at specific quanAzed frequencies. It was the effort to exp ...
... With the use of spectroscopy in the late 19th century, it was found that the radiaAon from hydrogen, as well as other atoms, was emiNed at specific quanAzed frequencies. It was the effort to exp ...
The Wave Nature of Matter - Waterford Public Schools
... speed, v, other than the speed of light will have a wave nature consistent with a wavelength given by the equation: h λ= mν λ ...
... speed, v, other than the speed of light will have a wave nature consistent with a wavelength given by the equation: h λ= mν λ ...
1 - theozone
... spectrum includes light with a wavelength of 434 nanometers. This is caused by an electron moving from: a. b. c. d. ...
... spectrum includes light with a wavelength of 434 nanometers. This is caused by an electron moving from: a. b. c. d. ...
R - University of St Andrews
... Thus, energy levels turn out to be dependent on two quantum numbers, but only when one takes relativistic considerations into account. Without relativity, we get the same formula for E as before. Relativistic correction: electrons in very eccentric orbits have large velocities when they are near the ...
... Thus, energy levels turn out to be dependent on two quantum numbers, but only when one takes relativistic considerations into account. Without relativity, we get the same formula for E as before. Relativistic correction: electrons in very eccentric orbits have large velocities when they are near the ...
Ch. 6 notes
... Example 1 Calculate the energy required to excite the hydrogen electron from level n=1 to level n=2. Also calculate the wavelength of light that must be absorbed by a hydrogen atom in its ground state to reach this excited state. ...
... Example 1 Calculate the energy required to excite the hydrogen electron from level n=1 to level n=2. Also calculate the wavelength of light that must be absorbed by a hydrogen atom in its ground state to reach this excited state. ...
powerpoint on Bohr/Quantum File
... We can not know both the position and momentum of a particle at a given time. ...
... We can not know both the position and momentum of a particle at a given time. ...
Ionization

Ionization is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons to form ions, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. Ionization can result from the loss of an electron after collisions with sub atomic particles, collisions with other atoms, molecules and ions, or through the interaction with light. Heterolytic bond cleavage and heterolytic substitution reactions can result in the formation of ion pairs. Ionization can occur through radioactive decay by the internal conversion process, in which an excited nucleus transfers its energy to one of the inner-shell electrons causing it to be ejected.