Citrate Cycle Supplemental Reading Key Concepts
... Figure 4 shows the eight citrate cycle reactions. The citrate cycle is distinguished from linear metabolic pathways in that oxaloacetate is both the substrate for the first reaction (citrate synthase) and the product of the last reaction (malate dehydrogenase), which means that it must be regenerate ...
... Figure 4 shows the eight citrate cycle reactions. The citrate cycle is distinguished from linear metabolic pathways in that oxaloacetate is both the substrate for the first reaction (citrate synthase) and the product of the last reaction (malate dehydrogenase), which means that it must be regenerate ...
Respiration
... ATP pupil demo • ADP travels to the respiration reaction and second phosphate picks up energy voucher. • This energy is used for a third Pi to join on = ATP. • ATP transfers the energy to the energy requiring reaction. ...
... ATP pupil demo • ADP travels to the respiration reaction and second phosphate picks up energy voucher. • This energy is used for a third Pi to join on = ATP. • ATP transfers the energy to the energy requiring reaction. ...
Metabolic Enzymes
... produced during glycolysis that enter the mitochondria. Copyright © 2015 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved ...
... produced during glycolysis that enter the mitochondria. Copyright © 2015 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved ...
physiological limitations on phytoplankton productivity in the ocean
... The Principle of the Pump and Probe Fluorometer The pump and probe fluorometer delivers a series, usually three, microsecond flashes (I). The fluorescence elicited by the first, weak, probe flash is recorded. To measure the maximum photosynthetic capacity, a second, strong, pump flash is delivered. ...
... The Principle of the Pump and Probe Fluorometer The pump and probe fluorometer delivers a series, usually three, microsecond flashes (I). The fluorescence elicited by the first, weak, probe flash is recorded. To measure the maximum photosynthetic capacity, a second, strong, pump flash is delivered. ...
Chem 32 Solutions to Section 15.4 – 15.6 Homework Problems
... 15.78 Only pathway “c” produces energy that can be harnessed to make ATP. Pathway “a” does not produce or consume a significant amount of energy. Pathway “b” is an activation step, and consumes energy (the body breaks down ATP in this step). 15.86 The starting materials of the citric acid cycle are ...
... 15.78 Only pathway “c” produces energy that can be harnessed to make ATP. Pathway “a” does not produce or consume a significant amount of energy. Pathway “b” is an activation step, and consumes energy (the body breaks down ATP in this step). 15.86 The starting materials of the citric acid cycle are ...
Glucose Metabolism Glycolysis Expectations
... • Production of 2 ATP • VERY high energy bond allows formation of _________ while still being irreversible • Regulation: F‐1,6‐BP can act as a feed‐forward activator to ensure fast glycolysis ...
... • Production of 2 ATP • VERY high energy bond allows formation of _________ while still being irreversible • Regulation: F‐1,6‐BP can act as a feed‐forward activator to ensure fast glycolysis ...
Chap 4. Growth and Metabolism
... 3. The Q10 - The rate of respiration doubles when temperature rises 10 oC (18 oF) - Respiration can be reduced by lowering O2 and increasing CO2 ...
... 3. The Q10 - The rate of respiration doubles when temperature rises 10 oC (18 oF) - Respiration can be reduced by lowering O2 and increasing CO2 ...
Export To Word
... explain how they work in tandem to convert sunlight into energy that cells can use. This lesson will allow students to observe and identify evidence of an enzyme's activity, lactase, and its function, and action on a substrate found in milk, lactose. They will then relate the absence of lactase to t ...
... explain how they work in tandem to convert sunlight into energy that cells can use. This lesson will allow students to observe and identify evidence of an enzyme's activity, lactase, and its function, and action on a substrate found in milk, lactose. They will then relate the absence of lactase to t ...
Respiration and Metabolism
... - produce ____________. - NAD NADH (reduced / oxidized). 1C6H12O6 2 Pyruvates ________ + 2 ATP ____ + 2NADH _______ 1glucose + 2NAD + 2ADP + 2Pi 2 pyruvates + 2NADH + (2H+)+ 2 ATP - Oxygen required? (Yes / No) *All cells undergo glycolysis in either aerobic or anaerobic resp. Designed by Pye ...
... - produce ____________. - NAD NADH (reduced / oxidized). 1C6H12O6 2 Pyruvates ________ + 2 ATP ____ + 2NADH _______ 1glucose + 2NAD + 2ADP + 2Pi 2 pyruvates + 2NADH + (2H+)+ 2 ATP - Oxygen required? (Yes / No) *All cells undergo glycolysis in either aerobic or anaerobic resp. Designed by Pye ...
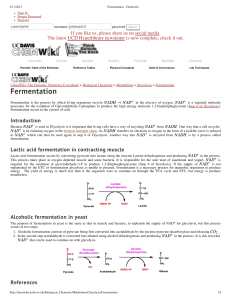
Fermentation - Chemwiki
... Lactic acid fermentation occurs by converting pyruvate into lactate using the enzyme Lactate dehydrogenase and producing in the process. This process takes place in oxygen depleted muscle and some bacteria. It is responsible for the sour taste of sauerkraut and yogurt. is required for the oxidation ...
... Lactic acid fermentation occurs by converting pyruvate into lactate using the enzyme Lactate dehydrogenase and producing in the process. This process takes place in oxygen depleted muscle and some bacteria. It is responsible for the sour taste of sauerkraut and yogurt. is required for the oxidation ...
1 Glucose: evolution`s favorite flavor… In any metabolism course
... requirements of carbon in these organic molecules is so predictable. Organic chemists use either the middle representation, or the “no hydrogen” versions a lot, or some hybrid of those two to get their points across. But sometimes the full “every bond and atom” version has its uses, as you will see ...
... requirements of carbon in these organic molecules is so predictable. Organic chemists use either the middle representation, or the “no hydrogen” versions a lot, or some hybrid of those two to get their points across. But sometimes the full “every bond and atom” version has its uses, as you will see ...
3 hours - The University of Winnipeg
... Question 40. Ketogenic amino acids are broken down to acetoacetate or ______. a. ? -hydroxybutyrate b. acetone c. fatty acids d. acetyl-CoA e. pyruvate ...
... Question 40. Ketogenic amino acids are broken down to acetoacetate or ______. a. ? -hydroxybutyrate b. acetone c. fatty acids d. acetyl-CoA e. pyruvate ...
Life 9e - Garvness
... 41. Photophosphorylation provides the Calvin–Benson cycle with a. protons and electrons. b. CO2 and glucose. c. water and photons. d. light and chlorophyll. e. ATP and NADPH. Answer: e Textbook Reference: 10.2 How Does Photosynthesis Convert Light Energy into Chemical Energy? Page: 198 Bloom’s Categ ...
... 41. Photophosphorylation provides the Calvin–Benson cycle with a. protons and electrons. b. CO2 and glucose. c. water and photons. d. light and chlorophyll. e. ATP and NADPH. Answer: e Textbook Reference: 10.2 How Does Photosynthesis Convert Light Energy into Chemical Energy? Page: 198 Bloom’s Categ ...
AP Chemistry
... (A) determine the mass of solute that was added. represented above, the entropy change might be expected to (B) determine the mass of the thermometer. be positive. However, S for the process is actually negative. (C) determine the mass of water that evaporated. Which best helps to account for the n ...
... (A) determine the mass of solute that was added. represented above, the entropy change might be expected to (B) determine the mass of the thermometer. be positive. However, S for the process is actually negative. (C) determine the mass of water that evaporated. Which best helps to account for the n ...
Chem101, 2nd Major Exam, term061
... Chem101, 2nd Major Exam, Term 122: (All Answers are A) 1. A candle which is made of 151.2 g of an organic acid (Molar Mass = 284 g/mol) was burned and used to warm 500.0 g of water, which was initially at 22.6C. When the burning was stopped the temperature of the water was 33.5C. Assuming all heat ...
... Chem101, 2nd Major Exam, Term 122: (All Answers are A) 1. A candle which is made of 151.2 g of an organic acid (Molar Mass = 284 g/mol) was burned and used to warm 500.0 g of water, which was initially at 22.6C. When the burning was stopped the temperature of the water was 33.5C. Assuming all heat ...
AP UNIT 3
... • Heat (thermal energy) is kinetic energy associated with random movement of atoms or molecules • Potential energy is energy that matter possesses because of its location or structure • Chemical energy is potential energy available for release in a chemical reaction • Energy can be converted from on ...
... • Heat (thermal energy) is kinetic energy associated with random movement of atoms or molecules • Potential energy is energy that matter possesses because of its location or structure • Chemical energy is potential energy available for release in a chemical reaction • Energy can be converted from on ...
Derived copy of Bis2A 07.1 Glycolysis
... Step 1. The rst step in glycolysis (Figure 1) is catalyzed by hexokinase, an enzyme with broad speci city that catalyzes the phosphorylation of six-carbon sugars. Hexokinase phosphorylates glucose using ATP as the source of the phosphate, producing glucose-6-phosphate, a more reactive form of gluco ...
... Step 1. The rst step in glycolysis (Figure 1) is catalyzed by hexokinase, an enzyme with broad speci city that catalyzes the phosphorylation of six-carbon sugars. Hexokinase phosphorylates glucose using ATP as the source of the phosphate, producing glucose-6-phosphate, a more reactive form of gluco ...
Lab 6 - CELLULAR RESPIRATION: THE CITRIC ACID CYCLE
... respiration occurs. Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of cells, while the others occur in mitochondria. Mitochondria are a double membrane-bound organelle. The interior membrane is folded into repeated structures called cristae, and it is here that the ETS is located. The citric acid cycle occurs l ...
... respiration occurs. Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of cells, while the others occur in mitochondria. Mitochondria are a double membrane-bound organelle. The interior membrane is folded into repeated structures called cristae, and it is here that the ETS is located. The citric acid cycle occurs l ...
MCAT 2015
... Digestion, mobilization, and transport of fats Oxidation of fatty acids o Saturated fats o Unsaturated fats Ketone bodies (BC) Anabolism of fats (BIO) Non-‐template synthesis: biosynthesis of lipids and polys ...
... Digestion, mobilization, and transport of fats Oxidation of fatty acids o Saturated fats o Unsaturated fats Ketone bodies (BC) Anabolism of fats (BIO) Non-‐template synthesis: biosynthesis of lipids and polys ...
Cellular Respiration
... - Where does the Krebs Cycle take place? Inside the Matrix of the Mitochondrion - The ETC uses electrons to ______ ...
... - Where does the Krebs Cycle take place? Inside the Matrix of the Mitochondrion - The ETC uses electrons to ______ ...
Revision IB2 Topic 1
... formula showing the numbers of atoms present in a compound formula showing the numbers of elements present in a compound formula showing the actual numbers of atoms of each element in a compound formula showing the simplest ratio of numbers of atoms of each element in a compound ...
... formula showing the numbers of atoms present in a compound formula showing the numbers of elements present in a compound formula showing the actual numbers of atoms of each element in a compound formula showing the simplest ratio of numbers of atoms of each element in a compound ...
Name: Class: ______ Date: ______ ID: A Intro to College Biology
... 7. Which of the following is possible due to the high surface tension of water? a. Lakes don't freeze solid in winter, despite low temperatures, b. A water strider can walk across the surface of a small pond. c. Organisms resist temperature changes, although they give off heat due to chemical reacti ...
... 7. Which of the following is possible due to the high surface tension of water? a. Lakes don't freeze solid in winter, despite low temperatures, b. A water strider can walk across the surface of a small pond. c. Organisms resist temperature changes, although they give off heat due to chemical reacti ...
Biochemistry
... Oxygenase activity ↑ as temperature ↑. – C4 and CAM plants use different mechanisms to overcome this “problem” allowing them to grow efficiently in hot climates. ...
... Oxygenase activity ↑ as temperature ↑. – C4 and CAM plants use different mechanisms to overcome this “problem” allowing them to grow efficiently in hot climates. ...
Energetics and carbon metabolism during growth
... Fig. 1 shows the metabolic networks for autotrophic, heterotrophic and mixotrophic cultures. The relevant reactions are listed in Appendix A. The manner in which the networks have been obtained is described below. Algae cells can use light as the energy source. Light quanta absorbed by pigments driv ...
... Fig. 1 shows the metabolic networks for autotrophic, heterotrophic and mixotrophic cultures. The relevant reactions are listed in Appendix A. The manner in which the networks have been obtained is described below. Algae cells can use light as the energy source. Light quanta absorbed by pigments driv ...