Pathways that Harvest and Store Chemical Energy
... ATP is needed for carbon-fixation pathways. The noncyclic light reactions would not provide enough ATP. Cyclic electron transport uses only photosystem I and produces only ATP. An electron is passed from an excited chlorophyll, through the electron transport chain, and recycles back to the same ...
... ATP is needed for carbon-fixation pathways. The noncyclic light reactions would not provide enough ATP. Cyclic electron transport uses only photosystem I and produces only ATP. An electron is passed from an excited chlorophyll, through the electron transport chain, and recycles back to the same ...
7.014 Quiz I Handout
... b) ATP is generated by photophosphorylation using the energy from the electrochemical proton gradient formed by the passing of electrons through the photosystems. c) Carbon fixation is changing CO 2 to an organic form by covalently binding it to an organic molecule, usually a sugar. One example is s ...
... b) ATP is generated by photophosphorylation using the energy from the electrochemical proton gradient formed by the passing of electrons through the photosystems. c) Carbon fixation is changing CO 2 to an organic form by covalently binding it to an organic molecule, usually a sugar. One example is s ...
Cellular Respiration
... – transfer energy in the form of e- and H+ into the electron transport chain. • e- are used to pump the H+ across the membrane to create a concentration gradient ...
... – transfer energy in the form of e- and H+ into the electron transport chain. • e- are used to pump the H+ across the membrane to create a concentration gradient ...
university of east anglia
... a) Electron transfer in mitochondria is accompanied by an asymmetric release of protons on one side of the inner mitochondrial membrane b) It predicts that oxidative phosphorylation can occur even in the absence of an intact inner mitochondrial membrane c) The effect of uncoupling reagents is a cons ...
... a) Electron transfer in mitochondria is accompanied by an asymmetric release of protons on one side of the inner mitochondrial membrane b) It predicts that oxidative phosphorylation can occur even in the absence of an intact inner mitochondrial membrane c) The effect of uncoupling reagents is a cons ...
Final Exam - Dawson College
... Condensed ground-state electron configuration is [Ne] 3s23p2 The period 4 member whose (2-) ion is isoelectronic with Kr A transition metal ion with a charge of 1+ having 5 unpaired “4d” electrons The element with the highest first ionization energy in period 4 The excited electron configuration is ...
... Condensed ground-state electron configuration is [Ne] 3s23p2 The period 4 member whose (2-) ion is isoelectronic with Kr A transition metal ion with a charge of 1+ having 5 unpaired “4d” electrons The element with the highest first ionization energy in period 4 The excited electron configuration is ...
Chapter05, 06 代谢引论糖代谢
... Rationale for this enzyme - repositions the phosphate to make PEP Note the phospho-histidine intermediates! Zelda Rose showed that a bit of 2,3-BPG is required to phosphorylate His Rx 9: Enolase 2-P-Gly to PEP How can such a reaction create a PEP? "Energy content" of 2-PG and PEP are similar Enolase ...
... Rationale for this enzyme - repositions the phosphate to make PEP Note the phospho-histidine intermediates! Zelda Rose showed that a bit of 2,3-BPG is required to phosphorylate His Rx 9: Enolase 2-P-Gly to PEP How can such a reaction create a PEP? "Energy content" of 2-PG and PEP are similar Enolase ...
Respiration - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
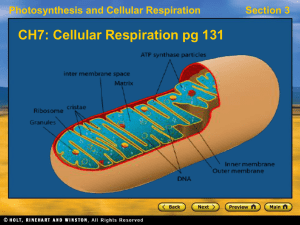
... • Process of extracting to energy from NADH and FADH2 to form ATP. • Function: Convert NADH and FADH2 into ATP. • Location: Mitochondria cristae. ...
... • Process of extracting to energy from NADH and FADH2 to form ATP. • Function: Convert NADH and FADH2 into ATP. • Location: Mitochondria cristae. ...
INTRODUCTORY BIOCHEMISTRY BI 28 Second Midterm
... showed that the production of CO2 by the extract increased when succinate was added. In fact, for every mole of succinate added, many extra moles of CO2 were produced. Explain this effect in terms of the known catabolic pathways. Ans: Succinate is an intermediate in the citric acid cycle that is not ...
... showed that the production of CO2 by the extract increased when succinate was added. In fact, for every mole of succinate added, many extra moles of CO2 were produced. Explain this effect in terms of the known catabolic pathways. Ans: Succinate is an intermediate in the citric acid cycle that is not ...
Detailed Objectives
... Overall reaction Citric Acid Cycle A. Citrate synthase mechanism B. Isocitrate dehydrogenase mechanism C. Reactions of cycle D. Overall reaction, oxidative phosphorylation Mitochondrial Electron Transport Chain A. Enzyme complexes B. Electron carriers; electron flow C. Proton gradient generation; pr ...
... Overall reaction Citric Acid Cycle A. Citrate synthase mechanism B. Isocitrate dehydrogenase mechanism C. Reactions of cycle D. Overall reaction, oxidative phosphorylation Mitochondrial Electron Transport Chain A. Enzyme complexes B. Electron carriers; electron flow C. Proton gradient generation; pr ...
Glycolysis Puzzle: Concept Map of "Splitting of Glucose"
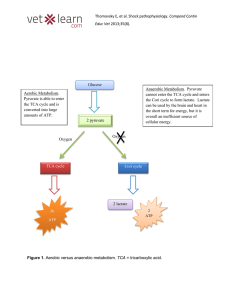
... Pyruvate has two biochemical fates, depending upon whether or not oxygen is present. In the absence of oxygen, anaerobic respiration (fermentation) occurs. In animal cells ________________________ is reduced to lactic acid (lactate) By the oxidation of the coenzyme __________________________ In yeas ...
... Pyruvate has two biochemical fates, depending upon whether or not oxygen is present. In the absence of oxygen, anaerobic respiration (fermentation) occurs. In animal cells ________________________ is reduced to lactic acid (lactate) By the oxidation of the coenzyme __________________________ In yeas ...
Cellular Respiration Chapter 8 Outline Glycolysis Transition
... During glycolysis, glucose is broken down in cytoplasm to two molecules of pyruvate. During transition reaction, pyruvate is oxidized, NADH is formed, and waste carbon dioxide is removed. Citric acid cycle results in NADH and FADH2, release of carbon dioxide, and production of additional ATP. Electr ...
... During glycolysis, glucose is broken down in cytoplasm to two molecules of pyruvate. During transition reaction, pyruvate is oxidized, NADH is formed, and waste carbon dioxide is removed. Citric acid cycle results in NADH and FADH2, release of carbon dioxide, and production of additional ATP. Electr ...
Glycolysis
... more stable) than the reactants. This means: The energy released when the products form is greater than the energy absorbed when the reactants’ bonds broke. Some of this difference in energy is now available or “free” to do work – move, produce light, sound. Some is lost as heat. Reactions that rele ...
... more stable) than the reactants. This means: The energy released when the products form is greater than the energy absorbed when the reactants’ bonds broke. Some of this difference in energy is now available or “free” to do work – move, produce light, sound. Some is lost as heat. Reactions that rele ...
Enzyme Thermodynamics - University of San Diego Home Pages
... Phosphorylation of ATP by a kinase is called substrate level phosphorylation. Uses a higher energy compound than ATP. (phosphate group transfer from a high transfer potential to a lower (ATP) transfer potential compound) - important to note other compounds have higher group transfer potential… ATP A ...
... Phosphorylation of ATP by a kinase is called substrate level phosphorylation. Uses a higher energy compound than ATP. (phosphate group transfer from a high transfer potential to a lower (ATP) transfer potential compound) - important to note other compounds have higher group transfer potential… ATP A ...
What happened to my cousin Patrick O’Neill?
... – new bonds formed release more energy than the energy required to break the bond ...
... – new bonds formed release more energy than the energy required to break the bond ...
Purified Mouse Anti-ATP Synthase α — 612516
... ATP synthase is a large enzyme complex that uses an electrochemical H+ or Na+ gradient to synthesize ATP from ADP and Pi, providing the organism with the ATP needed for energy. The complex consists of two major units, F0 and F1. F0 is embedded in the inner membrane of the mitochondria and, due to it ...
... ATP synthase is a large enzyme complex that uses an electrochemical H+ or Na+ gradient to synthesize ATP from ADP and Pi, providing the organism with the ATP needed for energy. The complex consists of two major units, F0 and F1. F0 is embedded in the inner membrane of the mitochondria and, due to it ...
Red Earth, White Earth, Green Earth, Black Earth
... across a membrane) until it reaches a second type of chlorophyll, P700, which can also be excited by sunlight. When that happens, the P700 is able to transfer an electron into a pathway that ultimately results in the transformation of carbon dioxide into organic carbon. To replace the electron that ...
... across a membrane) until it reaches a second type of chlorophyll, P700, which can also be excited by sunlight. When that happens, the P700 is able to transfer an electron into a pathway that ultimately results in the transformation of carbon dioxide into organic carbon. To replace the electron that ...
No Slide Title - Suffolk County Community College
... access to substrate) Factors that influence enzyme activity: 1. Temperature temp = reaction rate until denaturation -Enzymes have an optimal temperature = temp at which the enzyme catalyzes the reaction at its maximum rate -above this they become denatured denatured = unfolded, enzyme no longer ...
... access to substrate) Factors that influence enzyme activity: 1. Temperature temp = reaction rate until denaturation -Enzymes have an optimal temperature = temp at which the enzyme catalyzes the reaction at its maximum rate -above this they become denatured denatured = unfolded, enzyme no longer ...
The Aerobic Fate of Pyruvate
... I could tell that some of you were not impressed by the mere 2 ATPs produced per glucose by glycolysis. The 2 ATP’s produced are only a small fraction of the potential energy available from glucose. Under anaerobic conditions, animals convert glucose into 2 molecules of lactate. Much of the potentia ...
... I could tell that some of you were not impressed by the mere 2 ATPs produced per glucose by glycolysis. The 2 ATP’s produced are only a small fraction of the potential energy available from glucose. Under anaerobic conditions, animals convert glucose into 2 molecules of lactate. Much of the potentia ...
File - Biology withMrs. Ellsworth
... Adhesion causes H2O molecules to hold to XYLEM TUBES in plants. This adhesion combined with the cohesive property of water causes the H2O molecules to move upward ...
... Adhesion causes H2O molecules to hold to XYLEM TUBES in plants. This adhesion combined with the cohesive property of water causes the H2O molecules to move upward ...
Enzyme
... 9. Occurs in chloroplasts 10. Total photosynthesis must exceed total respiration for growth to occur ...
... 9. Occurs in chloroplasts 10. Total photosynthesis must exceed total respiration for growth to occur ...
1 - Intro to energy
... initially/ATP breaks down to ADP + P + energy C. ATP-PC/system/phosphocreatine system/alactic system D. PC = C + P(i) + energy/creatine + phosphate/PC broken down; E. Energy used for ATP resynthesis/ADP + P + energy = ATP/ADP + PC = ATP + C; F. Lasts 5-10 seconds/limited supply ...
... initially/ATP breaks down to ADP + P + energy C. ATP-PC/system/phosphocreatine system/alactic system D. PC = C + P(i) + energy/creatine + phosphate/PC broken down; E. Energy used for ATP resynthesis/ADP + P + energy = ATP/ADP + PC = ATP + C; F. Lasts 5-10 seconds/limited supply ...
Photosystems
... In cyclic electron flow • In cyclic electron flow – Electrons cycle back to the first ETC – Only ATP is produced Primary acceptor ...
... In cyclic electron flow • In cyclic electron flow – Electrons cycle back to the first ETC – Only ATP is produced Primary acceptor ...