SADDLEBACK COLLEGE BIOLOGY 20 EXAMINATION 2 STUDY
... • what’s the role of the photosynthetic pigments? Why are many plants green? What colors of light are being absorbed/reflected by chlorophyll? What are accessory pigments and their function? • Know how plants produce O2 & sugar. • What do plants do with CO2 & H20? What’s the function of sunlight wit ...
... • what’s the role of the photosynthetic pigments? Why are many plants green? What colors of light are being absorbed/reflected by chlorophyll? What are accessory pigments and their function? • Know how plants produce O2 & sugar. • What do plants do with CO2 & H20? What’s the function of sunlight wit ...
Bio 6 – Fermentation & Cellular Respiration Lab INTRODUCTION
... As shown above, NAD+, an empty electron carrier, is converted to NADH, a full electron carrier (the electrons being “carried” are associated with the hydrogen atom) during glycolysis. Fermentation is simply one or more biochemical steps that transfer the H in NADH and an extra electron to a molecule ...
... As shown above, NAD+, an empty electron carrier, is converted to NADH, a full electron carrier (the electrons being “carried” are associated with the hydrogen atom) during glycolysis. Fermentation is simply one or more biochemical steps that transfer the H in NADH and an extra electron to a molecule ...
Glycolysis Questions
... Glycolysis Questions Using the diagram provided and page 65-66, answer the following questions. 1. Where does glycolysis occur? ...
... Glycolysis Questions Using the diagram provided and page 65-66, answer the following questions. 1. Where does glycolysis occur? ...
Chapter 8: An Introduction to Metabolism - Biology E
... …and energy is released. For the exergonic reaction ADP + Pi g ATP + H2O, ΔG is 7.3 kcal/mol (30.5 kJ/mol). 13. What is energy coupling? Energy coupling is the use of an exergonic process to drive an endergonic one. ATP is responsible for mediating most energy coupling in cells, and in most cases i ...
... …and energy is released. For the exergonic reaction ADP + Pi g ATP + H2O, ΔG is 7.3 kcal/mol (30.5 kJ/mol). 13. What is energy coupling? Energy coupling is the use of an exergonic process to drive an endergonic one. ATP is responsible for mediating most energy coupling in cells, and in most cases i ...
File
... electrons from carbon fuels 1. The cycle itself neither generates ATP nor includes O2 as a reactant 1. Instead, it removes electrons from acetyl CoA & uses them to form NADH & FADH2 (high-energy electron carriers) 1. In oxidative phosphorylation, electrons from reoxidation of NADH & FADH2 flow throu ...
... electrons from carbon fuels 1. The cycle itself neither generates ATP nor includes O2 as a reactant 1. Instead, it removes electrons from acetyl CoA & uses them to form NADH & FADH2 (high-energy electron carriers) 1. In oxidative phosphorylation, electrons from reoxidation of NADH & FADH2 flow throu ...
metabolism
... NADH and FADH2 (from TCA cycle) ETS shuttles electrons down the chain, energy is released and subsequently captured and used by ATP synthase complexes to produce ATP. – oxidative phosphorylation ...
... NADH and FADH2 (from TCA cycle) ETS shuttles electrons down the chain, energy is released and subsequently captured and used by ATP synthase complexes to produce ATP. – oxidative phosphorylation ...
FREE Sample Here - Find the cheapest test bank for your
... Mechanism 1: Covalent modification – no change in the abundance of a protein. Here, preexisting protein is made active or inactive by covalently modifying it (involves making or breaking covalent bonds). Examples include phosphorylation, carboxylation, glycosylation, or proenzyme activation by break ...
... Mechanism 1: Covalent modification – no change in the abundance of a protein. Here, preexisting protein is made active or inactive by covalently modifying it (involves making or breaking covalent bonds). Examples include phosphorylation, carboxylation, glycosylation, or proenzyme activation by break ...
NoB1ch05QUICKcheck-ed
... Cows do not produce any enzymes that can digest cellulose to its glucose sub-units. Instead, cows (and other foregut-fermenting herbivores) depend on fermentation by bacteria in their stomach to digest cellulose. Cows have large four-chambered stomachs that can accommodate large volumes of bacteria ...
... Cows do not produce any enzymes that can digest cellulose to its glucose sub-units. Instead, cows (and other foregut-fermenting herbivores) depend on fermentation by bacteria in their stomach to digest cellulose. Cows have large four-chambered stomachs that can accommodate large volumes of bacteria ...
Respiration 2 PPT
... Ubiquinone (= small hydrophobic non-protein that’s mobile within the membrane system) transfers e- from multiprotein complex I II ...
... Ubiquinone (= small hydrophobic non-protein that’s mobile within the membrane system) transfers e- from multiprotein complex I II ...
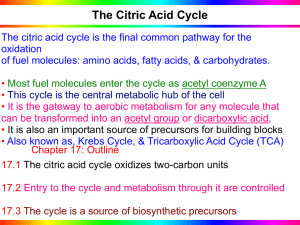
BSC 2010 - Exam I Lectures and Text Pages Citric Acid Cycle • Citric
... Ubiquinone (= small hydrophobic non-protein that’s mobile within the membrane system) transfers e- from multiprotein complex I → II ...
... Ubiquinone (= small hydrophobic non-protein that’s mobile within the membrane system) transfers e- from multiprotein complex I → II ...
Biochem01 - Amit Kessel Ph.D
... your carpet. Being an awesome biochemist, you figure out bacteria are feeding off your carpet. But wait, your carpet is made of nylon! How can this be? Perhaps the landfill and nuclear power plant next to your house have something to do with it... You set out to determine how the bacteria can live o ...
... your carpet. Being an awesome biochemist, you figure out bacteria are feeding off your carpet. But wait, your carpet is made of nylon! How can this be? Perhaps the landfill and nuclear power plant next to your house have something to do with it... You set out to determine how the bacteria can live o ...
23. electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation
... chains, succinate dehydrogenase and ATP-synthesizing enzymes. The inner membrane of a single liver mitochondrion may have over 10,000 sets of electron-transport chains and ATP synthetase molecules. The heart mitochondria have profuse cristae and therefore contain about 3 times more sets of electron- ...
... chains, succinate dehydrogenase and ATP-synthesizing enzymes. The inner membrane of a single liver mitochondrion may have over 10,000 sets of electron-transport chains and ATP synthetase molecules. The heart mitochondria have profuse cristae and therefore contain about 3 times more sets of electron- ...
GYURE handout, organisms of the Winogradsky Column
... At first it was thought they could not use sulfide as electron donor. But in reality they can -it's just that higher levels like those preferred by sulfur purples - is toxic to them. They can respire in the dark aerobically, using organic carbon or hydrogen. They can also ferment. Interestingly , th ...
... At first it was thought they could not use sulfide as electron donor. But in reality they can -it's just that higher levels like those preferred by sulfur purples - is toxic to them. They can respire in the dark aerobically, using organic carbon or hydrogen. They can also ferment. Interestingly , th ...
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
... Both autotrophs and heterotrophs undergo cellular respiration. Plants break down glucose for energy Plant cells have mitochondria ...
... Both autotrophs and heterotrophs undergo cellular respiration. Plants break down glucose for energy Plant cells have mitochondria ...
Cell ENERGY & ENZYMES
... Chlorophylls absorb most strongly in the ____________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ This is why plant parts that contain chlorophyll appear green to the human eye. ...
... Chlorophylls absorb most strongly in the ____________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ This is why plant parts that contain chlorophyll appear green to the human eye. ...
enzymes - JonesHonorsBioGreen
... Chlorophylls absorb most strongly in the ____________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ This is why plant parts that contain chlorophyll appear green to the human eye. ...
... Chlorophylls absorb most strongly in the ____________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ This is why plant parts that contain chlorophyll appear green to the human eye. ...
In this essay you should have written it as two
... occurs in the central liquid matrix of the mitochondrion 3C Pyruvic acid is converted to 2C Acetyl which binds to CoA Carbon is lost as CO2 H2 released is bound to NAD to form NADH2 A 4C compound joins with the Acetyl CoA to form citric acid (6C) CoA is released to be used again Citric acid is conve ...
... occurs in the central liquid matrix of the mitochondrion 3C Pyruvic acid is converted to 2C Acetyl which binds to CoA Carbon is lost as CO2 H2 released is bound to NAD to form NADH2 A 4C compound joins with the Acetyl CoA to form citric acid (6C) CoA is released to be used again Citric acid is conve ...
The most efficient light harvesting and energy transfer systems are
... and transduction systems are found in nature with the process of photosynthesis. In the photosynthetic system light energy is absorbed by antenna chlorophylls and this energy is then passed onto a reaction centre chlorophyll molecule where charge separation occurs [1] in less than 100 ps and at abou ...
... and transduction systems are found in nature with the process of photosynthesis. In the photosynthetic system light energy is absorbed by antenna chlorophylls and this energy is then passed onto a reaction centre chlorophyll molecule where charge separation occurs [1] in less than 100 ps and at abou ...
CHAPTER 6
... 6 CO2 + 10 NADH + 10 H+ + 2 FADH2 (b) 10 NADH + 10 H+ + 2 FADH2 + 6 O2 → 12 H2O + 10 NAD+ + 2 FAD ...
... 6 CO2 + 10 NADH + 10 H+ + 2 FADH2 (b) 10 NADH + 10 H+ + 2 FADH2 + 6 O2 → 12 H2O + 10 NAD+ + 2 FAD ...
Energy Yields from Aerobic Respiration: Some Alternatives
... the citric acid cycle. When glycolysis occurs under anaerobic conditions, it is followed by fermentation reactions, such as the lactate and alcohol fermentations. These reactions reduce pyruvate—or a molecule produced from pyruvate—and simultaneously oxidize the NADH produced in glycolysis. As a res ...
... the citric acid cycle. When glycolysis occurs under anaerobic conditions, it is followed by fermentation reactions, such as the lactate and alcohol fermentations. These reactions reduce pyruvate—or a molecule produced from pyruvate—and simultaneously oxidize the NADH produced in glycolysis. As a res ...
7 energizing porters by proton-motive force
... carriers in an arrangement that will transport electrons across membranes, proton translocation could be coupled to the transport of electrons and the primitive photosynthetic and respiratory electron transport systems were evolved (Mitchell, 1968). Concomitant with these events, ATP-dependent proto ...
... carriers in an arrangement that will transport electrons across membranes, proton translocation could be coupled to the transport of electrons and the primitive photosynthetic and respiratory electron transport systems were evolved (Mitchell, 1968). Concomitant with these events, ATP-dependent proto ...
Slide 1
... To used the energy banked in NADH and FADH2 The cell must shuttle their electrons to the Electron Transport Chain Where energy from the oxidation of organic fuel will power the oxidative phosphorylation of ADP to ATP ...
... To used the energy banked in NADH and FADH2 The cell must shuttle their electrons to the Electron Transport Chain Where energy from the oxidation of organic fuel will power the oxidative phosphorylation of ADP to ATP ...
Autotrophs, Heterotrophs, and ATP Practice
... Identify the type of organism shown below, and state whether it is an autotroph or a heterotroph. Animal ...
... Identify the type of organism shown below, and state whether it is an autotroph or a heterotroph. Animal ...