Schuenemann_Cytochrome P450
... the ferric low-spin to the ferric high-spin state (S=5/2). The transfer of the first electron originating from NAD(P)H via redox proteins (flavin and iron-sulfur proteins) reduces the iron to the ferrous high-spin state (S=2). Subsequent binding of molecular oxygen to the iron forms a diamagnetic Fe ...
... the ferric low-spin to the ferric high-spin state (S=5/2). The transfer of the first electron originating from NAD(P)H via redox proteins (flavin and iron-sulfur proteins) reduces the iron to the ferrous high-spin state (S=2). Subsequent binding of molecular oxygen to the iron forms a diamagnetic Fe ...
2.-lactic-acid-metabolism
... must be present for glycolysis to continue). But as more and more lactic acid builds up, muscle fatigue is caused and an oxygen debt is created. ...
... must be present for glycolysis to continue). But as more and more lactic acid builds up, muscle fatigue is caused and an oxygen debt is created. ...
A report published August 2006 demonstrated that peptide YY:
... • NAD+ : Shuttles electrons from fuel to electron transport chain – Dehydrogenase enzymes strip 2 H atoms (2 electrons and 2 protons) from fuel • One H atom + 1 extra electron passed to NAD+ to form NADH • One H ion (H+ : proton minus electron) released to solution ...
... • NAD+ : Shuttles electrons from fuel to electron transport chain – Dehydrogenase enzymes strip 2 H atoms (2 electrons and 2 protons) from fuel • One H atom + 1 extra electron passed to NAD+ to form NADH • One H ion (H+ : proton minus electron) released to solution ...
General Chemistry 110 Quiz 1
... Name (Last, First):_________________________Chem 3550, Professor David L. Huffman, Test 3, FORM A ...
... Name (Last, First):_________________________Chem 3550, Professor David L. Huffman, Test 3, FORM A ...
How plants get their food - gesci
... 6 molecules of carbon dioxide combine with 6 molecules of water to make one molecule of glucose and 6 molecules of oxygen ...
... 6 molecules of carbon dioxide combine with 6 molecules of water to make one molecule of glucose and 6 molecules of oxygen ...
Introduction to Cellular and Molecular Biology (BIOL 190)
... nucleus and assemble into ribosomes in the cytoplasm 4. Explain that ribosomes are the sites of protein synthesis and can exist free in the cytosol or bound to endoplamic reticulum or the nuclear envelope The Endomembrane System: smooth ER, rough ER, Golgi, lysosomes, vacuoles 1. Identify the differ ...
... nucleus and assemble into ribosomes in the cytoplasm 4. Explain that ribosomes are the sites of protein synthesis and can exist free in the cytosol or bound to endoplamic reticulum or the nuclear envelope The Endomembrane System: smooth ER, rough ER, Golgi, lysosomes, vacuoles 1. Identify the differ ...
IIIb
... 1. (8 Pts) What are the requirements for biological nitrogen fixation in terms of electrons/nitrogen molecule and ATP consumed /nitrogen molecule fixed. Does the reaction require the same amount of electrons as chemical fixation? If not, how do these numbers differ and why are they different? ...
... 1. (8 Pts) What are the requirements for biological nitrogen fixation in terms of electrons/nitrogen molecule and ATP consumed /nitrogen molecule fixed. Does the reaction require the same amount of electrons as chemical fixation? If not, how do these numbers differ and why are they different? ...
Atomic Systems and Bonding
... outside shell had only one electron When the valence electron in any atom gains sufficient energy from some outside force, it can break away from the parent atom and become what is called a free electron Atoms with few electrons in their valence shell tend to have more free electrons since these val ...
... outside shell had only one electron When the valence electron in any atom gains sufficient energy from some outside force, it can break away from the parent atom and become what is called a free electron Atoms with few electrons in their valence shell tend to have more free electrons since these val ...
Metabolism
... Metabolic Rate and Body Heat Production • Basic metabolic rate (BMR) reflects the amount of energy spent per unit of time by a body at rest ...
... Metabolic Rate and Body Heat Production • Basic metabolic rate (BMR) reflects the amount of energy spent per unit of time by a body at rest ...
Handout
... proteins under organic molecules). Catalyst = a compound or molecule that accelerates a reaction without being permanently altered or consumed by the reaction. In living systems, complex chemical reactions involving many steps are necessary to convert substrate into a final product. An enzyme is spe ...
... proteins under organic molecules). Catalyst = a compound or molecule that accelerates a reaction without being permanently altered or consumed by the reaction. In living systems, complex chemical reactions involving many steps are necessary to convert substrate into a final product. An enzyme is spe ...
Cells part 2 - fog.ccsf.edu
... Diffusion is the movement of a substance from a high concentration to a low concentration ...
... Diffusion is the movement of a substance from a high concentration to a low concentration ...
Chapter 1: Prelude
... their environment, and synthesizing building blocks for the cells´macromolecules. These processes are driven by a limited set of reaction mechanisms, revealing their ancient origins. Energetic Coupling of Various Biochemical Reactions A thermodynamically unfavorable (uphill ) reaction within metabol ...
... their environment, and synthesizing building blocks for the cells´macromolecules. These processes are driven by a limited set of reaction mechanisms, revealing their ancient origins. Energetic Coupling of Various Biochemical Reactions A thermodynamically unfavorable (uphill ) reaction within metabol ...
An Hypothetical Structure for an Intermolecular Electron Transfer
... found to be a general property of reactions of reversibly bound electron carriers wit,h their physiological oxidoreductases, ...
... found to be a general property of reactions of reversibly bound electron carriers wit,h their physiological oxidoreductases, ...
Atomic Systems and Bonding
... outside shell had only one electron When the valence electron in any atom gains sufficient energy from some outside force, it can break away from the parent atom and become what is called a free electron Atoms with few electrons in their valence shell tend to have more free electrons since these val ...
... outside shell had only one electron When the valence electron in any atom gains sufficient energy from some outside force, it can break away from the parent atom and become what is called a free electron Atoms with few electrons in their valence shell tend to have more free electrons since these val ...
Kate Buckman Modified session plan: Fermentation: one part in a
... respiration in the past, it was solely through lecture style transmission of information. This was not effective for me personally. I can’t remember much about respiration at all now, so in spite of having been taught it at least three times, I never really learned it. I do remember drawing the diff ...
... respiration in the past, it was solely through lecture style transmission of information. This was not effective for me personally. I can’t remember much about respiration at all now, so in spite of having been taught it at least three times, I never really learned it. I do remember drawing the diff ...
Name Biology Chemistry of Life What can reduce the effect of a
... / allows light to pass through for photosynthesis; cohesion of water molecules allow transport in plants; solvent – chemical reactions take place in water; many substances dissolve in water and can be transported; high boiling point making liquid water available to organisms / water is liquid over a ...
... / allows light to pass through for photosynthesis; cohesion of water molecules allow transport in plants; solvent – chemical reactions take place in water; many substances dissolve in water and can be transported; high boiling point making liquid water available to organisms / water is liquid over a ...
AP Biology
... a. Where does the C “go” that is removed? b. What is happening when NAD+ NADH + H+? ...
... a. Where does the C “go” that is removed? b. What is happening when NAD+ NADH + H+? ...
11A
... ____ATP molecules produced during aerobic cellular respiration a) remain in the mitochondria in which they are formed b) are stored in chlorolplasts of the same cell in which they are formed c) enter the cell's cytoplasm through membranes of the mitochondria in which they are formed d) are distrubut ...
... ____ATP molecules produced during aerobic cellular respiration a) remain in the mitochondria in which they are formed b) are stored in chlorolplasts of the same cell in which they are formed c) enter the cell's cytoplasm through membranes of the mitochondria in which they are formed d) are distrubut ...
Cell Biology
... o If oxygen available, pyruvate fed into TCA cycle where it generates some ATP and more NADH(H+) and FADH2 are used to generate ATP by oxidative phosphorylation and chemiosmotic coupling via ETS. Oxidized to carbon dioxide. o If there is no oxygen available or cannot be used another way to regenerat ...
... o If oxygen available, pyruvate fed into TCA cycle where it generates some ATP and more NADH(H+) and FADH2 are used to generate ATP by oxidative phosphorylation and chemiosmotic coupling via ETS. Oxidized to carbon dioxide. o If there is no oxygen available or cannot be used another way to regenerat ...
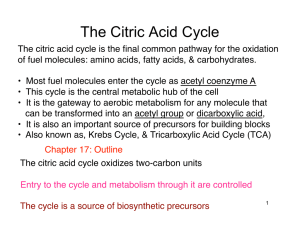
The Citric Acid Cycle
... electrons from carbon fuels 2. The cycle itself neither generates ATP nor includes O2 as a reactant 3. Instead, it removes electrons from acetyl CoA & uses them to form NADH & FADH2 (high-energy electron carriers) 4. In oxidative phosphorylation, electrons from reoxidation of NADH & FADH2 ...
... electrons from carbon fuels 2. The cycle itself neither generates ATP nor includes O2 as a reactant 3. Instead, it removes electrons from acetyl CoA & uses them to form NADH & FADH2 (high-energy electron carriers) 4. In oxidative phosphorylation, electrons from reoxidation of NADH & FADH2 ...
213lec3
... a. Transcription b. Translation 3. They can also be used for energy if other sources of energy are low or energy demands are high. V. How are minerals, vitamins, and water absorbed and transported in the body? A. These nutrients do not have to be broken into smaller units. B. Digestion does help to ...
... a. Transcription b. Translation 3. They can also be used for energy if other sources of energy are low or energy demands are high. V. How are minerals, vitamins, and water absorbed and transported in the body? A. These nutrients do not have to be broken into smaller units. B. Digestion does help to ...
PowerPoint - New Mexico FFA
... forming new molecules that support growth and/or release energy as this matter moves through an organism. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on describing that molecules are broken apart and put back together and that in this process, energy is released.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not ...
... forming new molecules that support growth and/or release energy as this matter moves through an organism. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on describing that molecules are broken apart and put back together and that in this process, energy is released.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not ...