Chapter 9 Cell Respiration
... • 2. electron transport is a fall in energy during each step to control release of fuel energy ...
... • 2. electron transport is a fall in energy during each step to control release of fuel energy ...
Exam 1 2007 - chem.uwec.edu
... 5. What two 3-carbon molecules are generated by the cleavage of fructose-1,6bisphosphate? A) glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and 3-phosphoglycerate B) glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate C) pyruvate and phosphoenolpyruvate D) enolase and 2-phosphoglycerate E) glyceraldehyde-3-phosph ...
... 5. What two 3-carbon molecules are generated by the cleavage of fructose-1,6bisphosphate? A) glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and 3-phosphoglycerate B) glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate C) pyruvate and phosphoenolpyruvate D) enolase and 2-phosphoglycerate E) glyceraldehyde-3-phosph ...
Chapter 2 Chemistry of Life - OnCourse Systems For Education
... • Protein – macromolecules that contain N, C, H, and O – Made of polymers of molecules called amino acids – Protein is functional molecule built from one or more polypeptides ...
... • Protein – macromolecules that contain N, C, H, and O – Made of polymers of molecules called amino acids – Protein is functional molecule built from one or more polypeptides ...
8.2 Cells and Energy
... Respiration is the process of breathing. Cellular respiration is not the same thing as breathing but they are closely related. You breathe in to get oxygen. You breathe out to get rid of carbon dioxide. Cellular respiration is a chemical reaction that uses oxygen and glucose to produce carbon dioxid ...
... Respiration is the process of breathing. Cellular respiration is not the same thing as breathing but they are closely related. You breathe in to get oxygen. You breathe out to get rid of carbon dioxide. Cellular respiration is a chemical reaction that uses oxygen and glucose to produce carbon dioxid ...
Citric acid cycle ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN AND
... Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
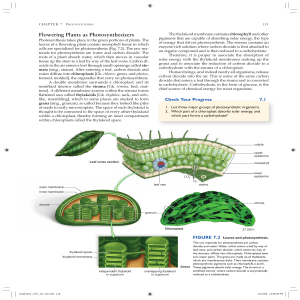
Flowering Plants as Photosynthesizers
... through ATP synthase complexes, ATP production occurs (see page 124). Notice that this ATP will be used by the Calvin cycle reactions in the stroma to reduce carbon dioxide to a carbohydrate. When the PS I pigment complex absorbs solar energy, energized electrons leave its reaction center and are ca ...
... through ATP synthase complexes, ATP production occurs (see page 124). Notice that this ATP will be used by the Calvin cycle reactions in the stroma to reduce carbon dioxide to a carbohydrate. When the PS I pigment complex absorbs solar energy, energized electrons leave its reaction center and are ca ...
1495/Chapter 03
... synthase complex that is embedded in the inner membrane, as shown in Figure 3.11. Because of the crucial role played by oxygen, this process of A As electrons (e− ) move through the electron transport chain, hydrogen ions (H+ ) are pumped from the matrix into the intermembrane space. H+ ...
... synthase complex that is embedded in the inner membrane, as shown in Figure 3.11. Because of the crucial role played by oxygen, this process of A As electrons (e− ) move through the electron transport chain, hydrogen ions (H+ ) are pumped from the matrix into the intermembrane space. H+ ...
Cellular Respiration:
... Phase 3: The Electron Transport System (ETS) Reactions. Gets rid of NADH & FADH Reactions take place in the inner membrane Cristae of a mitochondria. ...
... Phase 3: The Electron Transport System (ETS) Reactions. Gets rid of NADH & FADH Reactions take place in the inner membrane Cristae of a mitochondria. ...
ppt
... Oxidative phosphorylation: electrons of NADH, FADH2 combine with O2; energy released drives synthesis of ATP. • Passage of e- through carriers: electron transport chain, inner mitochondrial membrane of eukaryotes (inner plasma membrane of prokaryotes) • H+ are pumped out → electrochemical gradient • ...
... Oxidative phosphorylation: electrons of NADH, FADH2 combine with O2; energy released drives synthesis of ATP. • Passage of e- through carriers: electron transport chain, inner mitochondrial membrane of eukaryotes (inner plasma membrane of prokaryotes) • H+ are pumped out → electrochemical gradient • ...
Energy and Enzymes
... The formation of ATP in the cytoplasm is substrate-level phosphorylation. Energy from a high-energy substrate is used to transfer a phosphate group to ADP to form ATP. ...
... The formation of ATP in the cytoplasm is substrate-level phosphorylation. Energy from a high-energy substrate is used to transfer a phosphate group to ADP to form ATP. ...
Photosynthesis - Cloudfront.net
... BREAKING DOWN PHOTOSYNTHESIS Write the equation for photosynthesis, using different colors to represent the reactants, requirements, and products of photosynthesis. Draw the products of Photosynthesis in a creative way that will help you remember what they are. ...
... BREAKING DOWN PHOTOSYNTHESIS Write the equation for photosynthesis, using different colors to represent the reactants, requirements, and products of photosynthesis. Draw the products of Photosynthesis in a creative way that will help you remember what they are. ...
7 - Anaerobic Respiration
... until after exercise finishes, or if exercise intensity drops significantly (as high levels of O2 availability are required for aerobic respiration) – fatigue occurs. •If exercise continues after the depletion of the PCr stores then other energy systems must be used to resynthesise ATP. •Only 1 ATP ...
... until after exercise finishes, or if exercise intensity drops significantly (as high levels of O2 availability are required for aerobic respiration) – fatigue occurs. •If exercise continues after the depletion of the PCr stores then other energy systems must be used to resynthesise ATP. •Only 1 ATP ...
Document
... – Both use an inorganic final electron acceptor • Aerobic respiration uses O2 • Anaerobic respiration uses an inorganic compound other than O2 (Ex. NO3-) ...
... – Both use an inorganic final electron acceptor • Aerobic respiration uses O2 • Anaerobic respiration uses an inorganic compound other than O2 (Ex. NO3-) ...
PPT
... – Both use an inorganic final electron acceptor • Aerobic respiration uses O2 • Anaerobic respiration uses an inorganic compound other than O2 (Ex. NO3-) ...
... – Both use an inorganic final electron acceptor • Aerobic respiration uses O2 • Anaerobic respiration uses an inorganic compound other than O2 (Ex. NO3-) ...
Solution
... b. Estimate the ΔG′° for this reaction and provide a brief explanation (1-2 sentences). Approximately 0. Standard free energy is close to 0 because the standard free energy for each ½ reaction is the same (see part a). ...
... b. Estimate the ΔG′° for this reaction and provide a brief explanation (1-2 sentences). Approximately 0. Standard free energy is close to 0 because the standard free energy for each ½ reaction is the same (see part a). ...
Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
... Advantages of using triacylglycerols for energy storage 1. Fats are highly reduced hydrocarbons with a large energy of oxidation. 2. Fats are insoluble molecules that aggregate into droplets. They are unsolvated and no storage mass is water. 3. Fats are chemically inert. They can be stored without ...
... Advantages of using triacylglycerols for energy storage 1. Fats are highly reduced hydrocarbons with a large energy of oxidation. 2. Fats are insoluble molecules that aggregate into droplets. They are unsolvated and no storage mass is water. 3. Fats are chemically inert. They can be stored without ...
Cellular Respiration
... •Krebs Cycle The Krebs cycle is a series of reactions that produce energy-storing molecules during aerobic respiration. •Electron Transport Chain During aerobic respiration, large amounts of ATP are made in an electron transport chain. ...
... •Krebs Cycle The Krebs cycle is a series of reactions that produce energy-storing molecules during aerobic respiration. •Electron Transport Chain During aerobic respiration, large amounts of ATP are made in an electron transport chain. ...
Document
... Anabolic Pathways • Anabolic & catabolic pathways involving the same compounds are not the same • Some steps may be common to both ...
... Anabolic Pathways • Anabolic & catabolic pathways involving the same compounds are not the same • Some steps may be common to both ...
Respiration II
... glycolytic enzymes are found in nearly all organisms. enzymes are found in nearly all organisms What does this observation imply about the evolution of ...
... glycolytic enzymes are found in nearly all organisms. enzymes are found in nearly all organisms What does this observation imply about the evolution of ...
Recitation 4: glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, and the citric acid cycle
... • Synthesis of fats, amino acids, nucleotides and complex biological molecules ...
... • Synthesis of fats, amino acids, nucleotides and complex biological molecules ...
Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy
... • When glucose burns, energy is released as heat and light: g C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H20 + energy • The same equation applies to the metabolism of g glucose by y cells, but the reaction is accomplished in many separate steps so that the energy can be captured as ATP with ith minimal i i l loss l ...
... • When glucose burns, energy is released as heat and light: g C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H20 + energy • The same equation applies to the metabolism of g glucose by y cells, but the reaction is accomplished in many separate steps so that the energy can be captured as ATP with ith minimal i i l loss l ...
How Cells Harvest Energy from Food
... to CH4 (methane), using hydrogens derived from organic molecules produced by other organisms. Sulfur Bacteria. A second anaerobic respiratory process is carried out by certain primitive bacteria. In this sulfate respiration, the bacteria derive energy from the reduction of inorganic sulfate (SO4) to ...
... to CH4 (methane), using hydrogens derived from organic molecules produced by other organisms. Sulfur Bacteria. A second anaerobic respiratory process is carried out by certain primitive bacteria. In this sulfate respiration, the bacteria derive energy from the reduction of inorganic sulfate (SO4) to ...
2.277 December 2004 Final Exam
... B) One GDP is phosphorylated by direct chemical coupling (substrate level phosphorylation). C) One carbon-carbon bond is oxidized by FAD at the reaction step catalyzed by succinate dehydrogenase. D) One molecule of water is consumed at the reaction step catalyzed by fumarase. E) Two molecules of CO2 ...
... B) One GDP is phosphorylated by direct chemical coupling (substrate level phosphorylation). C) One carbon-carbon bond is oxidized by FAD at the reaction step catalyzed by succinate dehydrogenase. D) One molecule of water is consumed at the reaction step catalyzed by fumarase. E) Two molecules of CO2 ...
new04CH4E28.62W
... which 2H and 18O diffuses throughout the body’s water and bicarbonate stores and leaves the body is monitored and used to calculate how much energy is expended ...
... which 2H and 18O diffuses throughout the body’s water and bicarbonate stores and leaves the body is monitored and used to calculate how much energy is expended ...