chapter-6-rev - HCC Learning Web
... Why is it important to regenerate NAD+ molecules during fermentation? __________ is the only state in glucose metabolism that does not require oxygen to proceed. Two possible end products of fermentation are __________ as is produced by our muscle cell under anaerobic conditions and __________ by ye ...
... Why is it important to regenerate NAD+ molecules during fermentation? __________ is the only state in glucose metabolism that does not require oxygen to proceed. Two possible end products of fermentation are __________ as is produced by our muscle cell under anaerobic conditions and __________ by ye ...
Cellular respiration - Jocha
... • Inner mitochondrion membrane pathway Æ etransported by NADH and FADH2 are released in the inner membrane system ...
... • Inner mitochondrion membrane pathway Æ etransported by NADH and FADH2 are released in the inner membrane system ...
The Chemical Context of Life by Dr. Ty C.M. Hoffman
... created or destroyed in this process, but a rearrangement of electrons results in products that have different properties compared to the reactants from which they are produced. ...
... created or destroyed in this process, but a rearrangement of electrons results in products that have different properties compared to the reactants from which they are produced. ...
Detection Systems in Immunohistochemistry
... to antibodies, producing a system capable of detecting antigens by peroxidase staining. Incubation of HRP in a solution containing hydrogen peroxide and DiaminoBenzidine (DAB) results in the reduction of DAB to an insoluble brown precipitate, visible under the light microscope. Alkaline phosphatase ...
... to antibodies, producing a system capable of detecting antigens by peroxidase staining. Incubation of HRP in a solution containing hydrogen peroxide and DiaminoBenzidine (DAB) results in the reduction of DAB to an insoluble brown precipitate, visible under the light microscope. Alkaline phosphatase ...
42P PROCEEDINGS OF THE BIOCHEMICAL SOCIETY
... by plant chloroplasts but into protochlorophyll via protoporphyrin IX in plant proplastids (Granick, 1961). Thusthechloroplastinitsimmatureproplastid form seems competent to synthesize both haem and chlorophylls from ALA. It was now decided to test whether the plant proplastids also possess the abil ...
... by plant chloroplasts but into protochlorophyll via protoporphyrin IX in plant proplastids (Granick, 1961). Thusthechloroplastinitsimmatureproplastid form seems competent to synthesize both haem and chlorophylls from ALA. It was now decided to test whether the plant proplastids also possess the abil ...
BOOK NOTES ch9_sec3
... • Hydrogen ions diffuse through ATP synthase, providing energy to produce several ATP molecules from ADP. • At the end of the electron transport chain, the electrons combine with an oxygen atom and two hydrogen ions to form two water molecules. • If oxygen is not present, the electron transport chai ...
... • Hydrogen ions diffuse through ATP synthase, providing energy to produce several ATP molecules from ADP. • At the end of the electron transport chain, the electrons combine with an oxygen atom and two hydrogen ions to form two water molecules. • If oxygen is not present, the electron transport chai ...
SADDLEBACK COLLEGE BIOLOGY 20 EXAMINATION 2 STUDY
... • what’s the role of the photosynthetic pigments? Why are many plants green? What colors of light are being absorbed/reflected by chlorophyll? What are accessory pigments and their function? • Know how plants produce O2 & sugar. • What do plants do with CO2 & H20? What’s the function of sunlight wit ...
... • what’s the role of the photosynthetic pigments? Why are many plants green? What colors of light are being absorbed/reflected by chlorophyll? What are accessory pigments and their function? • Know how plants produce O2 & sugar. • What do plants do with CO2 & H20? What’s the function of sunlight wit ...
Karbohidrat Metabolizması
... isocitrate which has a secondary -OH, which can be oxidized • Aconitase uses an iron-sulfur cluster to position citrate (binds –OH and carboxyl of central carbon) ...
... isocitrate which has a secondary -OH, which can be oxidized • Aconitase uses an iron-sulfur cluster to position citrate (binds –OH and carboxyl of central carbon) ...
Cellular respiration - Lake City Public Schools High School
... 1. A chemical reaction in which a substance loses electrons is called oxidation. Substances gain electrons through the chemical process of reduction. Electrons released during oxidation cannot exist independently. Therefore, every oxidation reaction is accompanied by a reduction reaction. These oxid ...
... 1. A chemical reaction in which a substance loses electrons is called oxidation. Substances gain electrons through the chemical process of reduction. Electrons released during oxidation cannot exist independently. Therefore, every oxidation reaction is accompanied by a reduction reaction. These oxid ...
PHOTOSYNTHESIS: The HILL REACTION light 6 CO2 + 12 H2O
... to the tubes. Once the DCPIP has been added, you cannot stop until the entire experiment is completed. Rehearse the following steps before you add DCPIP to any of your tubes. Immediately after the dye is added mix thoroughly by inverting it 3 times, then hand it to your partner at the “Spec 20” who ...
... to the tubes. Once the DCPIP has been added, you cannot stop until the entire experiment is completed. Rehearse the following steps before you add DCPIP to any of your tubes. Immediately after the dye is added mix thoroughly by inverting it 3 times, then hand it to your partner at the “Spec 20” who ...
4 Plant Physiology
... apoplast of a plant; thus, the water molecules move unimpeded through the apoplast until they reach the endodermis. The innermost layer of the cortex consists of a specialized cylinder of cells known as the endodermis. The presence of a Casparian strip on the walls of the endodermal cells regulates ...
... apoplast of a plant; thus, the water molecules move unimpeded through the apoplast until they reach the endodermis. The innermost layer of the cortex consists of a specialized cylinder of cells known as the endodermis. The presence of a Casparian strip on the walls of the endodermal cells regulates ...
Powering the Cell: Cellular Respiration
... energy to split glucose is provided by two molecules of ATP. As glycolysis proceeds, energy is released, and the energy is used to make four molecules of ATP. As a result, there is a net gain of two ATP molecules during glycolysis. During this stage, highenergy electrons are also transferred to mol ...
... energy to split glucose is provided by two molecules of ATP. As glycolysis proceeds, energy is released, and the energy is used to make four molecules of ATP. As a result, there is a net gain of two ATP molecules during glycolysis. During this stage, highenergy electrons are also transferred to mol ...
What photosynthetic pigments exist in plants?
... Practical exercise: What photosynthetic pigments exist in plants? Introduction: The photosynthesis is a photochemical process that occurs in green leaves, where the light is captured by organic molecules - the pigments - found in thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts. The separation of pigments contai ...
... Practical exercise: What photosynthetic pigments exist in plants? Introduction: The photosynthesis is a photochemical process that occurs in green leaves, where the light is captured by organic molecules - the pigments - found in thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts. The separation of pigments contai ...
PowerPoint: Cell Test Review
... diagram and why? Active transport-requires energy (see diagram) ...
... diagram and why? Active transport-requires energy (see diagram) ...
Cell Energy Part 3 – Respiration
... 4 e- are removed from glucose and transferred to 2 NAD+ which become 2 NADH NAD+ must be present to accept e- from glucose, otherwise glycolysis cannot take place Small overall energy yield (2 ATP), but extremely fast process After a few seconds, all of a cell’s available NAD+ is used up ...
... 4 e- are removed from glucose and transferred to 2 NAD+ which become 2 NADH NAD+ must be present to accept e- from glucose, otherwise glycolysis cannot take place Small overall energy yield (2 ATP), but extremely fast process After a few seconds, all of a cell’s available NAD+ is used up ...
Cellular Respiration CPB
... uses H-E e- from Krebs to convert ADP ATP eukaryotes: series of proteins embedded in the inner membrane of mitochondrion prokaryotes: same chain in cell membrane H-E e- move from 1 carrier protein to the next E is used to move H ions across membrane (ATP synthase) every rotation of ATPas ...
... uses H-E e- from Krebs to convert ADP ATP eukaryotes: series of proteins embedded in the inner membrane of mitochondrion prokaryotes: same chain in cell membrane H-E e- move from 1 carrier protein to the next E is used to move H ions across membrane (ATP synthase) every rotation of ATPas ...
Section 2: Energy Flow in Ecosystems
... Aerobic Respiration, continued Krebs Cycle • Pyruvate (from glycolysis) is broken down and combined with other carbon compounds. • Each time the carbon-carbon bonds are rearranged during the Krebs cycle, energy is released. • The total yield of energy-storing products from one time through the Krebs ...
... Aerobic Respiration, continued Krebs Cycle • Pyruvate (from glycolysis) is broken down and combined with other carbon compounds. • Each time the carbon-carbon bonds are rearranged during the Krebs cycle, energy is released. • The total yield of energy-storing products from one time through the Krebs ...
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY NOTES , 2s , 2px , 2py , 2pz , 2s , 2px , 2py
... even less acidic, and would not favor presence of CH3CHOH- group dissociation. In the above diagram, Notice the formation of an Aldehyde in Step (2). The “H” present in (2) can also be an Alkyl Chain. The same test would also be useful in identifying CH3CO- group as aldehydes/ketones are already bei ...
... even less acidic, and would not favor presence of CH3CHOH- group dissociation. In the above diagram, Notice the formation of an Aldehyde in Step (2). The “H” present in (2) can also be an Alkyl Chain. The same test would also be useful in identifying CH3CO- group as aldehydes/ketones are already bei ...
File
... The role of ATP in the transfer of energy and the phosphorylation of molecules by ATP. Metabolic pathways of cellular respiration. The breakdown of glucose to pyruvate in the cytoplasm in glycolysis, and the progression pathways in the presence or absence of oxygen (fermentation). The role of the en ...
... The role of ATP in the transfer of energy and the phosphorylation of molecules by ATP. Metabolic pathways of cellular respiration. The breakdown of glucose to pyruvate in the cytoplasm in glycolysis, and the progression pathways in the presence or absence of oxygen (fermentation). The role of the en ...
CHE 105 Spring 2016 Exam 3
... A. Spectra A and B are emission spectra for the same element but at different wavelengths. ✓B. Spectra A and B are emission spectra for two different elements. C. Spectra A and B are absorption spectra for two different elements. D. A is an absorption spectrum and B is an emission spectrum for two d ...
... A. Spectra A and B are emission spectra for the same element but at different wavelengths. ✓B. Spectra A and B are emission spectra for two different elements. C. Spectra A and B are absorption spectra for two different elements. D. A is an absorption spectrum and B is an emission spectrum for two d ...
Second test - rci.rutgers.edu
... enzymes, and indicate all cofactors. 1/2 point per fact. Note, you may simply write out the entire pathway if that is easier for you. ...
... enzymes, and indicate all cofactors. 1/2 point per fact. Note, you may simply write out the entire pathway if that is easier for you. ...
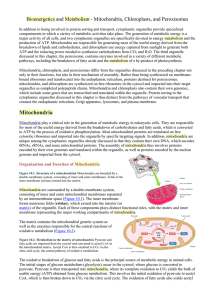
Mitochondria, Chloroplasts, and Peroxisomes
... discussed in the next section of this chapter, the transfer of high-energy electrons from NADH and FADH2 to molecular oxygen is coupled to the transfer of protons from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space. Since protons are charged particles, this transfer establishes an electric pote ...
... discussed in the next section of this chapter, the transfer of high-energy electrons from NADH and FADH2 to molecular oxygen is coupled to the transfer of protons from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space. Since protons are charged particles, this transfer establishes an electric pote ...
PCGHS March Test ~ Year 2009 ~ Upper Six BIOLOGY Mark
... α-Ketoglutarate is converted to succinyl CoA (4C). ...
... α-Ketoglutarate is converted to succinyl CoA (4C). ...
to find the lecture notes for lecture 1 click here
... investment” required to start a reaction – the reactants must absorb enough energy to cause their chemical bonds to become unstable and created new ones – as these bonds form – energy is released into the environment – if more energy is released than absorbed = heat (exothermic reaction) – two influ ...
... investment” required to start a reaction – the reactants must absorb enough energy to cause their chemical bonds to become unstable and created new ones – as these bonds form – energy is released into the environment – if more energy is released than absorbed = heat (exothermic reaction) – two influ ...