Chemistry Lecture *34". Ionic. Compounds I-P one atom trans
... Chemistry Lecture *34". Ionic. Compounds I-P one atom trans-Pers its electrons to another, they will stick together because one atom will have a positive charge and the other will have a negative charge. Electrostatic -Porce is the -Porce o£ attraction between opposite charges. Thus, anions and cati ...
... Chemistry Lecture *34". Ionic. Compounds I-P one atom trans-Pers its electrons to another, they will stick together because one atom will have a positive charge and the other will have a negative charge. Electrostatic -Porce is the -Porce o£ attraction between opposite charges. Thus, anions and cati ...
CHM_101_ASSIGNMENT_COPY_1_2
... attraction of the positive nucleus for the electron will increase. More energy is needed to remove the outermost electron, thus the ionization energy increases. 2. Size of the positive nuclear charge: As the nuclear charge increases, its attraction for the outermost electron increases, and so more ...
... attraction of the positive nucleus for the electron will increase. More energy is needed to remove the outermost electron, thus the ionization energy increases. 2. Size of the positive nuclear charge: As the nuclear charge increases, its attraction for the outermost electron increases, and so more ...
Bio 102 Lecture - chapter 2 The Chemical Basis of Life
... composed of six elements (carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, and sulfur—acronym CHNOPS) make up 98% of the body weight of organisms. ...
... composed of six elements (carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, and sulfur—acronym CHNOPS) make up 98% of the body weight of organisms. ...
Chapter 7:The Quantum-Mechanical Model of
... Dalton’s Indivisible Atom explained the Law of Constant Composition and the Law of Conservation of Mass and led to the Law of Multiple Proportions. J.J. Thomson, through Cathode Ray Tube experiments, discovered that electrons are small negatively charged particles inside a divisible atom and came up ...
... Dalton’s Indivisible Atom explained the Law of Constant Composition and the Law of Conservation of Mass and led to the Law of Multiple Proportions. J.J. Thomson, through Cathode Ray Tube experiments, discovered that electrons are small negatively charged particles inside a divisible atom and came up ...
Available here - Durham University
... stickier components of the gas (such as metals) behind. The process of removing material is variously known as milling, sputtering or etching, and it is widely used in the semiconductor industry for editing and failure analysis of integrated circuits. Adding material is done using a technique called ...
... stickier components of the gas (such as metals) behind. The process of removing material is variously known as milling, sputtering or etching, and it is widely used in the semiconductor industry for editing and failure analysis of integrated circuits. Adding material is done using a technique called ...
The Formation of Comets
... two words to epitomize the same-and-not-the-same nature of chemistry, would you not pick ferrous and ferric? The concept evolved at the end of the 19th century (not without confusion with “valency”), when the reality of ions in solution was established. As did a multiplicity of notations—ferrous iro ...
... two words to epitomize the same-and-not-the-same nature of chemistry, would you not pick ferrous and ferric? The concept evolved at the end of the 19th century (not without confusion with “valency”), when the reality of ions in solution was established. As did a multiplicity of notations—ferrous iro ...
Ch. 6 - Chemical Bonds I. Why Atoms Combine
... Write the names of both elements. Change the final ending to -ide. ...
... Write the names of both elements. Change the final ending to -ide. ...
HW / Unit 2
... 8. Identify the atoms which have the following electron configurations: a. [Ne]3s23p1 b. [Ar]4s2 c. [Ar]4s23d5 HW #2.9 1. Draw an orbital diagram for the following atoms: a. Mg b. Ar c. Rn 2. Which of the following electron configurations corresponds to an atom in its ground state? Which could be fo ...
... 8. Identify the atoms which have the following electron configurations: a. [Ne]3s23p1 b. [Ar]4s2 c. [Ar]4s23d5 HW #2.9 1. Draw an orbital diagram for the following atoms: a. Mg b. Ar c. Rn 2. Which of the following electron configurations corresponds to an atom in its ground state? Which could be fo ...
CHEMISTry is life - World of Teaching
... -Too often kids get to high school chemistry and they are scared before they even begin. -My goal is to shape a positive image in their minds about chemistry so that they can be more prepared mentally for high school. -I will do this by showing them how applicable chemistry is to every day life. It ...
... -Too often kids get to high school chemistry and they are scared before they even begin. -My goal is to shape a positive image in their minds about chemistry so that they can be more prepared mentally for high school. -I will do this by showing them how applicable chemistry is to every day life. It ...
Atomic Systems and Bonding
... thus are not too tightly bound (making it easier to ‘move out’) outside shell had only one electron When the valence electron in any atom gains sufficient energy from some outside force, it can break away from the parent atom and become what is called a free electron Atoms with few electrons in thei ...
... thus are not too tightly bound (making it easier to ‘move out’) outside shell had only one electron When the valence electron in any atom gains sufficient energy from some outside force, it can break away from the parent atom and become what is called a free electron Atoms with few electrons in thei ...
Chapter 5/6 Notes
... 6.1 Organizing the Elements and Classifying the Elements Origin of the Periodic Table Dimitri Mendeleev – published the first real periodic table in 1869 - Based upon chemical and physical properties - Listed elements in order of increasing atomic mass - Left spaces for undiscovered elements ...
... 6.1 Organizing the Elements and Classifying the Elements Origin of the Periodic Table Dimitri Mendeleev – published the first real periodic table in 1869 - Based upon chemical and physical properties - Listed elements in order of increasing atomic mass - Left spaces for undiscovered elements ...
What You Need To Know for the Chemistry Regents Exam
... Stable isotopes have a 1:1 ratio of protons and neutrons. Most radioactive isotopes have twice as many neutrons as protons. All elements with an atomic number higher than 83 are radioactive. 2. Each isotope has a specific mode and rate of decay. (see Table N) The rate of decay is called half l ...
... Stable isotopes have a 1:1 ratio of protons and neutrons. Most radioactive isotopes have twice as many neutrons as protons. All elements with an atomic number higher than 83 are radioactive. 2. Each isotope has a specific mode and rate of decay. (see Table N) The rate of decay is called half l ...
Need
... Stable isotopes have a 1:1 ratio of protons and neutrons. Most radioactive isotopes have twice as many neutrons as protons. All elements with an atomic number higher than 83 are radioactive. 2. Each isotope has a specific mode and rate of decay. (see Table N) The rate of decay is called half l ...
... Stable isotopes have a 1:1 ratio of protons and neutrons. Most radioactive isotopes have twice as many neutrons as protons. All elements with an atomic number higher than 83 are radioactive. 2. Each isotope has a specific mode and rate of decay. (see Table N) The rate of decay is called half l ...
Oxidation number and Electrolysis(電解)
... concentrated NaCl solution, only H + is discharged at the cathode. But if mercury electrode is used for the cathode, Na + is discharged because sodium metal forms an alloy with mercury. (This method is used in industry for the production of sodium.) ...
... concentrated NaCl solution, only H + is discharged at the cathode. But if mercury electrode is used for the cathode, Na + is discharged because sodium metal forms an alloy with mercury. (This method is used in industry for the production of sodium.) ...
June review January 2012 part A
... (l) A neutral nucleus is surrounded by one or more negatively charged electrons. (2) A neutral nucleus is surrounded by one or more positively charged electrons. (3) A positively charged nucleus is surrounded by one or more negatively charged electrons. (4) A positively charged nucleus is surrounded ...
... (l) A neutral nucleus is surrounded by one or more negatively charged electrons. (2) A neutral nucleus is surrounded by one or more positively charged electrons. (3) A positively charged nucleus is surrounded by one or more negatively charged electrons. (4) A positively charged nucleus is surrounded ...
vsepr_lite_oct_2011 - chemistry11crescentsummer
... fig 5. The Lewis structure of HOH. How many lone pair(s) of electrons are on the central atom, O? Adapt the molecular model of NH3 to get a model of HOH. How would you describe the shape of a water molecule? No fancy name required. Use the bond angles in CH4 and NH3 to predict the H–O–H bond angle i ...
... fig 5. The Lewis structure of HOH. How many lone pair(s) of electrons are on the central atom, O? Adapt the molecular model of NH3 to get a model of HOH. How would you describe the shape of a water molecule? No fancy name required. Use the bond angles in CH4 and NH3 to predict the H–O–H bond angle i ...
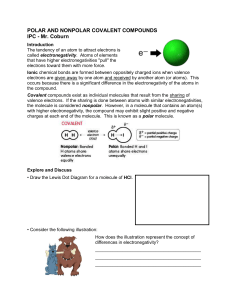
Polar and Nonpolar Covalent Compounds
... IPC - Mr. Coburn Introduction The tendency of an atom to attract electrons is called electronegativity. Atoms of elements that have higher electronegativities "pull" the electrons toward them with more force. Ionic chemical bonds are formed between oppositely charged ions when valence electrons are ...
... IPC - Mr. Coburn Introduction The tendency of an atom to attract electrons is called electronegativity. Atoms of elements that have higher electronegativities "pull" the electrons toward them with more force. Ionic chemical bonds are formed between oppositely charged ions when valence electrons are ...
Atomic Systems and Bonding
... thus are not too tightly bound (making it easier to ‘move out’) outside shell had only one electron When the valence electron in any atom gains sufficient energy from some outside force, it can break away from the parent atom and become what is called a free electron Atoms with few electrons in thei ...
... thus are not too tightly bound (making it easier to ‘move out’) outside shell had only one electron When the valence electron in any atom gains sufficient energy from some outside force, it can break away from the parent atom and become what is called a free electron Atoms with few electrons in thei ...
chem final review
... 30) In which of the following sets are the symbol of the element, the number of protons, and the number of electrons given correctly? A) In, 49 protons, 49 electrons B) Cs, 55 protons, 132.9 electrons C) Zn, 30 protons, 60 electrons D) He, 4 protons, 4 electrons E) F, 19 protons, 19 electrons 31) Co ...
... 30) In which of the following sets are the symbol of the element, the number of protons, and the number of electrons given correctly? A) In, 49 protons, 49 electrons B) Cs, 55 protons, 132.9 electrons C) Zn, 30 protons, 60 electrons D) He, 4 protons, 4 electrons E) F, 19 protons, 19 electrons 31) Co ...
1 - kurtniedenzu
... 16. In the particle model of the atom, which nuclei of atoms are surrounded by negatively charged electrons? a. all nuclei b. only nuclei with more electrons than protons c. only nuclei with more neutrons than protons d. only nuclei with the same number of protons as neutrons 17. How is an atom of 3 ...
... 16. In the particle model of the atom, which nuclei of atoms are surrounded by negatively charged electrons? a. all nuclei b. only nuclei with more electrons than protons c. only nuclei with more neutrons than protons d. only nuclei with the same number of protons as neutrons 17. How is an atom of 3 ...