200 Ways to Pass the Chemistry - Home 15-16
... 94. Atoms are most stable when they have 8 valence electrons (an octet) (except H & He) and tend to form ions to obtain such a configuration of electrons. Which of the following atoms forms a stable ion that does not have an octet structure? Li F Na Cl 95. Covalent bonds non-metal with non-metal for ...
... 94. Atoms are most stable when they have 8 valence electrons (an octet) (except H & He) and tend to form ions to obtain such a configuration of electrons. Which of the following atoms forms a stable ion that does not have an octet structure? Li F Na Cl 95. Covalent bonds non-metal with non-metal for ...
Nucleon number
... Isotopes of an element have the same: 1. number of protons (proton number) 2. charge of nucleus of the atoms (ionization energy; electron affinity; size of the atom; electronegativity are the same) 3. number of electrons in a neutral atom 4. electronic configuration (the number of valence electrons ...
... Isotopes of an element have the same: 1. number of protons (proton number) 2. charge of nucleus of the atoms (ionization energy; electron affinity; size of the atom; electronegativity are the same) 3. number of electrons in a neutral atom 4. electronic configuration (the number of valence electrons ...
g - Porterville College Home
... a. First word is the first element in the formula. Second word is the second element with the usual modified “-ide” ending. b. Prefixes are added to each word based on the subscript of each element. Refer to Greek prefix table (e.g. tri = 3 atoms) c. Prefix exception: Mono is never used on the first ...
... a. First word is the first element in the formula. Second word is the second element with the usual modified “-ide” ending. b. Prefixes are added to each word based on the subscript of each element. Refer to Greek prefix table (e.g. tri = 3 atoms) c. Prefix exception: Mono is never used on the first ...
Chapter 2 Name___________________________________
... MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) If an atom of sulfur (atomic number 16) were allowed to react with atoms of hydrogen (atomic number 1), which of the molecules below would be formed? H A) S H B) H S H C) H S H D) E) H S H ...
... MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) If an atom of sulfur (atomic number 16) were allowed to react with atoms of hydrogen (atomic number 1), which of the molecules below would be formed? H A) S H B) H S H C) H S H D) E) H S H ...
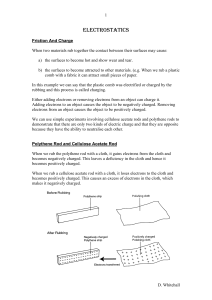
ELECTROSTATICS
... 2) The basic rule of like charges repelling and unlike charges attracting applies to these diagrams. 3) Electric fields around the object are symmetrical in all directions (dimensions) 4) There would always be an equal and opposite force acting on charged producing an electric field (Newton’s Third ...
... 2) The basic rule of like charges repelling and unlike charges attracting applies to these diagrams. 3) Electric fields around the object are symmetrical in all directions (dimensions) 4) There would always be an equal and opposite force acting on charged producing an electric field (Newton’s Third ...
Exam practice answers 5
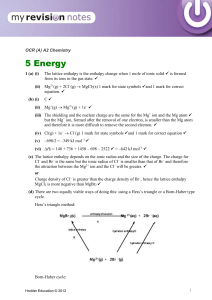
... be doubled because there are two Br–). H1 = 2440 – 1921 – (2 336) = –153 kJ mol–1 (e) (i) (ii) ...
... be doubled because there are two Br–). H1 = 2440 – 1921 – (2 336) = –153 kJ mol–1 (e) (i) (ii) ...
4.5 Solid fast-ion conductors 1
... face-centred cubic lattice would only allow penetration by a cation(0.15rA). however, in the case of I- ions(radius 220pm), interstices offer an aperture of only 34pm radius, the transport of Li+ (r3=55pm) is significant and the room temperature ionic Conductivity of LiI is 5×10-5 Sm-1 ...
... face-centred cubic lattice would only allow penetration by a cation(0.15rA). however, in the case of I- ions(radius 220pm), interstices offer an aperture of only 34pm radius, the transport of Li+ (r3=55pm) is significant and the room temperature ionic Conductivity of LiI is 5×10-5 Sm-1 ...
Using mass to calculate molecular formula
... Check that the number of atoms of each type is correct and that the masses are conserved. If 3.4 g of methane are burnt in excess oxygen, what mass of carbon dioxide is formed. 13.4 g of CH4 is 13.4/16 = 0.837 mol of CH4 Equation shows that 1 mol CH4 produces 1 mol CO2, therefore 0.837 mol CO2, mass ...
... Check that the number of atoms of each type is correct and that the masses are conserved. If 3.4 g of methane are burnt in excess oxygen, what mass of carbon dioxide is formed. 13.4 g of CH4 is 13.4/16 = 0.837 mol of CH4 Equation shows that 1 mol CH4 produces 1 mol CO2, therefore 0.837 mol CO2, mass ...
2-1 Checkpoint - Jordan High School
... • Ex: carbon – C12: 6 protons, 6 neutrons – C13: 6 protons, 7 neutrons ...
... • Ex: carbon – C12: 6 protons, 6 neutrons – C13: 6 protons, 7 neutrons ...
acids: bases - IDS-chem2-Rn-10
... of the solution can be determined visually. Hence a pH indicator is a chemical detector for hydronium ions (H3O+) or hydrogen ions (H+) in the Arrhenius model. ...
... of the solution can be determined visually. Hence a pH indicator is a chemical detector for hydronium ions (H3O+) or hydrogen ions (H+) in the Arrhenius model. ...
Chapter 2: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... C) Ernest Rutherford D) William Thomson E) John Dalton 17. Alpha particles beamed at thin metal foil may A) pass directly through without changing direction B) be slightly diverted by attraction to electrons C) be reflected by direct contact with nuclei D) A and C E) A, B, and C 18. Which one of th ...
... C) Ernest Rutherford D) William Thomson E) John Dalton 17. Alpha particles beamed at thin metal foil may A) pass directly through without changing direction B) be slightly diverted by attraction to electrons C) be reflected by direct contact with nuclei D) A and C E) A, B, and C 18. Which one of th ...
Energy Atoms and Elements Practice Problems
... A) A neutron has no charge and a mass of approximately 1 amu. B) An electron has a negative charge and a mass of approximately 1 amu. C) A proton has a positive charge and a mass of approximately 2 amu. D) A proton has a positive charge and a mass of approximately 1 amu. ...
... A) A neutron has no charge and a mass of approximately 1 amu. B) An electron has a negative charge and a mass of approximately 1 amu. C) A proton has a positive charge and a mass of approximately 2 amu. D) A proton has a positive charge and a mass of approximately 1 amu. ...
File
... 11. Electronegativity indicates how strongly an atom of an element attracts electrons in a chemical bond. These values are based on an arbitrary scale. 12. The electronegativity difference between two bonded atoms can determine the type of bond and its polarity. 0.0 - 0.4 = non-polar covalent 0.4-1. ...
... 11. Electronegativity indicates how strongly an atom of an element attracts electrons in a chemical bond. These values are based on an arbitrary scale. 12. The electronegativity difference between two bonded atoms can determine the type of bond and its polarity. 0.0 - 0.4 = non-polar covalent 0.4-1. ...
Name: (1 of 2) Math Set # 13 Protons,
... For example, if a hydrogen atom has one proton (+) and one electron (-‐) the two charges cancel each other out. When the electron is lost the hydrogen atom is only a single proton (+)! ...
... For example, if a hydrogen atom has one proton (+) and one electron (-‐) the two charges cancel each other out. When the electron is lost the hydrogen atom is only a single proton (+)! ...
What You Need To Know for the Chemistry Regents
... 11. Electronegativity indicates how strongly an atom of an element attracts electrons in a chemical bond. These values are based on an arbitrary scale. 12. The electronegativity difference between two bonded atoms can determine the type of bond and its polarity. 0.0 - 0.4 = non-polar covalent 0.4-1. ...
... 11. Electronegativity indicates how strongly an atom of an element attracts electrons in a chemical bond. These values are based on an arbitrary scale. 12. The electronegativity difference between two bonded atoms can determine the type of bond and its polarity. 0.0 - 0.4 = non-polar covalent 0.4-1. ...
The Periodic table
... A region of space within an electron subshell where an electron with a specific energy is most likely to be found. S subshell=1 orbital, p subshell=3 orbitals, d subshell=5 orbitals, f subshell=7 orbitals. Maximum number of electrons in a subshell is always 2. S orbital=spherical, p orbital ...
... A region of space within an electron subshell where an electron with a specific energy is most likely to be found. S subshell=1 orbital, p subshell=3 orbitals, d subshell=5 orbitals, f subshell=7 orbitals. Maximum number of electrons in a subshell is always 2. S orbital=spherical, p orbital ...
C2 Chemistry - Burton Borough School
... Catalysts speed up reactions without being used up Increase in pressure is the same as increase in ...
... Catalysts speed up reactions without being used up Increase in pressure is the same as increase in ...
Name - Madison County Schools
... A. Who first arranged the periodic table by atomic mass? Dmitri Mendeleev B. What characteristics did Mendeleev use to place the elements in order when creating the periodic table? Rows - Increasing mass Columns – Similar properties C. What are valence electrons? Electrons in the highest occupied en ...
... A. Who first arranged the periodic table by atomic mass? Dmitri Mendeleev B. What characteristics did Mendeleev use to place the elements in order when creating the periodic table? Rows - Increasing mass Columns – Similar properties C. What are valence electrons? Electrons in the highest occupied en ...
Ch 4 Review
... ____ 17. How are the elements in the periodic table arranged? a. in order of atomic charge c. in order of subatomic particles b. in order of atomic number d. in alphabetical order ____ 18. The attractive force between oppositely charged ions that result from the transfer of electrons from one atom t ...
... ____ 17. How are the elements in the periodic table arranged? a. in order of atomic charge c. in order of subatomic particles b. in order of atomic number d. in alphabetical order ____ 18. The attractive force between oppositely charged ions that result from the transfer of electrons from one atom t ...
Things to Know to Pass the Chemistry Regents
... 68. q = mHf (melting), q = mHv(vaporizing), q = mC(change in temperature) (raising/lowering) *Tables T and B 69. Combined gas law on Table T *If given STP, given temp and pressure (Table A) 70. Pressure and volume indirect, P up, V down (PVC pipe) 71. Temperature and pressure direct, T up, P up 72. ...
... 68. q = mHf (melting), q = mHv(vaporizing), q = mC(change in temperature) (raising/lowering) *Tables T and B 69. Combined gas law on Table T *If given STP, given temp and pressure (Table A) 70. Pressure and volume indirect, P up, V down (PVC pipe) 71. Temperature and pressure direct, T up, P up 72. ...
Name: (1 of 2) Math Set # 13 Protons, Neutrons, Electrons Proton
... An ionic bond is created between metals and nonmetals. This is because a metal in group 1 or 2 gives up electrons easily and nonmetals in groups 16 through 18 accept electrons easily. An ionic bond results in two or more ions being attracted to each other. The total charge of the molecule must be ze ...
... An ionic bond is created between metals and nonmetals. This is because a metal in group 1 or 2 gives up electrons easily and nonmetals in groups 16 through 18 accept electrons easily. An ionic bond results in two or more ions being attracted to each other. The total charge of the molecule must be ze ...
Final
... electronegativity (table will be provided) Given a Lewis structure, be able to: identify the shape identify the hybridization of the central atom draw the molecule with the correct shape give the bonding description for all bonds within the structure Be able to determine whether a bond is nonpolar c ...
... electronegativity (table will be provided) Given a Lewis structure, be able to: identify the shape identify the hybridization of the central atom draw the molecule with the correct shape give the bonding description for all bonds within the structure Be able to determine whether a bond is nonpolar c ...
What is Chemistry? Chemistry
... o Atoms that gain electrons to form compounds are called anions. Anions have a _________________________________. o Naming Anions: Drop the last few letters of the element name and add “ide”. o E.g. Group 17 (Halogens) gain electrons easily and release lots of energy in the process highly reactive ...
... o Atoms that gain electrons to form compounds are called anions. Anions have a _________________________________. o Naming Anions: Drop the last few letters of the element name and add “ide”. o E.g. Group 17 (Halogens) gain electrons easily and release lots of energy in the process highly reactive ...
Oxidation and Reduction Reactions
... Single Cell filled with electrolyte with +/- ions Attach battery to two electrodes. Electrodes are made of an inert substance (like platinum or graphite) that conducts. Electrodes don’t chemically change like in a battery, ...
... Single Cell filled with electrolyte with +/- ions Attach battery to two electrodes. Electrodes are made of an inert substance (like platinum or graphite) that conducts. Electrodes don’t chemically change like in a battery, ...