gr11chemreview
... 4. Why is the ionic radius of a negative ion larger than the atomic radius of the corresponding neutral atom? ...
... 4. Why is the ionic radius of a negative ion larger than the atomic radius of the corresponding neutral atom? ...
Unit 3 Review Questions - Unit #1-0
... 36. In a diatomic molecule of an element, the bond between the atoms must be: 1. ? metallic 2. ? polar covalent 3. ? nonpolar covalent 4. ? ionic ...
... 36. In a diatomic molecule of an element, the bond between the atoms must be: 1. ? metallic 2. ? polar covalent 3. ? nonpolar covalent 4. ? ionic ...
8th Grade: First Semester Final Review
... 26. react quickly with other elements such as oxygen Choose the letter of the term that matches it correctly. Each term is used only once. a. halogen d. oxygen and nitrogen b. noble gases e. carbon c. metalloids 29. do not form natural compounds 32. nonmetals in your body 30. nonmetal from group 14 ...
... 26. react quickly with other elements such as oxygen Choose the letter of the term that matches it correctly. Each term is used only once. a. halogen d. oxygen and nitrogen b. noble gases e. carbon c. metalloids 29. do not form natural compounds 32. nonmetals in your body 30. nonmetal from group 14 ...
Year End Chemistry Review
... 1. Homogeneous vs heterogeneous 2. Physical vs chemical changes 3. Metric System and metric conversions: 2 km = _____cm 100 cm = ____mm 5 m = ____km 4. Density as measured by water displacement: Find the density of a metal if its mass = 5.0 grams, the initial volume of water without metal = 10.0 mL ...
... 1. Homogeneous vs heterogeneous 2. Physical vs chemical changes 3. Metric System and metric conversions: 2 km = _____cm 100 cm = ____mm 5 m = ____km 4. Density as measured by water displacement: Find the density of a metal if its mass = 5.0 grams, the initial volume of water without metal = 10.0 mL ...
Chemistry Study Guide
... Chemistry Study Guide Atoms and Subatomic Particles Atom. Al matter is made up of unique particles called atoms. An atom contains: o Protons- Positively charged; have atomic mass of one; Located in the nucleus of the atom. o Neutrons- Neutral in charge; the same mass as the proton; also located in ...
... Chemistry Study Guide Atoms and Subatomic Particles Atom. Al matter is made up of unique particles called atoms. An atom contains: o Protons- Positively charged; have atomic mass of one; Located in the nucleus of the atom. o Neutrons- Neutral in charge; the same mass as the proton; also located in ...
Chemistry Study Guide
... Chemistry Study Guide Atoms and Subatomic Particles Atom. Al matter is made up of unique particles called atoms. An atom contains: o Protons- Positively charged; have atomic mass of one; Located in the nucleus of the atom. o Neutrons- Neutral in charge; the same mass as the proton; also located in ...
... Chemistry Study Guide Atoms and Subatomic Particles Atom. Al matter is made up of unique particles called atoms. An atom contains: o Protons- Positively charged; have atomic mass of one; Located in the nucleus of the atom. o Neutrons- Neutral in charge; the same mass as the proton; also located in ...
46 Pd Palladium 106.4
... ____ 4. What did Democritus, Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, and Bohr all have in common? A. They each identified new elements. B. They each identified new isotopes of atoms. C. They each contributed to the development of the atomic theory. D. They each conducted experiments in which particles collided ...
... ____ 4. What did Democritus, Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, and Bohr all have in common? A. They each identified new elements. B. They each identified new isotopes of atoms. C. They each contributed to the development of the atomic theory. D. They each conducted experiments in which particles collided ...
BIOCHEMISTRY: The Chemistry of Life Chemistry of Life: ATOMS
... Chemistry of Life: ATOMS • Atomic #: –# of Protons in an atom –Order on the Periodic Table of Elements • Atomic Mass: –Sum of the Protons & Neutrons in the nucleus of the Atom – Atomic Mass – Atomic # = # of Neutrons ...
... Chemistry of Life: ATOMS • Atomic #: –# of Protons in an atom –Order on the Periodic Table of Elements • Atomic Mass: –Sum of the Protons & Neutrons in the nucleus of the Atom – Atomic Mass – Atomic # = # of Neutrons ...
probability = ψ 2
... The nucleus is the very dense region consisting of nucleons (protons and neutrons) at the center of an atom. Almost all of the mass in an atom is made up from the protons and neutrons in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the orbiting electrons. The diameter of the nucleus is in the ...
... The nucleus is the very dense region consisting of nucleons (protons and neutrons) at the center of an atom. Almost all of the mass in an atom is made up from the protons and neutrons in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the orbiting electrons. The diameter of the nucleus is in the ...
Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
... atoms tend to change also – atoms that have either lost or gained electrons are called ions. Atoms that have lost electrons (as a result, now contain more p+ than e-) are called cations which carry positive charges, while atoms that have gained excessive electrons (as a result, now contain more etha ...
... atoms tend to change also – atoms that have either lost or gained electrons are called ions. Atoms that have lost electrons (as a result, now contain more p+ than e-) are called cations which carry positive charges, while atoms that have gained excessive electrons (as a result, now contain more etha ...
Atomic Theories and Models - MrD-Home
... The chemical equation for the reaction of methane and oxygen is ______ yet properly balanced because the atoms of the elements on the product side do not ______ the atoms of each element on the reactant side of the equation. The _________________________, which states that matter can neither be ____ ...
... The chemical equation for the reaction of methane and oxygen is ______ yet properly balanced because the atoms of the elements on the product side do not ______ the atoms of each element on the reactant side of the equation. The _________________________, which states that matter can neither be ____ ...
Chemistry Fall-2016 Final
... AA. any metal in Group 2A of the periodic table; generally harder, denser, stronger, and have higher melting points than alkali metals ...
... AA. any metal in Group 2A of the periodic table; generally harder, denser, stronger, and have higher melting points than alkali metals ...
Ch 2 Atomic History
... Atoms of the same element are exactly the same; atoms of different elements are different. ...
... Atoms of the same element are exactly the same; atoms of different elements are different. ...
Semester 1 Final Review Powerpoint
... A. Two Hydrogen atoms will form a helium atom in the fusion process. B. The other by-product of fusion is a huge quantity of energy. C. Fusion requires H as a fuel source (available in any water molecule on Earth). D. There are no radioactive by-products of ...
... A. Two Hydrogen atoms will form a helium atom in the fusion process. B. The other by-product of fusion is a huge quantity of energy. C. Fusion requires H as a fuel source (available in any water molecule on Earth). D. There are no radioactive by-products of ...
Midterm Review 4
... 54. The tendency to lose electrons ______________ as we move across a period on the periodic table a. increases b. remains the same c. decreases d. no trend exists 55. Generally, members of a ____________ have the same number of valence electrons. a. period b. series c. row d. family 56. An element ...
... 54. The tendency to lose electrons ______________ as we move across a period on the periodic table a. increases b. remains the same c. decreases d. no trend exists 55. Generally, members of a ____________ have the same number of valence electrons. a. period b. series c. row d. family 56. An element ...
Prerequisite Knowledge for Chemistry
... All atoms of one element will have the same number of protons. If you change the number of protons then the element changes. For instance, all carbon atoms have 6 protons. If a proton is added to a carbon atom, the atom would become nitrogen. All atoms with 7 protons are nitrogen. ...
... All atoms of one element will have the same number of protons. If you change the number of protons then the element changes. For instance, all carbon atoms have 6 protons. If a proton is added to a carbon atom, the atom would become nitrogen. All atoms with 7 protons are nitrogen. ...
water, h2o
... It has long been recognized – remarkably, for 200 years - that protons have the potential for a unique mode of transport in water and, by extension, in other highly connected hydrogen bonding systems. The Grotthuss mechanism involves a simple shift of hydrogen bonds to effectively relocate a net pro ...
... It has long been recognized – remarkably, for 200 years - that protons have the potential for a unique mode of transport in water and, by extension, in other highly connected hydrogen bonding systems. The Grotthuss mechanism involves a simple shift of hydrogen bonds to effectively relocate a net pro ...
1st Semester Exam in High School Chemistry
... A. transition metals B. alkali series C. lanthanide elements D. actinide series ...
... A. transition metals B. alkali series C. lanthanide elements D. actinide series ...
CHEMISTRY
... Recall – compounds are pure substances that contain more than one type of element that are bonded together in a fixed ratio. Water (H2O) is an example of a compound. In water, the two hydrogen atoms are stuck to the oxygen and can’t be separated without undergoing a chemical change. There are two ty ...
... Recall – compounds are pure substances that contain more than one type of element that are bonded together in a fixed ratio. Water (H2O) is an example of a compound. In water, the two hydrogen atoms are stuck to the oxygen and can’t be separated without undergoing a chemical change. There are two ty ...
Total view of the AFM
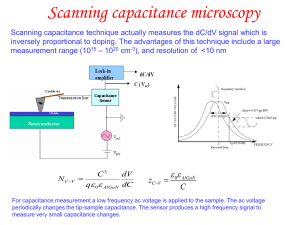
... • There are mainly three types of electron sources – Tungsten hairpin filament: This is simply a tip that is heated to an extremely high temperature of ~2500 C to make electrons have high enough energy to overcome the surface work function of ~4.5 eV – To get higher electron current stable materials ...
... • There are mainly three types of electron sources – Tungsten hairpin filament: This is simply a tip that is heated to an extremely high temperature of ~2500 C to make electrons have high enough energy to overcome the surface work function of ~4.5 eV – To get higher electron current stable materials ...
HonorsChem.final.rev.probs
... 34. Suppose that a balloon is launched when the temperature is 26°C and the barometric pressure is 735 mm Hg. If the balloon’s volume is 20.4 L, what will it be at a height of 10 miles, where the pressure is 110.0 mm Hg and the temperature is 0°C? ...
... 34. Suppose that a balloon is launched when the temperature is 26°C and the barometric pressure is 735 mm Hg. If the balloon’s volume is 20.4 L, what will it be at a height of 10 miles, where the pressure is 110.0 mm Hg and the temperature is 0°C? ...
Types of Measurement
... 1. Ionic: made up of ions of opposite charge A. strong electrostatic force of attraction; ionic bond B. electrons are transferred 2. Covalent: made up of two or more nonmetals A. electrons are shared ...
... 1. Ionic: made up of ions of opposite charge A. strong electrostatic force of attraction; ionic bond B. electrons are transferred 2. Covalent: made up of two or more nonmetals A. electrons are shared ...
Name
... that are arranged __asymmetrically in a bent shape___________. 14. Describe properties that are common in typical molecular compounds. ...
... that are arranged __asymmetrically in a bent shape___________. 14. Describe properties that are common in typical molecular compounds. ...