Chapter 15 - Cloudfront.net
... We know that all matter consists of tiny particles called atoms which contain protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and electrons have a certain amount of “electric charge.” This electric charge enables them to attract and repel each other. ...
... We know that all matter consists of tiny particles called atoms which contain protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and electrons have a certain amount of “electric charge.” This electric charge enables them to attract and repel each other. ...
Working with solutions
... O Ionic solids in water- positive and negative ions are attracted to polar water molecules. O Molecular solids in water- break up into individual neutral molecules and are surrounded by water. O Ionic compounds conducted electricity molecular compounds do not. ...
... O Ionic solids in water- positive and negative ions are attracted to polar water molecules. O Molecular solids in water- break up into individual neutral molecules and are surrounded by water. O Ionic compounds conducted electricity molecular compounds do not. ...
electric field
... A NEGATIVE charge occurs when there are more electrons than protons, the object is gaining electrons. A POSITIVE charge occurs when there are less electrons than protons, the object is losing electrons. ...
... A NEGATIVE charge occurs when there are more electrons than protons, the object is gaining electrons. A POSITIVE charge occurs when there are less electrons than protons, the object is losing electrons. ...
Adv review key
... A) Electrons are transferred between atoms B) Valence electrons- outer shell electrons C) Metals a. Lend valence electrons b. 1 – 4 valence electrons c. Form positive ions ( more protons than electrons) D) Nonmetals a. Borrow valence electrons b. 4 - 8 valence electrons c. Form negative ions (more e ...
... A) Electrons are transferred between atoms B) Valence electrons- outer shell electrons C) Metals a. Lend valence electrons b. 1 – 4 valence electrons c. Form positive ions ( more protons than electrons) D) Nonmetals a. Borrow valence electrons b. 4 - 8 valence electrons c. Form negative ions (more e ...
APS 1st semester exam review 2016
... A) Electrons are transferred between atoms B) Valence electrons- outer shell electrons C) Metals a. Lend valence electrons b. 1 – 4 valence electrons c. Form positive ions ( more protons than electrons) D) Nonmetals a. Borrow valence electrons b. 4 - 8 valence electrons c. Form negative ions (more e ...
... A) Electrons are transferred between atoms B) Valence electrons- outer shell electrons C) Metals a. Lend valence electrons b. 1 – 4 valence electrons c. Form positive ions ( more protons than electrons) D) Nonmetals a. Borrow valence electrons b. 4 - 8 valence electrons c. Form negative ions (more e ...
SLE133 – “Chemistry in Our World” Summary Notes Week 1
... Isotopes are atoms with identical atomic numbers but different mass numbers. Eg: Isotopes of Hydrogen; Isotope Symbol Atomic Number Mass Number ...
... Isotopes are atoms with identical atomic numbers but different mass numbers. Eg: Isotopes of Hydrogen; Isotope Symbol Atomic Number Mass Number ...
PAP Chemistry - Fall Final Review
... a. sodium-23 b. calcium-40 c. Cu d. Ag 10. How does mass number relate to number of protons when talking about isotopes? ...
... a. sodium-23 b. calcium-40 c. Cu d. Ag 10. How does mass number relate to number of protons when talking about isotopes? ...
Chapter 2
... Models of the Atom Orbital model: current model used by chemists Depicts probable regions of greatest electron density (an electron cloud) Useful for predicting chemical behavior of atoms ...
... Models of the Atom Orbital model: current model used by chemists Depicts probable regions of greatest electron density (an electron cloud) Useful for predicting chemical behavior of atoms ...
Atoms and Nuclei
... • The positively-charged nucleus of an atom occupies a central location. It contains at least 99.95% of the atom’s mass. (It is made up of one of more nucleons, namely protons and neutrons. See below.) • Negatively-charged electrons surround the nucleus, bound to the nucleus by the electrical attrac ...
... • The positively-charged nucleus of an atom occupies a central location. It contains at least 99.95% of the atom’s mass. (It is made up of one of more nucleons, namely protons and neutrons. See below.) • Negatively-charged electrons surround the nucleus, bound to the nucleus by the electrical attrac ...
- gst boces
... 68. q = mHf (melting), q = mHv(vaporizing), q = mC(change in temperature) (raising/lowering) *Tables T and B 69. Combined gas law on Table T *If given STP, given temp and pressure (Table A) 70. Pressure and volume indirect, P up, V down (PVC pipe) 71. Temperature and pressure direct, T up, P up 72. ...
... 68. q = mHf (melting), q = mHv(vaporizing), q = mC(change in temperature) (raising/lowering) *Tables T and B 69. Combined gas law on Table T *If given STP, given temp and pressure (Table A) 70. Pressure and volume indirect, P up, V down (PVC pipe) 71. Temperature and pressure direct, T up, P up 72. ...
chapter 7-Chemical Bonding
... • Na+ sodium ion, Ca2+, Al3+ -- cations • Cl- chloride ion, O2-, N3- -- anions ...
... • Na+ sodium ion, Ca2+, Al3+ -- cations • Cl- chloride ion, O2-, N3- -- anions ...
Chapter 4 - Aqueous Reactions
... In the last two reactions, the Ca atom lost two electrons. Where did they go? When one substance is oxidized, another is reduced. An oxidation-reduction reaction occurs. Or a redox reaction occurs. Oxidation: loss of electrons (more positive) Reduction: gain of electrons (less positive) ...
... In the last two reactions, the Ca atom lost two electrons. Where did they go? When one substance is oxidized, another is reduced. An oxidation-reduction reaction occurs. Or a redox reaction occurs. Oxidation: loss of electrons (more positive) Reduction: gain of electrons (less positive) ...
Worksheet - Velocity & Speed
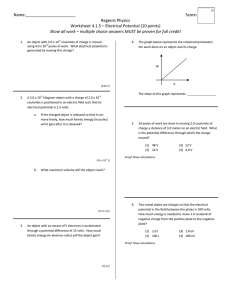
... potential in the field between the plates is 100 volts. How much energy is needed to move 1.0 coulomb of negative charge from the positive plate to the negative ...
... potential in the field between the plates is 100 volts. How much energy is needed to move 1.0 coulomb of negative charge from the positive plate to the negative ...
Preview Sample 1
... D) are always some form of carbohydrate. E) are naturally similar to sugars. 102) Alaska Natives have a lower incidence of heart disease even though their diets are high in fat and cholesterol. This may be due to the large amount of ________ in their diets. A) steroids B) omega-3 fatty acids C) trig ...
... D) are always some form of carbohydrate. E) are naturally similar to sugars. 102) Alaska Natives have a lower incidence of heart disease even though their diets are high in fat and cholesterol. This may be due to the large amount of ________ in their diets. A) steroids B) omega-3 fatty acids C) trig ...
Chapter 8 - TeacherWeb
... The compound has different properties from the elements that make up the compound Ex- NaCl- common table salt ...
... The compound has different properties from the elements that make up the compound Ex- NaCl- common table salt ...
Interaction of Radiation with Matter
... In order to reach stability, these atoms give off, or emit, the excess energy or mass. These emissions are called radiation. ...
... In order to reach stability, these atoms give off, or emit, the excess energy or mass. These emissions are called radiation. ...
Chapter 8
... Hydrogen Atoms (b) Energy Profile as a Function of the Distance Between the Nuclei of the Hydrogen Atoms ...
... Hydrogen Atoms (b) Energy Profile as a Function of the Distance Between the Nuclei of the Hydrogen Atoms ...
- Catalyst
... other elements in nuclear reactions in which protons are changed. 3. All atoms of an element have the same number of protons and electrons, which determine the chemical behavior of the element. Isotopes of an element differ in the number of neutrons, and thus in mass number, but not in chemical beha ...
... other elements in nuclear reactions in which protons are changed. 3. All atoms of an element have the same number of protons and electrons, which determine the chemical behavior of the element. Isotopes of an element differ in the number of neutrons, and thus in mass number, but not in chemical beha ...
Standards Practice
... know chemical bonds between atoms in molecules such as Hz , CH4, NH3, HzCCHz , Nz, Clz, and many large biological molecules are covalent. 5. Which do not form covalent bonds? A. diatomic molecules B. large biological molecules C. molecules containing carbon D. salts 6. The bonds found in C2H4 are A. ...
... know chemical bonds between atoms in molecules such as Hz , CH4, NH3, HzCCHz , Nz, Clz, and many large biological molecules are covalent. 5. Which do not form covalent bonds? A. diatomic molecules B. large biological molecules C. molecules containing carbon D. salts 6. The bonds found in C2H4 are A. ...
Chapter 4 REVIEW
... 21. Ionic compounds and metals have different physical properties because of the different forces involved. For example, while sodium chloride and nickel have nearly identical molar masses, their melting points, conductivity, and solubility in water are quite different. (a) Explain the large differe ...
... 21. Ionic compounds and metals have different physical properties because of the different forces involved. For example, while sodium chloride and nickel have nearly identical molar masses, their melting points, conductivity, and solubility in water are quite different. (a) Explain the large differe ...
Miss Pang`s 2012 Review
... 20. Rutherford modified the atomic model after doing experiments where alpha particles were dispersed by a sheet of gold foil. Consider the following: ...
... 20. Rutherford modified the atomic model after doing experiments where alpha particles were dispersed by a sheet of gold foil. Consider the following: ...
Chapter 8 & 9 PowerPoint
... 2. Connect atoms together with bonds. In molecules with a single atom of one element and several atoms of another element, the single atom is generally in the center with the other atoms attached to it. 3. Add electrons around outside of atoms to give each atom 8 electrons (or 2 in the case of hydro ...
... 2. Connect atoms together with bonds. In molecules with a single atom of one element and several atoms of another element, the single atom is generally in the center with the other atoms attached to it. 3. Add electrons around outside of atoms to give each atom 8 electrons (or 2 in the case of hydro ...
What You Need to Know to Pass the Chemistry
... 6. Nuclear reactions can be represented by equations that include symbols which represent atomic nuclei (with mass number and atomic number), subatomic particles (with mass and charge) and emitted particles. 7. Energy from nuclear reactions comes from the very small fraction of mass that is lost – t ...
... 6. Nuclear reactions can be represented by equations that include symbols which represent atomic nuclei (with mass number and atomic number), subatomic particles (with mass and charge) and emitted particles. 7. Energy from nuclear reactions comes from the very small fraction of mass that is lost – t ...
gr11chemreview
... 4. Why is the ionic radius of a negative ion larger than the atomic radius of the corresponding neutral atom? ...
... 4. Why is the ionic radius of a negative ion larger than the atomic radius of the corresponding neutral atom? ...