* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download electric field
Electron mobility wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatic generator wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Insulator (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Corona discharge wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electric current wikipedia , lookup
Static electricity wikipedia , lookup
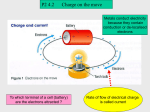
STATIC …the word static comes from the ancient Greek for “not moving” Static electricity is a stationary electrical charge that is built up on the surface of a material. Where do electrical charges come from? Matter is made up of atoms. Proton (positive charge) Neutron (neutral, no charge) Electron (negative charge) atom nucleus A NEUTRAL charge occurs when the number of electrons equals the number of protons. A NEGATIVE charge occurs when there are more electrons than protons, the object is gaining electrons. A POSITIVE charge occurs when there are less electrons than protons, the object is losing electrons. • The difference between a positive and a negative charge has to do with how they behave and the forces they exert. A FORCE is a push or a pull on an object. • When charged particles come near each other two different types of forces can occur… • A force that pulls objects together is a force of ATTRACTION. This force exists between two objects that have opposite charges, ex: one object has a positive charge and the other has a negative charge. • A force that pushes objects apart is a force of REPULSION. A force of repulsion happens when two objects have the same charge, ex: both objects have a positive charge or both objects have a negative charge. Electric charges behave according to this simple rule: Like charges repel each other, unlike charges attract each other. ELECTRIC FIELDS • The attraction or repulsion of charged particles occurs because charged particles have electric fields around them. An ELECTRIC FIELD is an area over which an electric charge exerts a force. • The electric field is strongest near the charged particle. As the distance from the charged particle increases, the strength of the electric field decreases. • When a charged particle moves into the electric field of another charged particle, it is either pushed or pulled depending on the charge of the two particles. • A neutral object acquires an electric charge when it either gains or loses electrons. How do you give an object an electric charge? ...by rubbing two objects together, such as a balloon being rubbed by a cloth. This method of giving an object an electric charge is called the FRICTION method. When a balloon rubs a piece of wool... Electrons are pulled from the wool to the balloon. The balloon has more electrons than usual. wool The balloon: – charged, The wool: +charged When a charged rod is brought close to an uncharged scrap of paper... - - - - - - - paper molecules of paper align. ⇒ attraction between the attraction rod and + charge > repulsion between the rod and charge. repulsion • Rubbing materials does NOT create electric charges. It just transfers electrons from one material to the other. • …another method of charging an object is by CONDUCTION. In conduction, a charged object is touched by an uncharged object. and electrons flow from the charged object to the uncharged object. Materials that permit electric charges to flow freely are called CONDUCTORS. The Earth and certain metals are good conductors because they allow electrons to flow through them easily. A material that does not allow electrons to flow through it easily is called an INSULATOR. Insulators do not conduct electric charge well because the electrons in the atoms of insulators are tightly bound and cannot move throughout the material. Good insulators include rubber, glass, wood, plastic and air. …a third method of charging is by INDUCTION. Induction involves a rearrangement of electric charges. For induction to occur, a neutral object needs to only come close to a charged object. No contact is necessary. When a negatively charged rod is put near a metal can... electrons of the can are - - - - - - pushed away from the rod. induced charges metal can attraction ⇒ top of the can: positive ++ + + + - - - repulsion & attraction > repulsion buttom of the can: negative Quick Quiz: A balloon gains a negative charge when rubbed by a woolen cloth. The charge on the woolen cloth is now….. A. Neutral B. Positive C. Negative During rubbing, what has been transferred from the woolen cloth to the balloon? A. Electrons B. Protons C. Neutrons Static Discharge The loss of static electricity as electric charges move off an object is called ELECTRIC DISCHARGE. Lightning is the most dramatic example of electric discharge. How can a person be safe from electric discharge? One way to be safe is to remove the excess positive or negative charge by GROUNDING. When a charged object is grounded, the excess charge is balanced by the transfer of electrons between the charged object and a ground. A ground is simply an object that serves as a reservoir of electrons. To ground a positively charged object…. You have to balance the positive charge with negative electrons from a ground (which can be another object, a person or the Earth) GROUNDING… When we touch a metal ball of positive charge... electrons flow from the earth to the metal ball to neutralize the metal ball. Metal ball becomes neutral. To ground a negatively charged object…. • You have to remove the extra electrons from the object. This is usually done by having a “conducting pathway”, that is somewhere for the electrons to go. Again this can be another object, a person or the Earth. GROUNDING… Similarly, if the metal ball is of negative charge... extra electrons flow from the metal ball to the earth and the ball becomes neutral. Lightning rods are used to protect houses from the energy of a lightning strike by grounding it. DO NOW… Write a paragraph about the cartoon. Tell what he is trying to do. Will it work and why? What do you think will happen? Use the following words, static electricity, lightning, electrons, positive and negative charges. The End