* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Worksheet - Velocity & Speed
Electrodynamic tether wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Insulator (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electroactive polymers wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
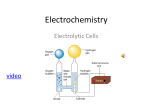
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
High voltage wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Electric current wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
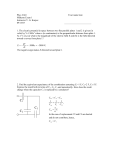
10 Name:______________________ Score: Regents Physics Worksheet 4.1.5 – Electrical Potential (10 points) Show all work – multiple choice answers MUST be proven for full credit! 1. -6 An object with 2.0 x 10 coulombs of charge is moved -8 using 4.0 x 10 joules of work. What electrical potential is generated by moving this charge? 4. The graph below represents the relationship between the work done on an object and its charge. W q [0.02 V] 2. -3 The slope of this graph represents: _________________ -5 A 5.0 x 10 kilogram object with a charge of 2.0 x 10 coulombs is positioned in an electric field such that its electrical potential is 1.5 volts. a. If the charged object is released so that it can move freely, how much kinetic energy (in joules) will it gain after it is released? 5. 24 joules of work are done in moving 2.0 coulombs of charge a distance of 3.0 meters in an electric field. What is the potential difference through which the charge moved? (1) 48 V (2) 16 V -5 (3) 12 V (4) 4.0 V Proof: Show calculations. [3.0 x 10 J] b. What maximum velocity will the object reach? 6. [0.11 m/s] 3. An object with an excess of 5 electrons is accelerated through a potential difference of 15 volts. How much kinetic energy (in electron-volts) will the object gain? Two metal plates are charges so that the electrical potential in the field between the plates is 100 volts. How much energy is needed to move 1.0 coulomb of negative charge from the positive plate to the negative plate? (1) 1.0 J (2) 100 J Proof: Show calculations. [75 eV] (3) 1.0 eV (4) 100 eV 7. The work needed to move 3.0 electrons through a potential difference of 12 volts is (1) 4.0 J (2) 36 J (3) 4.0 eV (4) 36 eV Proof: Show calculations. 8. In which case is electrical potential energy increasing? (1) (2) (3) (4) An electron moving away from a negative plate Two protons moving toward each other. A proton moving parallel to a negative plate. An electron and proton moving closer together Proof: Explain your reasoning. 9. The order of magnitude of the electrical potential generated when 5000 electron-volts of work are done on 10 electrons is (1) 1 (2) 2 (3) 3 Proof: Explain your reasoning / show calculations. (4) 4