Ionic And Covalent Bonds
... a. Know the particles of radiation and how they are different from each other. b. Be able to fill in the missing particle from a nuclear reaction. c. Be able to look at a nuclear reaction and describe it as either alpha, beta, or gama decay. d. Be able to calculate how much of a sample is left after ...
... a. Know the particles of radiation and how they are different from each other. b. Be able to fill in the missing particle from a nuclear reaction. c. Be able to look at a nuclear reaction and describe it as either alpha, beta, or gama decay. d. Be able to calculate how much of a sample is left after ...
ch-4-earth-chemistry
... Example: A neutral sodium atom has a charge of zero (equal # of protons and neutrons) and only 1 valence electron. Once it loses that valence electron, it will have 8 valence electrons and be stable and most likely, not gain or lose anymore electrons. What would be the charge on a sodium atom that l ...
... Example: A neutral sodium atom has a charge of zero (equal # of protons and neutrons) and only 1 valence electron. Once it loses that valence electron, it will have 8 valence electrons and be stable and most likely, not gain or lose anymore electrons. What would be the charge on a sodium atom that l ...
Oxidation numbers
... metals. They are also oxidized by nonmetals, losing their electrons to the nonmetal and forming ionic compounds. However, many Transition metals exhibit multiple oxidation states, forming cations with different positive charges. This is due to the fact that many Transition Metals are characterized b ...
... metals. They are also oxidized by nonmetals, losing their electrons to the nonmetal and forming ionic compounds. However, many Transition metals exhibit multiple oxidation states, forming cations with different positive charges. This is due to the fact that many Transition Metals are characterized b ...
An element`s properties depend on the structure of its atoms
... hybridization to explain chemical bond formation. Hybridization is the mixing of atomic orbitals in an atom to generate a set of new atomic orbitals called hybrid orbitals. • Mixing an s orbital with one of the p orbitals generates two equivalent sp hybrid orbitals. Note that the number of hybrid or ...
... hybridization to explain chemical bond formation. Hybridization is the mixing of atomic orbitals in an atom to generate a set of new atomic orbitals called hybrid orbitals. • Mixing an s orbital with one of the p orbitals generates two equivalent sp hybrid orbitals. Note that the number of hybrid or ...
H 2 SO 4
... attracted to the negative electrode and the Cl- anions are attracted to the positive electrode. This movement sets up an electric current that is equivalent to the flow of electrons along a metal wire. Because NaCl conducts electricity, we say that NaCl is an electrolyte. Pure Water contains very fe ...
... attracted to the negative electrode and the Cl- anions are attracted to the positive electrode. This movement sets up an electric current that is equivalent to the flow of electrons along a metal wire. Because NaCl conducts electricity, we say that NaCl is an electrolyte. Pure Water contains very fe ...
Document
... 38) Elements that are shiny conductive solids at room temperature are likely to be classified as which of the following? a) metals b) nonmetals c) inert gases ...
... 38) Elements that are shiny conductive solids at room temperature are likely to be classified as which of the following? a) metals b) nonmetals c) inert gases ...
8.P.1.1 Warm-Up Questions for Website
... B.It can be formed through a physical reaction. C.It can be changed into simpler substances through a physical change. D.It is a pure substance containing elements that are chemically combined. ...
... B.It can be formed through a physical reaction. C.It can be changed into simpler substances through a physical change. D.It is a pure substance containing elements that are chemically combined. ...
Dec. 15 , 2012, 9:00 am – noon - Dr. K. Brown
... (b) Draw a Lewis dot structure for the following molecules and indicate whether they are polar or non-polar. (3 marks) The central atom has been underlined in each molecule. i) CF4 ...
... (b) Draw a Lewis dot structure for the following molecules and indicate whether they are polar or non-polar. (3 marks) The central atom has been underlined in each molecule. i) CF4 ...
+1/2 and
... Lines of sharp and the principal series split into 2 lines (doublets), those of the diffuse and the fundamental series split into three lines (triplets). Next slide: term diagram (Grotrian diagram) of the potassium spectrum, transitions of these series, the lines of these series, and their sum, the ...
... Lines of sharp and the principal series split into 2 lines (doublets), those of the diffuse and the fundamental series split into three lines (triplets). Next slide: term diagram (Grotrian diagram) of the potassium spectrum, transitions of these series, the lines of these series, and their sum, the ...
heats of reaction
... 8.) One of the most widespread environmental carcinogens is benzo[α]pyrene (mm = 252.30 g/mole). It is found in coal dust, cigarette smoke, and in charcoal grilled meat. Analysis of this hydrocarbon shows 95.21 mass % carbon and 4.79 mass % hydrogen. What is the empirical formula of benzo[α]pyrene? ...
... 8.) One of the most widespread environmental carcinogens is benzo[α]pyrene (mm = 252.30 g/mole). It is found in coal dust, cigarette smoke, and in charcoal grilled meat. Analysis of this hydrocarbon shows 95.21 mass % carbon and 4.79 mass % hydrogen. What is the empirical formula of benzo[α]pyrene? ...
objectives chm 1025 - Miami Dade College
... b. Using the structure of the periodic table to classify elements (e.g., metal, nonmetal, metalloid, noble gas, representative element, transition element, inner transition element, alkali metal, alkaline earth metal, and/or halogen). c. Using the periodic table to identify common patterns such as a ...
... b. Using the structure of the periodic table to classify elements (e.g., metal, nonmetal, metalloid, noble gas, representative element, transition element, inner transition element, alkali metal, alkaline earth metal, and/or halogen). c. Using the periodic table to identify common patterns such as a ...
The s-Block Elements - GCG-42
... BeCl2 is essentially covalent, with comparatively low m.pt. The lower members in group II form essentially ionic chlorides, with Mg having intermediate properties. ...
... BeCl2 is essentially covalent, with comparatively low m.pt. The lower members in group II form essentially ionic chlorides, with Mg having intermediate properties. ...
OCR_AS_Level_Chemistry_Unit_F321_Atoms
... Hydrogen chloride gas will also dissolve in organic solvents, such as hexane. It stays as HCl molecules in these solvents. It does not split up into ions and, so, does not behave as an acid e.g. does not release CO2 from a carbonate ...
... Hydrogen chloride gas will also dissolve in organic solvents, such as hexane. It stays as HCl molecules in these solvents. It does not split up into ions and, so, does not behave as an acid e.g. does not release CO2 from a carbonate ...
Notes
... 2. Electron gain and loss 3. Agents Electrochemistry is the study of the interchange of chemical and electrical energy. Reactions with electron transfers are commonly called oxidation-reduction reactions (redox reactions) Not all reactions involve an electron transfer – these reactions are refer ...
... 2. Electron gain and loss 3. Agents Electrochemistry is the study of the interchange of chemical and electrical energy. Reactions with electron transfers are commonly called oxidation-reduction reactions (redox reactions) Not all reactions involve an electron transfer – these reactions are refer ...
PAP Chemistry - Fall Final Review
... 6. What did Rutherford discover from the Gold Foil Experiment – p.72 The nucleus and that the atom was mostly empty space 7. When is a bright-line spectrum produced by an atom? IE – How does an atom give off color (especially when burned)? The resting state or the ground state is when the electron i ...
... 6. What did Rutherford discover from the Gold Foil Experiment – p.72 The nucleus and that the atom was mostly empty space 7. When is a bright-line spectrum produced by an atom? IE – How does an atom give off color (especially when burned)? The resting state or the ground state is when the electron i ...
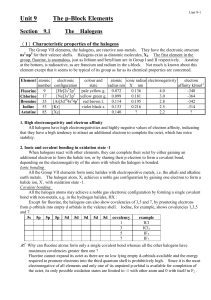
Unit 9 The p-Block Elements
... surrounded by four carbon atoms whose centers are at the corners of the tetrahedron. Within the structure, every carbon atom forms four covalent bonds by sharing electrons with each of its four nearest neighbours. Silicon and germanium crystallize in the same giant covalent structure as diamond. In ...
... surrounded by four carbon atoms whose centers are at the corners of the tetrahedron. Within the structure, every carbon atom forms four covalent bonds by sharing electrons with each of its four nearest neighbours. Silicon and germanium crystallize in the same giant covalent structure as diamond. In ...
ouble Replacement or (Metathesis) Reactions
... Since all these happens on the negative electrode. So, H2 gas forms from the negative electrode and that's exactly what happens when water reduces at the cathode. 8. (Trick #2) When CuSO4(aq) is electrolyzed, you know that Cu° metal is going to form because copper's potential is higher than water. S ...
... Since all these happens on the negative electrode. So, H2 gas forms from the negative electrode and that's exactly what happens when water reduces at the cathode. 8. (Trick #2) When CuSO4(aq) is electrolyzed, you know that Cu° metal is going to form because copper's potential is higher than water. S ...
Group II Elements - Innovative Education.org
... As for any group in the Periodic Table the Group 2 atoms get larger. So do their ions. The ions have a charge of +2 when the atoms lose the two outermost-level electrons, leaving this level empty. The two electrons of the Be2+ ion occupy the first energy level only so the ion is very small. Ions suc ...
... As for any group in the Periodic Table the Group 2 atoms get larger. So do their ions. The ions have a charge of +2 when the atoms lose the two outermost-level electrons, leaving this level empty. The two electrons of the Be2+ ion occupy the first energy level only so the ion is very small. Ions suc ...
Name Date Class Period ______
... Name ______________________________________ Date __________________ Class Period _________ Atoms, Elements, and Compound Test Study Guide I. ...
... Name ______________________________________ Date __________________ Class Period _________ Atoms, Elements, and Compound Test Study Guide I. ...
What are atoms? Notes - Riverdale Middle School
... Atoms have energy levels where electrons are found in the electron cloud. Each energy level can hold a certain number of electrons: 1st energy level = 2 electrons (closest to the nucleus) When full, electrons begin to fill the second level. 2nd energy level = 8 electrons When full, electrons go to t ...
... Atoms have energy levels where electrons are found in the electron cloud. Each energy level can hold a certain number of electrons: 1st energy level = 2 electrons (closest to the nucleus) When full, electrons begin to fill the second level. 2nd energy level = 8 electrons When full, electrons go to t ...
Chemistry 1 Lectures
... Transition metal ionic compounds have variable charges – Iron can be +2 or +3 – Smaller charge is sometimes named as an ‘ic’ ion higher charge as an ‘ous’ ion – So in ferric chloride (FeCl2) iron ion is Fe2+ – Modern method is to indicate charge on the metal with Roman numerals – So FeCl2 is now nam ...
... Transition metal ionic compounds have variable charges – Iron can be +2 or +3 – Smaller charge is sometimes named as an ‘ic’ ion higher charge as an ‘ous’ ion – So in ferric chloride (FeCl2) iron ion is Fe2+ – Modern method is to indicate charge on the metal with Roman numerals – So FeCl2 is now nam ...
unit 5 hw packet - District 196 e
... 1. Add the number of valence electrons in each atom to determine the total number of valence electrons. (For polyatomic anions, add one electron for each unit of negative charge. For polyatomic cations, subtract one electron for each unit of positive charge.) 2. Put electrons around each atom. Start ...
... 1. Add the number of valence electrons in each atom to determine the total number of valence electrons. (For polyatomic anions, add one electron for each unit of negative charge. For polyatomic cations, subtract one electron for each unit of positive charge.) 2. Put electrons around each atom. Start ...
Plasmonics: Fundamentals and Applications
... theory treats the molecules of a gas as identical solid spheres, which move in straight lines until they collide with one another. Although there is only one type of particle in the simplest gases, in metal there must be at least two. The electrons must be compensated by positive carriers to leave t ...
... theory treats the molecules of a gas as identical solid spheres, which move in straight lines until they collide with one another. Although there is only one type of particle in the simplest gases, in metal there must be at least two. The electrons must be compensated by positive carriers to leave t ...
國立嘉義大學95學年度
... 30. An element with the electron configuration [Xe]4f 14 5d 5 6s 2 would be belong to which class on the periodic table? (A) transition metal (B) alkaline earth elements ...
... 30. An element with the electron configuration [Xe]4f 14 5d 5 6s 2 would be belong to which class on the periodic table? (A) transition metal (B) alkaline earth elements ...