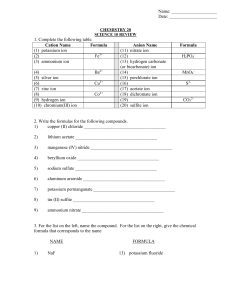
CHM121 Exam I Review
... factors, periodic table (periods/groups), chemical formula, balancing equations, nomenclature, molecular/formula weight, percent composition (mass percent), stoichiometry. Be able to define the following terms: states of matter, element, compound, ionic vs. molecular compounds, atom, atomic symbol, ...
... factors, periodic table (periods/groups), chemical formula, balancing equations, nomenclature, molecular/formula weight, percent composition (mass percent), stoichiometry. Be able to define the following terms: states of matter, element, compound, ionic vs. molecular compounds, atom, atomic symbol, ...
Chapter 1: Quiz Review - Wetaskiwin Composite High School
... B. The bonding forces in they are very weak D. The bonding forces in them are very strong 15. Which property of ionic substance leads scientists to infer that ionic substance can break down into mobile, electrically charged particles? A. Regular crystalline form in solid state C. Relatively high mel ...
... B. The bonding forces in they are very weak D. The bonding forces in them are very strong 15. Which property of ionic substance leads scientists to infer that ionic substance can break down into mobile, electrically charged particles? A. Regular crystalline form in solid state C. Relatively high mel ...
The Atom
... 1) Determine the mass in amu of each isotope and then find the total mass by adding up the masses of each isotope. ...
... 1) Determine the mass in amu of each isotope and then find the total mass by adding up the masses of each isotope. ...
Study Guide for Composition of Matter Test - seys
... - all of the atoms of a particular atom are identical but are different from atoms of all other elements - one of the several people who changed the model of the atom - electrons in the electron cloud - move about the nucleus very quickly - not possible to determine their exact position exactly - th ...
... - all of the atoms of a particular atom are identical but are different from atoms of all other elements - one of the several people who changed the model of the atom - electrons in the electron cloud - move about the nucleus very quickly - not possible to determine their exact position exactly - th ...
Unit 3C Standards for Quiz
... It will be similar to the last exam but there will be at least three questions per standard. Remember that since no calculators are allowed on the standards exam that we will be modeling this in this assessment of progress. Atomic and Molecular Structure 1. The Periodic Table displays the elements i ...
... It will be similar to the last exam but there will be at least three questions per standard. Remember that since no calculators are allowed on the standards exam that we will be modeling this in this assessment of progress. Atomic and Molecular Structure 1. The Periodic Table displays the elements i ...
Ch 4 Types of Chemical Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... Always zero for elements The oxidation state of a monatomic ions is the same as its charge Fluorine is always -1 , oxygen is almost always -2 (exceptions— peroxides where it is -1 , or OF 2 where it is +2) Hydrogen is almost always +1; metal hydrides are an exception, where it is -1 (in thes ...
... Always zero for elements The oxidation state of a monatomic ions is the same as its charge Fluorine is always -1 , oxygen is almost always -2 (exceptions— peroxides where it is -1 , or OF 2 where it is +2) Hydrogen is almost always +1; metal hydrides are an exception, where it is -1 (in thes ...
Chem 11 Study Guide SCH3U Unit 1 Definitions: SATP: Standard
... nuc charge, increases to the left cuz of less nuc charge for same number of lvls) ➢ Ionic Radius: radius as an atom becomes an ion (decreases since an element has one fewer energy level as it becomes a positive ion loses electrons) *increases downwards cuz more energy lvls to begin with even after l ...
... nuc charge, increases to the left cuz of less nuc charge for same number of lvls) ➢ Ionic Radius: radius as an atom becomes an ion (decreases since an element has one fewer energy level as it becomes a positive ion loses electrons) *increases downwards cuz more energy lvls to begin with even after l ...
Chemical Reactions
... whose solutes do not settle out Suspensions – heterogeneous mixtures with visible solutes that tend to settle out ...
... whose solutes do not settle out Suspensions – heterogeneous mixtures with visible solutes that tend to settle out ...
Fundamentals of Chemistry
... • The number of electrons in the valence shell determines the relative activity of an element. • The arrangement of electrons in the outer shell explains why some elements are chemically very active, some are not very active, and others are inert. • Group I has 1 valence electron, which makes it eas ...
... • The number of electrons in the valence shell determines the relative activity of an element. • The arrangement of electrons in the outer shell explains why some elements are chemically very active, some are not very active, and others are inert. • Group I has 1 valence electron, which makes it eas ...
PRACTICE PROBLEMS EXAM 1,2 and 3 1311
... C) +3 D) -5 E) -6 30) Horizontal rows of the periodic table are known as __________. A) periods B) groups C) metalloids D) metals E) nonmetals 31) Elements in Group 7A are known as the __________. A) chalcogens B) alkali metals C) alkaline earth metals D) halogens E) noble gases 32) When a metal and ...
... C) +3 D) -5 E) -6 30) Horizontal rows of the periodic table are known as __________. A) periods B) groups C) metalloids D) metals E) nonmetals 31) Elements in Group 7A are known as the __________. A) chalcogens B) alkali metals C) alkaline earth metals D) halogens E) noble gases 32) When a metal and ...
Types of Reactions notes 02 Types of chemical reactions
... disolved in water. In this case it would be salt dissolved in water. ...
... disolved in water. In this case it would be salt dissolved in water. ...
Feasibility Study of using FAIMS to Detect Carbonyl Sulfide in Propane
... Sample preparation and introduction FAIMS can be used to detect volatiles in aqueous, solid and gaseous matrices and can consequently be used for a wide variety of applications. The user requirements and sample matrix for each application define the sample preparation and introduction steps required ...
... Sample preparation and introduction FAIMS can be used to detect volatiles in aqueous, solid and gaseous matrices and can consequently be used for a wide variety of applications. The user requirements and sample matrix for each application define the sample preparation and introduction steps required ...
Lab Science 9 Pacing Guide
... particles and/or high energy wavelike radiation. 4. Show that when elements are listed in order according to the number of protons (called the atomic number), the repeating patterns of physical and chemical properties identify families of elements. Recognize that the periodic table was formed as a r ...
... particles and/or high energy wavelike radiation. 4. Show that when elements are listed in order according to the number of protons (called the atomic number), the repeating patterns of physical and chemical properties identify families of elements. Recognize that the periodic table was formed as a r ...
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy - An introduction
... A surface is really the interface between different phases (solid, liquid or gas). We can think of the surface as the top layer of atoms but in reality the state of this layer is very much influenced by the 2 – 10 atomic layers below it (~0.5 – 3 nm). Surface modification treatments are often in the ...
... A surface is really the interface between different phases (solid, liquid or gas). We can think of the surface as the top layer of atoms but in reality the state of this layer is very much influenced by the 2 – 10 atomic layers below it (~0.5 – 3 nm). Surface modification treatments are often in the ...
UNIVERSITY REVISION GURU Covalent Bonds • Covalent bonds
... A common example of this is oil. Oil and water do not mix, since oil is nonpolar, demonstrated by the separation of the two when attempted to be mixed. This is known as the ‘Hydrophobic effect’. ...
... A common example of this is oil. Oil and water do not mix, since oil is nonpolar, demonstrated by the separation of the two when attempted to be mixed. This is known as the ‘Hydrophobic effect’. ...
Chapter 4 Stoichiometry Power Point
... attracted to the negative electrode and the Cl- anions are attracted to the positive electrode. This movement sets up an electric current that is equivalent to the flow of electrons along a metal wire. Because NaCl conducts electricity, we say that NaCl is an electrolyte. Pure Water contains very fe ...
... attracted to the negative electrode and the Cl- anions are attracted to the positive electrode. This movement sets up an electric current that is equivalent to the flow of electrons along a metal wire. Because NaCl conducts electricity, we say that NaCl is an electrolyte. Pure Water contains very fe ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment - 2015
... EX. 2NaCl(l) → 2Na(s) + Cl2(g) : Use the solubility rules to decide whether a product of an ionic reaction is insoluble in water and will thus form a precipitate. If a compound is soluble in water then it should be shown as being in aqueous solution, or left as separate ions. It is, in fact, often m ...
... EX. 2NaCl(l) → 2Na(s) + Cl2(g) : Use the solubility rules to decide whether a product of an ionic reaction is insoluble in water and will thus form a precipitate. If a compound is soluble in water then it should be shown as being in aqueous solution, or left as separate ions. It is, in fact, often m ...
Click to download. - Life Learning Cloud
... Atoms, Molecules and Ions. AN ATOM is the smallest particle of an element. They cannot be split into smaller particles in chemical reactions. Iron is made of iron atoms (Fe). Sulphur is made of sulphur atoms (S) A MOLECULE is a small group of atoms joined together. The atoms may be the same (e.g. O ...
... Atoms, Molecules and Ions. AN ATOM is the smallest particle of an element. They cannot be split into smaller particles in chemical reactions. Iron is made of iron atoms (Fe). Sulphur is made of sulphur atoms (S) A MOLECULE is a small group of atoms joined together. The atoms may be the same (e.g. O ...
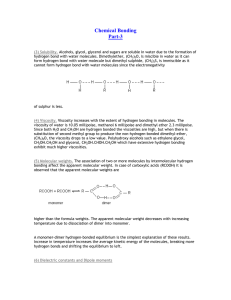
Chemical Bonding
... It is generally assumed that covalent and ionic bonds are entirely distinct but this is probably not a totally valid assumption. Bonds intermediate between ionic and covalent do occur through a process of deformation or polarization. ...
... It is generally assumed that covalent and ionic bonds are entirely distinct but this is probably not a totally valid assumption. Bonds intermediate between ionic and covalent do occur through a process of deformation or polarization. ...
Fall Final 2009
... 1. A sample that cannot be separated into two or more substances by physical means is: a. A compound b. An element c. Either a compound or an element d. A homogeneous mixture e. A heterogenous mixture 2. Given the following enthalpies of formation, Hf°: CH4(g), -74.8 kJ/mol; H2O(g), -242 kJ/mol; CO ...
... 1. A sample that cannot be separated into two or more substances by physical means is: a. A compound b. An element c. Either a compound or an element d. A homogeneous mixture e. A heterogenous mixture 2. Given the following enthalpies of formation, Hf°: CH4(g), -74.8 kJ/mol; H2O(g), -242 kJ/mol; CO ...
CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... Aqueous Solutions • Solution: homogeneous mixture or more than one compound • Aqueous solution: Water is the solvent and the other species (present in small amounts) are the solutes. • The symbol aq means the compound is dissolved in water. E.g. KCl(aq), MgCl2(aq) ...
... Aqueous Solutions • Solution: homogeneous mixture or more than one compound • Aqueous solution: Water is the solvent and the other species (present in small amounts) are the solutes. • The symbol aq means the compound is dissolved in water. E.g. KCl(aq), MgCl2(aq) ...
Ionic And Covalent Bonds
... a. Know the particles of radiation and how they are different from each other. b. Be able to fill in the missing particle from a nuclear reaction. c. Be able to look at a nuclear reaction and describe it as either alpha, beta, or gama decay. d. Be able to calculate how much of a sample is left after ...
... a. Know the particles of radiation and how they are different from each other. b. Be able to fill in the missing particle from a nuclear reaction. c. Be able to look at a nuclear reaction and describe it as either alpha, beta, or gama decay. d. Be able to calculate how much of a sample is left after ...