* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Polar and Nonpolar Covalent Compounds
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Metastable inner-shell molecular state wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Biological aspects of fluorine wikipedia , lookup
Oxidation state wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Franck–Condon principle wikipedia , lookup
Properties of water wikipedia , lookup
Water splitting wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Self-assembled monolayer wikipedia , lookup
Organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Artificial photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Coordination complex wikipedia , lookup
Organosulfur compounds wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Bond valence method wikipedia , lookup
Bent's rule wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital diagram wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Metallic bonding wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen bond wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Implicit solvation wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Aromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Resonance (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Molecular scale electronics wikipedia , lookup
Electronegativity wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
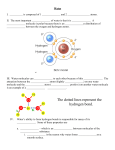
POLAR AND NONPOLAR COVALENT COMPOUNDS IPC - Mr. Coburn Introduction The tendency of an atom to attract electrons is called electronegativity. Atoms of elements that have higher electronegativities "pull" the electrons toward them with more force. Ionic chemical bonds are formed between oppositely charged ions when valence electrons are given away by one atom and received by another atom (or atoms). This occurs because there is a significant difference in the electronegativity of the atoms in the compound. Covalent compounds exist as individual molecules that result from the sharing of valence electrons. If the sharing is done between atoms with similar electronegativities, the molecule is considered nonpolar. However, in a molecule that contains an atom(s) with higher electronegativity, the compound may exhibit slight positive and negative charges at each end of the molecule. This is known as a polar molecule. Explore and Discuss • Draw the Lewis Dot Diagram for a molecule of HCl. • Consider the following illustration: How does the illustration represent the concept of differences in electronegativity? __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ • Consider the following illustration: If the penguin represents a hydrogen atom and the polar bear represents a chlorine atom, what does the ice cream represent in the drawing? What do you you think the picture is trying to illustrate? Cl H ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ • Draw the Lewis Dot Diagram for a molecule of chlorine gas ( Cl2 ) • Consider the following illustration: If both polar bears represent chlorine atoms, atom what do you think the drawing is trying to illustrate? Is the molecule of Cl2 polar or nonpolar? Cl Cl ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ Apply Draw the Lewis Dot Diagrams for the following compounds and identify them as either polar or nonpolar compounds. HBr O2 CO2 Polar Bonds and Polar Molecules Recall that polarity refers to an unequal sharing of electrons resulting from differences in electronegativity. There is a distinction between polar bonds and polar molecules. A polar covalent bond occurs when bonding electrons are more attracted to an atom with a higher electronegativity. The polarity in the bond is commonly represented by a arrow indicating a dipole two charges separated by a distance). The tip of the arrow points toward the more electronegative atom. The polarity of a molecule is the sum of all of the bond polarities in the molecule. If there is a greater overall polarity present in a molecule, then the molecule is polar. A comparison of formaldehyde and carbon dioxide is shown below. Both contain polar bonds but formaldehyde is a polar molecule while carbon dioxide is nonpolar. Since CO2 is a linear molecule, the dipoles cancel each other. Practice - Draw the Lewis Dot Diagrams for each of the following molecules. Show the polarity of the bonds. Then determine if the molecules are polar or non-polar. For the polar molecules, assign a positive and negative pole. HF H2CO NaCl CH4 For the following covalent molecules, identify them as either polar or nonpolar. If the molecule is polar, assign a negative and positive pole. H2O CH4 _____________________ ______________________ NH3 Cl2 _____________________ ____________________ Polarity of Water Water is a covalent compound, consisting of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. It is covalently bonded, that is, there is an attractive force between electrons but they are shared by the atoms. Write the formula for water here _________________ Water is a Polar compound. This means that the electrons are not shared evenly throughout the molecule. The oxygen attracts the shared electrons more strongly than the hydrogen. As a result, the oxygen atom has a partial negative charge and each hydrogen atom has a partial positive charge. The bond angle (the angle between the hydrogen atoms) is 104o. Using a protractor, draw a water molecule in the box below. Label the atoms and the bond angle. Then, label the sides of the water molecule as positive and negative. Polarity and Solubility Sodium chloride dissolves easily in water due to the polar nature of water. Sodium ions are attracted to the negative side of the water molecules and chloride ions are attracted to the positive side of the water molecules. In the boxes below, show the arrangement of water molecules as they would exist around sodium and chlorine ions. Label the charge of the ions and distribution of charges on the sides of the water molecules (as you did above). Na Cl Another interesting characteristic of polar and nonpolar covalent compounds is their solubility in certain solvents. A general rule of chemistry regarding this is "like dissolves like". In other words, polar covalent compounds will dissolve in polar solvents and nonpolar covalent compounds will form a solution with a nonpolar solvent. Step 1. Pour just enough milk into the petri dish to cover the bottom. Step 2. Place one drop of food coloring at 12:00, 3:00, 6:00 and 9:00 (as though the petri dish were a clock). Step 3. Observe the disposition of the food coloring and record your observations by drawing a diagram below. Step 4. Place one drop of soap in the center of the petri dish. Step 5. Observe the disposition of the food coloring and record your observations by drawing a diagram below. Before the Addition of Soap After the Addition of Soap Since milk is comprised mostly of water (a polar molecule), explain the role of the soap molecules as a means to allow the food coloring to move in the solution. ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________