Print this article - University of Toronto Journal of Undergraduate Life
... The treatment of Parkinson’s disease (PD) relies heavily on levodopa therapy. Although highly effective in ameliorating the debilitating symptoms of PD, levodopa treatment is largely associated with the development of abnormal involuntary movements. Several studies have suggested that these motor co ...
... The treatment of Parkinson’s disease (PD) relies heavily on levodopa therapy. Although highly effective in ameliorating the debilitating symptoms of PD, levodopa treatment is largely associated with the development of abnormal involuntary movements. Several studies have suggested that these motor co ...
Nervous System
... of pleasure or fear, recognition of fear in others. • Hippocampus: formation of memories. ...
... of pleasure or fear, recognition of fear in others. • Hippocampus: formation of memories. ...
chapter29_Sections 6
... • Action potentials occur only at nodes, where there are gated ion channels and no myelin • After an action potential occurs at a node, positive ions diffuse quickly through the cytoplasm to the next node because myelin prevents them from leaking out across the membrane • Arrival of positive ions at ...
... • Action potentials occur only at nodes, where there are gated ion channels and no myelin • After an action potential occurs at a node, positive ions diffuse quickly through the cytoplasm to the next node because myelin prevents them from leaking out across the membrane • Arrival of positive ions at ...
Chapter 3
... • (negative inside/positive outside) = resting potential • Neurons are selectively permeable (usually blocking POSITIVELY charged sodium ions until given the signal to fire • Depolarization occurs when neurons allow sodium ions inside causing neurological firing ...
... • (negative inside/positive outside) = resting potential • Neurons are selectively permeable (usually blocking POSITIVELY charged sodium ions until given the signal to fire • Depolarization occurs when neurons allow sodium ions inside causing neurological firing ...
to Psychology 3
... - glia cells exist throughout the nervous system and provide structural support and insulation for neurons - glia cells may supply nutrients, remove wastes, repair damage, or perform other non neural tasks for neurons 2. Neurons: The Communication Links - defined as "individual cells in the nervous ...
... - glia cells exist throughout the nervous system and provide structural support and insulation for neurons - glia cells may supply nutrients, remove wastes, repair damage, or perform other non neural tasks for neurons 2. Neurons: The Communication Links - defined as "individual cells in the nervous ...
20-NervousSystem
... Nerve impulses jump from node to node Multiple sclerosis and Tay-Sachs disease result from degeneration of the myelin sheath ...
... Nerve impulses jump from node to node Multiple sclerosis and Tay-Sachs disease result from degeneration of the myelin sheath ...
PSYB1 Revision sheet Biopsychology JM09
... The function of a motor neuron is to carry information from the central nervous system to the muscles/glands/effectors, whereas the function of a sensory neuron is to carry information from the sense organs to the central nervous system. Synaptic Transmission ...
... The function of a motor neuron is to carry information from the central nervous system to the muscles/glands/effectors, whereas the function of a sensory neuron is to carry information from the sense organs to the central nervous system. Synaptic Transmission ...
Information Processing SG
... The nervous system is like an information highway. It is responsible for controlling and coordinating all the functions and movements in the body and allows you to respond to changes in your environment The nervous system is made up of _____________ that are strings of long thin cells called _______ ...
... The nervous system is like an information highway. It is responsible for controlling and coordinating all the functions and movements in the body and allows you to respond to changes in your environment The nervous system is made up of _____________ that are strings of long thin cells called _______ ...
Guided Notes
... iv. Action potential (electrical signal) begins on ______________ neuron (or muscle or gland) v. NT quickly removed from synapse by _________________________ or _____________________________________ c. As you learn: i. Axon terminals widen so more NT can be released (more surface area) ii. Synaptic ...
... iv. Action potential (electrical signal) begins on ______________ neuron (or muscle or gland) v. NT quickly removed from synapse by _________________________ or _____________________________________ c. As you learn: i. Axon terminals widen so more NT can be released (more surface area) ii. Synaptic ...
APP Ch_3 Outline
... Action Potential – A very brief shift in a Neuron’s electrical charge that travels along an axon. Absolute Refractory Period – Minimum length of time after an action potential during which another action potential cannot begin. Only about 1 or 2 Milliseconds. All-Or-None Law – Neural Impulses ...
... Action Potential – A very brief shift in a Neuron’s electrical charge that travels along an axon. Absolute Refractory Period – Minimum length of time after an action potential during which another action potential cannot begin. Only about 1 or 2 Milliseconds. All-Or-None Law – Neural Impulses ...
Slide () - AccessAnesthesiology
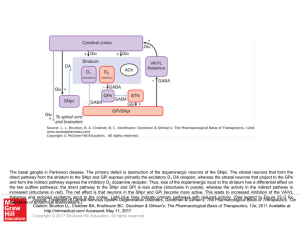
... direct pathway from the striatum to the SNpr and GPi express primarily the excitatory D1 DA receptor, whereas the striatal neurons that project to the GPe and form the indirect pathway express the inhibitory D2 dopamine receptor. Thus, loss of the dopaminergic input to the striatum has a differentia ...
... direct pathway from the striatum to the SNpr and GPi express primarily the excitatory D1 DA receptor, whereas the striatal neurons that project to the GPe and form the indirect pathway express the inhibitory D2 dopamine receptor. Thus, loss of the dopaminergic input to the striatum has a differentia ...
Document
... -_______________- _______________-, but _______________- _______________2. ______________- - hormones-proteins “chemical messengers” -______________- to _______________- but _______________- Lasting. * Through 1 & 2 – ______________- is maintained. Like a car on cruise control the body is constantly ...
... -_______________- _______________-, but _______________- _______________2. ______________- - hormones-proteins “chemical messengers” -______________- to _______________- but _______________- Lasting. * Through 1 & 2 – ______________- is maintained. Like a car on cruise control the body is constantly ...
Sensory function
... • Motor function. Once sensory information is integrated, the nervous system may elicit an appropriate motor response by activating effectors (muscles and glands) through cranial and spinal nerves. Stimulation of the effectors causes muscles to contract and glands to secrete. ...
... • Motor function. Once sensory information is integrated, the nervous system may elicit an appropriate motor response by activating effectors (muscles and glands) through cranial and spinal nerves. Stimulation of the effectors causes muscles to contract and glands to secrete. ...
Chp3 Weiten - Napa Valley College
... Two types of branches extend from the cell body: axons and ...
... Two types of branches extend from the cell body: axons and ...
Small System of Neurons
... The circuit contains 24 mechanoreceptor sensory neurons that innervate the siphon skin. These sensory neurons make direct monosynaptic connections with 6 gill motor cells. The sensory neurons also made indirect connection to the gill motor cells through interneurons (excitatory and inhibitory). This ...
... The circuit contains 24 mechanoreceptor sensory neurons that innervate the siphon skin. These sensory neurons make direct monosynaptic connections with 6 gill motor cells. The sensory neurons also made indirect connection to the gill motor cells through interneurons (excitatory and inhibitory). This ...
Slide ()
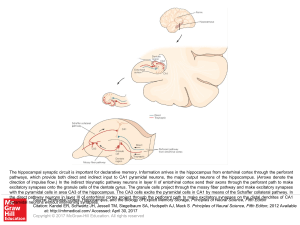
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
Development of the Brain
... Can the adult brain generate new neurons? Olfactory cells must…. Why? stem cells in the interior of the brain scientists have observed new cells in hippocampus and cerebral cortex in monkeys of ages. Possible meaning of new neural development? ...
... Can the adult brain generate new neurons? Olfactory cells must…. Why? stem cells in the interior of the brain scientists have observed new cells in hippocampus and cerebral cortex in monkeys of ages. Possible meaning of new neural development? ...
Slide ()
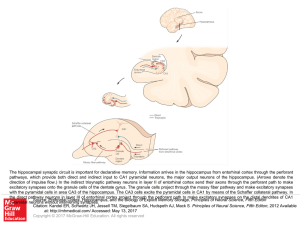
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
Synaptic Transmission
... message and can be inhibitory. When they bind to the post-synaptic neuron, they let potassium out instead of sodium in, which makes the neuron even more negative! ...
... message and can be inhibitory. When they bind to the post-synaptic neuron, they let potassium out instead of sodium in, which makes the neuron even more negative! ...