Reuptake, or re-uptake, is the reabsorption of a neurotransmitter by
... The largest and most abundant type of glia cell in the brain, accounting for nearly half of all glial tissue volume, is the astrocyte. Astrocytes provide structural support with their interweaving extensions acting as a scaffolding to anchor neurons in place (this is especially helpful to make sure ...
... The largest and most abundant type of glia cell in the brain, accounting for nearly half of all glial tissue volume, is the astrocyte. Astrocytes provide structural support with their interweaving extensions acting as a scaffolding to anchor neurons in place (this is especially helpful to make sure ...
Brain & Behavior
... recharge, so to speak • K(+) pumped out of cell, (-) charge restored • Refractory period – neuron cannot fire again during this process ...
... recharge, so to speak • K(+) pumped out of cell, (-) charge restored • Refractory period – neuron cannot fire again during this process ...
Chapter 2
... Interneurons carry information between other neurons only found in the brain and spinal cord ...
... Interneurons carry information between other neurons only found in the brain and spinal cord ...
The Human Brain
... colour under the microscope. This is where the phrase ‘using your grey matter’ comes from. Below this area are a large number of neuron tails (axons). These act as connectors between different parts of the cortex a bit like a very complicated telephone wiring system. They are white in colour under t ...
... colour under the microscope. This is where the phrase ‘using your grey matter’ comes from. Below this area are a large number of neuron tails (axons). These act as connectors between different parts of the cortex a bit like a very complicated telephone wiring system. They are white in colour under t ...
The First Open International Symposium
... We analyzed the behavior of animals cultivated at different salt concentrations and found that both klinokinesis and klinotaxis are reversed when cultivated at low salt concentration. By calcium imaging of sensory neurons and downstream interneurons, we find that experience-dependent change occurs b ...
... We analyzed the behavior of animals cultivated at different salt concentrations and found that both klinokinesis and klinotaxis are reversed when cultivated at low salt concentration. By calcium imaging of sensory neurons and downstream interneurons, we find that experience-dependent change occurs b ...
Nervous System - Belle Vernon Area School District
... VI. Effects of Aging A. Natural decline in functioning neurons, including sensory neurons. (balance loss, coordination, blood pressure, bladder) B. By the age of 60 up to 50% loss of lower motor neurons in lumbar region. (loss of muscle mass & increase fatigue) C. Size and weight of the brain decre ...
... VI. Effects of Aging A. Natural decline in functioning neurons, including sensory neurons. (balance loss, coordination, blood pressure, bladder) B. By the age of 60 up to 50% loss of lower motor neurons in lumbar region. (loss of muscle mass & increase fatigue) C. Size and weight of the brain decre ...
C8003 Psychobiology sample paper 2016-17
... Emotions can never be 'experienced' until the body has time to react The parasympathetic nervous system is responsible for the feeling of ...
... Emotions can never be 'experienced' until the body has time to react The parasympathetic nervous system is responsible for the feeling of ...
a PowerPoint Presentation of Module 24
... hippocampus is one of the last brain areas to develop. • Forgetting/retrieval: the adult mind thinks more in a linear verbal narrative and has trouble accessing preverbal memories as declarative memories. ...
... hippocampus is one of the last brain areas to develop. • Forgetting/retrieval: the adult mind thinks more in a linear verbal narrative and has trouble accessing preverbal memories as declarative memories. ...
Biological and Psychology Why are psychologists concerned about
... Over 200 types of neurons and glia cells Common Features of Neurons Dendrites Cell body or soma Axon Myelin sheath Terminal buttons Synapse - a junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron. This tiny gap is called the synaptic ...
... Over 200 types of neurons and glia cells Common Features of Neurons Dendrites Cell body or soma Axon Myelin sheath Terminal buttons Synapse - a junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron. This tiny gap is called the synaptic ...
International Baccalaureate Biology Option
... Controls speech. Damage to this area results in the person knowing what they want to say but they can only make sounds and are unable to make meaningful words and sentences. ...
... Controls speech. Damage to this area results in the person knowing what they want to say but they can only make sounds and are unable to make meaningful words and sentences. ...
2.2 Electrical Communication Study Guide by Hisrich
... The main person that treats neurological disorders is a Neurologist (one who studies nerves). That’s a special kind of doctor that specializes in the nervous system. People with these disorders also rely on Pharmacists to dispense their medication, Nurses to care for them, Pharmacologists to produce ...
... The main person that treats neurological disorders is a Neurologist (one who studies nerves). That’s a special kind of doctor that specializes in the nervous system. People with these disorders also rely on Pharmacists to dispense their medication, Nurses to care for them, Pharmacologists to produce ...
Capacity Analysis of Attractor Neural Networks with Binary Neurons and Discrete Synapses
... stable if all synapses are excitatory. With the introduction of inhibition, the dynamics can be stabilized, especially when the coding levels of patterns varies. The activity of neurons changes the efficacy of the synapses, and hence alters the attractor states. New memory is thus created and old me ...
... stable if all synapses are excitatory. With the introduction of inhibition, the dynamics can be stabilized, especially when the coding levels of patterns varies. The activity of neurons changes the efficacy of the synapses, and hence alters the attractor states. New memory is thus created and old me ...
Unit 5: Study Guide Biological Bases of Behavior (Neuroscience)
... 12. Describe the components of the brainstem, and summarize the functions of the brainstem, thalamus, and cerebellum. 13. Describe the structures and functions of the limbic system, and explain how one of these structures controls the pituitary gland. 14. Define cerebral cortex, and explain its impo ...
... 12. Describe the components of the brainstem, and summarize the functions of the brainstem, thalamus, and cerebellum. 13. Describe the structures and functions of the limbic system, and explain how one of these structures controls the pituitary gland. 14. Define cerebral cortex, and explain its impo ...
Slide ()
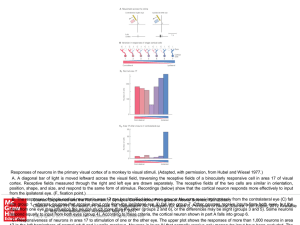
... Responses of neurons in the primary visual cortex of a monkey to visual stimuli. (Adapted, with permission, from Hubel and Wiesel 1977.) A. A diagonal bar of light is moved leftward across the visual field, traversing the receptive fields of a binocularly responsive cell in area 17 of visual cortex. ...
... Responses of neurons in the primary visual cortex of a monkey to visual stimuli. (Adapted, with permission, from Hubel and Wiesel 1977.) A. A diagonal bar of light is moved leftward across the visual field, traversing the receptive fields of a binocularly responsive cell in area 17 of visual cortex. ...
MMNeuropharm2011
... the synaptic cleft that interacts with specific receptors located in the membrane of the adjacent postsynaptic neuron. While the transduction from the presynaptic electrical signal into a chemical and back to an electrical is a complex and energy-consuming phenomenon, it has the advantage to allow fo ...
... the synaptic cleft that interacts with specific receptors located in the membrane of the adjacent postsynaptic neuron. While the transduction from the presynaptic electrical signal into a chemical and back to an electrical is a complex and energy-consuming phenomenon, it has the advantage to allow fo ...
The Journal of Neuroscience
... Nicolas Mallet, Alek Pogosyan, Andrew Sharott, Jozsef Csicsvari, J. Paul Bolam, Peter Brown, and Peter J. Magill Correction: In the April 9, 2008 issue’s “This Week in the Journal” summary of the Development/Plasticity/Repair article by Coate et al., there was an error in the third sentence. The ter ...
... Nicolas Mallet, Alek Pogosyan, Andrew Sharott, Jozsef Csicsvari, J. Paul Bolam, Peter Brown, and Peter J. Magill Correction: In the April 9, 2008 issue’s “This Week in the Journal” summary of the Development/Plasticity/Repair article by Coate et al., there was an error in the third sentence. The ter ...
GEOTRAN - Life Solutions Institute
... The brain has at least eight “capacitortype” electrical centers located within. These 8 capacitors are connected with 12 rings of the heart/mind connection. These 12 rings are in constant communication with our environment and continually relay the information to the 8 capacitors. ...
... The brain has at least eight “capacitortype” electrical centers located within. These 8 capacitors are connected with 12 rings of the heart/mind connection. These 12 rings are in constant communication with our environment and continually relay the information to the 8 capacitors. ...
Ms. Setzer-The Brain!
... Our Divided Brain Our brain is divided into two hemispheres. -The left hemisphere processes reading, writing, speaking, mathematics, and comprehension skills. In the 1960s, it was termed as the dominant brain. -The right hemisphere houses most spatial abilities-the ability to precieve or organize t ...
... Our Divided Brain Our brain is divided into two hemispheres. -The left hemisphere processes reading, writing, speaking, mathematics, and comprehension skills. In the 1960s, it was termed as the dominant brain. -The right hemisphere houses most spatial abilities-the ability to precieve or organize t ...
John F. MacDonald 2014 - Canadian Association for Neuroscience
... mammalian central nervous system. These receptors (eventually termed NMDA receptors) were later found to be blocked by magnesium in a voltage-dependent manner, and required for long-term synaptic modifications thought to underlie some forms of learning. By virtue of their voltage-dependence, NMDA re ...
... mammalian central nervous system. These receptors (eventually termed NMDA receptors) were later found to be blocked by magnesium in a voltage-dependent manner, and required for long-term synaptic modifications thought to underlie some forms of learning. By virtue of their voltage-dependence, NMDA re ...
Introduction to Psychology
... Involved in speaking & muscle movements Important for planning and making judgments Damage can alter personality (e.g., Phineas Gage) ...
... Involved in speaking & muscle movements Important for planning and making judgments Damage can alter personality (e.g., Phineas Gage) ...
11th International Conference Advances in Pneumology Cologne
... microinjection represented fiber populations providing excitatory drive into expiratory neurons at 2 levels (DLH1 - more synaptic connections with lower synaptic strength and DLH2 - less synaptic connections with higher synaptic strength). Our simulations manifested high level of analogy with cough ...
... microinjection represented fiber populations providing excitatory drive into expiratory neurons at 2 levels (DLH1 - more synaptic connections with lower synaptic strength and DLH2 - less synaptic connections with higher synaptic strength). Our simulations manifested high level of analogy with cough ...
Chapter 2 Notes Packet (Part 1)
... thousandth of a second it will not fire again regardless of the strength of the incoming message's Relative Refractory Period: during the resting state of a cell the neuron will only fire if the incoming message is considerably stronger than normal Otherwise after a neuron fires it returns to it ...
... thousandth of a second it will not fire again regardless of the strength of the incoming message's Relative Refractory Period: during the resting state of a cell the neuron will only fire if the incoming message is considerably stronger than normal Otherwise after a neuron fires it returns to it ...
Neural Development
... Signals from a finger and thumb of an uninjured person travel independently to separate regions in the brain's thalamus (left). After amputation, neurons that formerly responded to signals from the finger respond to signals from the thumb (right). ...
... Signals from a finger and thumb of an uninjured person travel independently to separate regions in the brain's thalamus (left). After amputation, neurons that formerly responded to signals from the finger respond to signals from the thumb (right). ...