The Nervous System
... – Sympathetic : accelerates body activities – Parasympathetic : slows down body activities ...
... – Sympathetic : accelerates body activities – Parasympathetic : slows down body activities ...
UNIT 3A: Biological Bases of Behavior – Neural Processing and the
... combined signals trigger action potential iv. Neuron’s reaction is all or nothing (ie. pulling a trigger of a gun) How do nerve cells communicate with other nerve cells? ...
... combined signals trigger action potential iv. Neuron’s reaction is all or nothing (ie. pulling a trigger of a gun) How do nerve cells communicate with other nerve cells? ...
Unit Outline_Ch17 - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
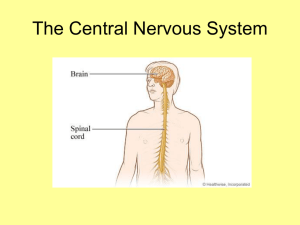
... The spinal cord and the brain make up the central nervous system (CNS). The Spinal Cord The spinal cord extends from the base of the brain through a large opening in the skull and into the vertebral canal. Structure of the Spinal Cord The spinal nerves project from the cord between the vertebrae. Fl ...
... The spinal cord and the brain make up the central nervous system (CNS). The Spinal Cord The spinal cord extends from the base of the brain through a large opening in the skull and into the vertebral canal. Structure of the Spinal Cord The spinal nerves project from the cord between the vertebrae. Fl ...
NEUROPHYSIOLOGY
... Explain how an impulse is transmitted from one nerve to another. Clinical Application: Influence of various drugs on nerve conduction. ...
... Explain how an impulse is transmitted from one nerve to another. Clinical Application: Influence of various drugs on nerve conduction. ...
The Zombie Diaries
... What’s the Big Idea?: To understand how information (messages) travel across the brain, and how messages are sent back across the pathways to the rest of the body (neurotransmission). 1.) Choose a partner 2.) Get a Chromebook and a packet from the end of the table 3. ) Review pages 4 - 10 of this Po ...
... What’s the Big Idea?: To understand how information (messages) travel across the brain, and how messages are sent back across the pathways to the rest of the body (neurotransmission). 1.) Choose a partner 2.) Get a Chromebook and a packet from the end of the table 3. ) Review pages 4 - 10 of this Po ...
The role of synaptic ion channels in synaptic
... through the removal of the Mg2+ block, whereas LTP maintenance is achieved by subsequent calcium-induced synapse alterations. One such modification engages AMPA receptor gating and transport. Signalling through the AMPA receptor is dynamically modulated by two principal mechanisms: direct phosphoryl ...
... through the removal of the Mg2+ block, whereas LTP maintenance is achieved by subsequent calcium-induced synapse alterations. One such modification engages AMPA receptor gating and transport. Signalling through the AMPA receptor is dynamically modulated by two principal mechanisms: direct phosphoryl ...
Brain Anatomy and Function p. 95
... Pyramidal system or corticospinal tract affects voluntary movement. ...
... Pyramidal system or corticospinal tract affects voluntary movement. ...
39_LectureSlides
... Mechanism for “winner-take-all” (open eye) and synapse elimination (closed eye) III. Topics/Controversies in recent research (not in the text book) ...
... Mechanism for “winner-take-all” (open eye) and synapse elimination (closed eye) III. Topics/Controversies in recent research (not in the text book) ...
outline unit III
... 1. Neuron is stimulated 1. it releases neurotransmitters 2. Neurotransmitters bind to receptor sites on the dendrites of the receiving neuron 3. If the threshold is reached, the cell membrane of the receiving neuron becomes permeable 1. positive ions rush in 2. action potential ...
... 1. Neuron is stimulated 1. it releases neurotransmitters 2. Neurotransmitters bind to receptor sites on the dendrites of the receiving neuron 3. If the threshold is reached, the cell membrane of the receiving neuron becomes permeable 1. positive ions rush in 2. action potential ...
intro to psych ch3 biological bases of behavior
... Resting state is restored After firing, the neuron dips below resting level and is less willing to fire ...
... Resting state is restored After firing, the neuron dips below resting level and is less willing to fire ...
the brain - Cloudfront.net
... 3. Your brain is an energy hog. It occupies 2% of your body but uses _____ of your energy when you are at rest. A. 10% C. 50% B. 20% D. 75% 4. The more you repeat something the more brain space is dedicated to it. For example, in musicians the part of the brain that controls fingers used to play an ...
... 3. Your brain is an energy hog. It occupies 2% of your body but uses _____ of your energy when you are at rest. A. 10% C. 50% B. 20% D. 75% 4. The more you repeat something the more brain space is dedicated to it. For example, in musicians the part of the brain that controls fingers used to play an ...
Test #1 Study Guide
... o Ego- prevents us from acting on our basic urges, mediates the demands of the id o Id- unconscious, satisfies basic urges, desires, and needs o Superego- acts socially appropriately, contradicts the id, sense of right and wrong synaptic cleft- the gap between the two neurons communicating with on ...
... o Ego- prevents us from acting on our basic urges, mediates the demands of the id o Id- unconscious, satisfies basic urges, desires, and needs o Superego- acts socially appropriately, contradicts the id, sense of right and wrong synaptic cleft- the gap between the two neurons communicating with on ...
Chronic Stress and The Body
... o Adrenaline increases the heart rate, elevates BP and boosts the supply of energy o Cortisol increases glucose in the blood stream, increases the use of glucose by the brain and increases our body’s ability to repair tissues “Fight-or-Flight” response is normally self-limiting, however if there is ...
... o Adrenaline increases the heart rate, elevates BP and boosts the supply of energy o Cortisol increases glucose in the blood stream, increases the use of glucose by the brain and increases our body’s ability to repair tissues “Fight-or-Flight” response is normally self-limiting, however if there is ...
Chapter Two Part Three - K-Dub
... the brain does not repair damaged neurons, BUT it can restore some functions it can form new connections, reassign existing networks, and insert new neurons, some grown from stem cells ...
... the brain does not repair damaged neurons, BUT it can restore some functions it can form new connections, reassign existing networks, and insert new neurons, some grown from stem cells ...
Leaving Certificate Biology Photosynthesis Quiz
... What name is given to the electrical-type message that travels along a neuron? ...
... What name is given to the electrical-type message that travels along a neuron? ...
48.5, .6, .7
... • Cerebral Cortex is divided into left and right halves • A thick band of axons known as the corpus callosum enables communication between the left and right cerebral cortices • Damage of one are of the cerebrum may cause redirection of its normal functions to other areas. • Live can be lived with ...
... • Cerebral Cortex is divided into left and right halves • A thick band of axons known as the corpus callosum enables communication between the left and right cerebral cortices • Damage of one are of the cerebrum may cause redirection of its normal functions to other areas. • Live can be lived with ...
Module 04
... Tens of billions of neurons, each communicating with thousands of other neurons, yield an everchanging wiring diagram. The complexity of the central nervous system allows or makes possible (enables) our thinking, feeling, and behavior. In this way, it is similar to the electronic circuitry (wiring ...
... Tens of billions of neurons, each communicating with thousands of other neurons, yield an everchanging wiring diagram. The complexity of the central nervous system allows or makes possible (enables) our thinking, feeling, and behavior. In this way, it is similar to the electronic circuitry (wiring ...
node of action heroin
... You can think of a brain pathway as a power line that connects two brain regions. Brain pathways are made up of interconnected neurons along which signals are transmitted from one brain region to another. Dopamine is the neurotransmitter used by the reward pathway. But there are two other important ...
... You can think of a brain pathway as a power line that connects two brain regions. Brain pathways are made up of interconnected neurons along which signals are transmitted from one brain region to another. Dopamine is the neurotransmitter used by the reward pathway. But there are two other important ...
Ch38-Nervous_system
... of pleasure or fear, recognition of fear in others. • Hippocampus: formation of memories. ...
... of pleasure or fear, recognition of fear in others. • Hippocampus: formation of memories. ...
Invitation to the Life Span by Kathleen Stassen Berger
... communicate with other neurons • This is followed by pruning where unused neurons and misconnected dendrites die ...
... communicate with other neurons • This is followed by pruning where unused neurons and misconnected dendrites die ...
Ch05LifespanPPT
... communicate with other neurons • This is followed by pruning where unused neurons and misconnected dendrites die ...
... communicate with other neurons • This is followed by pruning where unused neurons and misconnected dendrites die ...
ALH 1002 Chapter 5 - Biosocial Development
... communicate with other neurons • This is followed by pruning where unused neurons and misconnected dendrites die ...
... communicate with other neurons • This is followed by pruning where unused neurons and misconnected dendrites die ...
TBI Abstract - Stacey Lee, PhD
... novel therapeutic compounds to mitigate brain damage induced by TBI. The project aims to mitigate injury responses by improving astrocyte energy metabolism. Astrocytes are essential for maintaining neuronal function and homeostasis in the brain. They provide neurons with metabolic support, modulate ...
... novel therapeutic compounds to mitigate brain damage induced by TBI. The project aims to mitigate injury responses by improving astrocyte energy metabolism. Astrocytes are essential for maintaining neuronal function and homeostasis in the brain. They provide neurons with metabolic support, modulate ...
Answers to Test Your Knowledge questions for
... memory. This is particularly so when attempts are made to link memory to biological structures. The ability of humans to recall consciously and to articulate verbally what they recall reveals an important class of memory. Indeed, it is what most people consider to the index of memory. Explicit memor ...
... memory. This is particularly so when attempts are made to link memory to biological structures. The ability of humans to recall consciously and to articulate verbally what they recall reveals an important class of memory. Indeed, it is what most people consider to the index of memory. Explicit memor ...