CNS Introduction
... the synaptic cleft. -Inhibitors of the uptake of NE and/or 5-HT are used to treat depression and other behavioral disorders ...
... the synaptic cleft. -Inhibitors of the uptake of NE and/or 5-HT are used to treat depression and other behavioral disorders ...
Working Together for a World Free of Chemical Weapons
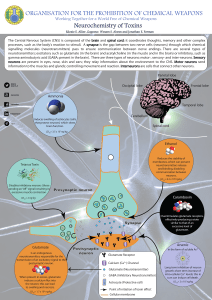
... signalling molecules (neurotransmitters) pass to ensure communication between nerve endings. There are several types of neurotransmitters; excitatory such as glutamate (in the brain) and acetylcholine (in the muscle and in the brain) or inhibitory, such as gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA; present in t ...
... signalling molecules (neurotransmitters) pass to ensure communication between nerve endings. There are several types of neurotransmitters; excitatory such as glutamate (in the brain) and acetylcholine (in the muscle and in the brain) or inhibitory, such as gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA; present in t ...
Human Anatomy and Physiology 3rd Nine Weeks Study Guide
... combination of the neuron and the muscle fiber it associates wit Acteylcholine… main neurotransmitter (for muscle contraction and nerve impulse) Other neurotransmitters include monoamines, some amino acids, and many neuropeptides Excitatory transmitters increase postsynaptic membrane permeability to ...
... combination of the neuron and the muscle fiber it associates wit Acteylcholine… main neurotransmitter (for muscle contraction and nerve impulse) Other neurotransmitters include monoamines, some amino acids, and many neuropeptides Excitatory transmitters increase postsynaptic membrane permeability to ...
The Nervous System
... • Found in the brain • Prevents the receptor nerve from being overstimulated • When it accumulates it has a sedative effect • Valium, Xanax and Ativan work by allowing GABA to accumulate – More GABA, more relaxed ...
... • Found in the brain • Prevents the receptor nerve from being overstimulated • When it accumulates it has a sedative effect • Valium, Xanax and Ativan work by allowing GABA to accumulate – More GABA, more relaxed ...
Nervous System - EMTStudyCenter.com
... 6. The different charge between the outside and the inside of a neuron at rest is called action potential. synaptic potential. resting membrane potential. equilibrium potential. 7. The stage in an action potential that immediately follows depolarization is polarization. repolarization. threshold. th ...
... 6. The different charge between the outside and the inside of a neuron at rest is called action potential. synaptic potential. resting membrane potential. equilibrium potential. 7. The stage in an action potential that immediately follows depolarization is polarization. repolarization. threshold. th ...
Lecture 3
... Positive sodium depolarizes the muscle membrane potential becomes more positive more sodium channels open Even more sodium ions enter the cells membrane potential even more positive and so on == Positive feedback loop == explosion == gun powder ...
... Positive sodium depolarizes the muscle membrane potential becomes more positive more sodium channels open Even more sodium ions enter the cells membrane potential even more positive and so on == Positive feedback loop == explosion == gun powder ...
Notes
... (c) amino acids (i) gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) (ii) glutamate (glutamic acid) (iii) aspartate (aspartic acid) (iv) glycine (d) peptides (i) endorphins (ii) somatostatin (iii) cholecystokinin (CCK) iii) mechanism (a) impulse reaches the synaptic end bulbs (b) voltage-gated Ca++ channels open (c) ...
... (c) amino acids (i) gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) (ii) glutamate (glutamic acid) (iii) aspartate (aspartic acid) (iv) glycine (d) peptides (i) endorphins (ii) somatostatin (iii) cholecystokinin (CCK) iii) mechanism (a) impulse reaches the synaptic end bulbs (b) voltage-gated Ca++ channels open (c) ...
Chapter 48 Reading Guide and Key Terms
... What properties of the nervous system could account for the rapid action of some ...
... What properties of the nervous system could account for the rapid action of some ...
The Nervous System
... the entire excitable membrane surface in a series of small steps. During saltatory propagation, the action potential appears to leap from node to node. ...
... the entire excitable membrane surface in a series of small steps. During saltatory propagation, the action potential appears to leap from node to node. ...
Slide 1 - AccessPharmacy
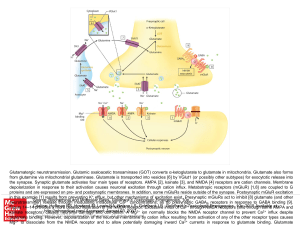
... Glutamatergic neurotransmission. Glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT) converts α-ketoglutarate to glutamate in mitochondria. Glutamate also forms from glutamine via mitochondrial glutaminase. Glutamate is transported into vesicles [6] by VGlut1 (or possibly other subtypes) for exocytotic release ...
... Glutamatergic neurotransmission. Glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT) converts α-ketoglutarate to glutamate in mitochondria. Glutamate also forms from glutamine via mitochondrial glutaminase. Glutamate is transported into vesicles [6] by VGlut1 (or possibly other subtypes) for exocytotic release ...
Neurophysiology Worksheet
... paralysis. Eventually, the muscles atrophy because of a lack of adequate activity involving contraction. ...
... paralysis. Eventually, the muscles atrophy because of a lack of adequate activity involving contraction. ...
Introduction to Autonomic Pharmacology
... – Acetyl coA (mitochondria) – Choline (dietary) – Catalyzed by choline acetyl transferase (ChAT) ...
... – Acetyl coA (mitochondria) – Choline (dietary) – Catalyzed by choline acetyl transferase (ChAT) ...
Name
... 10. nerve endings which are sensitive and respond to light energy 11. stimulus strength strong enough to cause a response 12. when one pre-synaptic neuron affects a response in two post-synaptic neurons 13. ovoid glial cells that are phagocytic 14. not having the ability to reproduce 15. clusters of ...
... 10. nerve endings which are sensitive and respond to light energy 11. stimulus strength strong enough to cause a response 12. when one pre-synaptic neuron affects a response in two post-synaptic neurons 13. ovoid glial cells that are phagocytic 14. not having the ability to reproduce 15. clusters of ...
(580.422) Lecture 7, Synaptic Transmission
... Examples of changes in the response properties of neurons in the hippocampus due to cAMP modulation. The effect occurs by reducing the conductance of SK type K(Ca) channels. These channels are gated by Ca++ and produce the afterhyperpolarization (ahp) that follows one or more action potentials, as ...
... Examples of changes in the response properties of neurons in the hippocampus due to cAMP modulation. The effect occurs by reducing the conductance of SK type K(Ca) channels. These channels are gated by Ca++ and produce the afterhyperpolarization (ahp) that follows one or more action potentials, as ...
2 - IS MU
... is an antagonist of acetylcholine that prevents channel opening. Succinylcholine is a myorelaxant that produces muscular end plate depolarization. ...
... is an antagonist of acetylcholine that prevents channel opening. Succinylcholine is a myorelaxant that produces muscular end plate depolarization. ...
Bio70 Psychobiology Fall 2006 First Midterm October 12 Version A
... c. Its surface may be lined with synaptic receptors. d. It receives information from other neurons or the environment. ...
... c. Its surface may be lined with synaptic receptors. d. It receives information from other neurons or the environment. ...
Outline14 Efferent NS
... cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, glands, adipose tissue sympathetic division parasympathetic division A. Somatic Motor Division - somatic motor neurons activate skeletal muscles - voluntary (mostly): control of movement, posture, breathing 1. Somatic Motor Pathway - one motor neuron pathway from CNS t ...
... cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, glands, adipose tissue sympathetic division parasympathetic division A. Somatic Motor Division - somatic motor neurons activate skeletal muscles - voluntary (mostly): control of movement, posture, breathing 1. Somatic Motor Pathway - one motor neuron pathway from CNS t ...
The Neuron MMHS Advanced Biomed Chitraroff
... A. Differ by their structure: 1. Bipolar = axons and dendrites extend from opposite ends (sensory) 2. Unipolar = axons and dendrites originate from the same location. (ganglia in brain, spinal cord) 3. Multipolar = multiple projections around the cell body. (most brain, spinal) ...
... A. Differ by their structure: 1. Bipolar = axons and dendrites extend from opposite ends (sensory) 2. Unipolar = axons and dendrites originate from the same location. (ganglia in brain, spinal cord) 3. Multipolar = multiple projections around the cell body. (most brain, spinal) ...
AP Psych – Summary of Neurotransmitters Table
... messages to other neurons, Huntington’s disease GABA (gamma helping to balance and produces tremors and aminobutyric acid) offset excitatory messages. loss of motor control, It is also involved in as well as personality allergies changes. ...
... messages to other neurons, Huntington’s disease GABA (gamma helping to balance and produces tremors and aminobutyric acid) offset excitatory messages. loss of motor control, It is also involved in as well as personality allergies changes. ...
Chapter 7
... Action Potential • Occurs when a stimulus of sufficient strength depolarizes the cell – Opens Na+ channels and Na+ diffuses into cell • Inside becomes more positive ...
... Action Potential • Occurs when a stimulus of sufficient strength depolarizes the cell – Opens Na+ channels and Na+ diffuses into cell • Inside becomes more positive ...
Neuromuscular junction

A neuromuscular junction (sometimes called a myoneural junction) is a junction between nerve and muscle; it is a chemical synapse formed by the contact between the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron and the postsynaptic membrane of a muscle fiber. It is at the neuromuscular junction that a motor neuron is able to transmit a signal to the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction.Muscles require innervation to function—and even just to maintain muscle tone, avoiding atrophy. Synaptic transmission at the neuromuscular junction begins when an action potential reaches the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron, which activates voltage-dependent calcium channels to allow calcium ions to enter the neuron. Calcium ions bind to sensor proteins (synaptotagmin) on synaptic vesicles, triggering vesicle fusion with the cell membrane and subsequent neurotransmitter release from the motor neuron into the synaptic cleft. In vertebrates, motor neurons release acetylcholine (ACh), a small molecule neurotransmitter, which diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) on the cell membrane of the muscle fiber, also known as the sarcolemma. nAChRs are ionotropic receptors, meaning they serve as ligand-gated ion channels. The binding of ACh to the receptor can depolarize the muscle fiber, causing a cascade that eventually results in muscle contraction.Neuromuscular junction diseases can be of genetic and autoimmune origin. Genetic disorders, such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy, can arise from mutated structural proteins that comprise the neuromuscular junction, whereas autoimmune diseases, such as myasthenia gravis, occur when antibodies are produced against nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on the sarcolemma.