Slide ()
... Neurogenic and myopathic diseases have different effects on the motor unit. A. A motor unit potential is recorded by inserting a needle electrode into the muscle. The muscle fibers innervated by a single motor neuron are not usually adjacent to one another, yet the highly effective transmission at t ...
... Neurogenic and myopathic diseases have different effects on the motor unit. A. A motor unit potential is recorded by inserting a needle electrode into the muscle. The muscle fibers innervated by a single motor neuron are not usually adjacent to one another, yet the highly effective transmission at t ...
Nerve cells (Neurons)
... between the _________ of one cell and the ___________ of another. The chemical then continues as an _____________________ along the next neuron until the next synapse. This electro-chemical process is ____________ until the message reaches its destination. ...
... between the _________ of one cell and the ___________ of another. The chemical then continues as an _____________________ along the next neuron until the next synapse. This electro-chemical process is ____________ until the message reaches its destination. ...
The Nervous Systeminofnotes
... • 4. The motor neuron sends the message to the muscles to carry out your response. ...
... • 4. The motor neuron sends the message to the muscles to carry out your response. ...
Nervous System Objectives
... 10. Label a diagram of a synaptic region and tell where neurotransmitters are released, direction of impulse travel, ion flow, and fusion of the neurotransmitter occur. 11. Identify the types of receptors and the structures found in the vision and hearing receptors. 12. Elaborate on the nervous syst ...
... 10. Label a diagram of a synaptic region and tell where neurotransmitters are released, direction of impulse travel, ion flow, and fusion of the neurotransmitter occur. 11. Identify the types of receptors and the structures found in the vision and hearing receptors. 12. Elaborate on the nervous syst ...
Slide ()
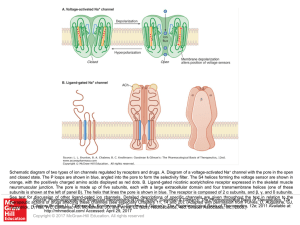
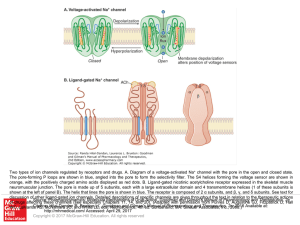
... Schematic diagram of two types of ion channels regulated by receptors and drugs. A. Diagram of a voltage-activated Na+ channel with the pore in the open and closed state. The P loops are shown in blue, angled into the pore to form the selectivity filter. The S4 helices forming the voltage sensor are ...
... Schematic diagram of two types of ion channels regulated by receptors and drugs. A. Diagram of a voltage-activated Na+ channel with the pore in the open and closed state. The P loops are shown in blue, angled into the pore to form the selectivity filter. The S4 helices forming the voltage sensor are ...
Biosc_48_Chapter_7_part_2_lecture
... Postsynaptic inhibition is produced by inhibitory neurotransmitters such as glycine (spinal cord) and GABA (brain). Hyperpolarizes the postsynaptic neuron and makes it less likely to reach threshold voltage at the axon hillock ...
... Postsynaptic inhibition is produced by inhibitory neurotransmitters such as glycine (spinal cord) and GABA (brain). Hyperpolarizes the postsynaptic neuron and makes it less likely to reach threshold voltage at the axon hillock ...
big
... – Myelin is lipoprotein – Inside myelin, diffusion is fast, but fades out – At nodes, new action potentials are triggered ...
... – Myelin is lipoprotein – Inside myelin, diffusion is fast, but fades out – At nodes, new action potentials are triggered ...
AP151 Neurotransmitters
... • Binding of NT to receptors on post synaptic membrane can cause EPSPs or IPSPs depending on the combination of NT and receptor at any given synapse. ...
... • Binding of NT to receptors on post synaptic membrane can cause EPSPs or IPSPs depending on the combination of NT and receptor at any given synapse. ...
SBI 4U Homeostasis 2
... travels through the cell to the next node. • This occurs at each node along the axon until it reaches the end of the neuron. • Because the action potentials are forced to jump from one node to the next due to the myelin sheath, the conduction of an impulse along a myelinated neuron is called saltato ...
... travels through the cell to the next node. • This occurs at each node along the axon until it reaches the end of the neuron. • Because the action potentials are forced to jump from one node to the next due to the myelin sheath, the conduction of an impulse along a myelinated neuron is called saltato ...
Biochemistry of Nerve Transmission - I-GaP
... bronchial tree of the lungs, and the vessels that supply blood to skeletal muscle. In addition to their effects as neurotransmitters, norepinephrine and epinephrine can influence the rate of metabolism. This influence works both by modulating endocrine function such as insulin secretion and by incre ...
... bronchial tree of the lungs, and the vessels that supply blood to skeletal muscle. In addition to their effects as neurotransmitters, norepinephrine and epinephrine can influence the rate of metabolism. This influence works both by modulating endocrine function such as insulin secretion and by incre ...
Slideshow
... Curare - poison made from frog skin and causes paralysis by blocking Ach receptors at the neuromuscular junction. ...
... Curare - poison made from frog skin and causes paralysis by blocking Ach receptors at the neuromuscular junction. ...
No Slide Title
... therefore there must be some delay at the synapses. 2. Summation: When a weak stimulus is applied (a pinch) a reflex may not be produced, however if several small pinches are rapidly applied they trigger a reflex. This is called temporal summation. ...
... therefore there must be some delay at the synapses. 2. Summation: When a weak stimulus is applied (a pinch) a reflex may not be produced, however if several small pinches are rapidly applied they trigger a reflex. This is called temporal summation. ...
Bioenergetics - Eastern Michigan University
... • It uses ATP to actively pump Na+ out of the cell and K+ into the cell • It takes energy (ATP) to maintain the pump and the gradient ...
... • It uses ATP to actively pump Na+ out of the cell and K+ into the cell • It takes energy (ATP) to maintain the pump and the gradient ...
nervous system
... open in the next neuron or effector Repolarization- ATP powers Na+ and K+ pump to reestablish resting potential Nerves can’t be stimulated during repolarization unless a huge stimulus occurs, “you stick your wet finger into an electrical outlet Ready to fire again in .001 sec ...
... open in the next neuron or effector Repolarization- ATP powers Na+ and K+ pump to reestablish resting potential Nerves can’t be stimulated during repolarization unless a huge stimulus occurs, “you stick your wet finger into an electrical outlet Ready to fire again in .001 sec ...
ppt
... •Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential (EPSP) •triggered by excitatory neurotransmitters •open ligand-gated Na+ channels •allows Na+ to flow inside the cell •causing a slight depolarization of the postsynaptic cell •moves the postsynaptic cell closer to firing an action potential ...
... •Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential (EPSP) •triggered by excitatory neurotransmitters •open ligand-gated Na+ channels •allows Na+ to flow inside the cell •causing a slight depolarization of the postsynaptic cell •moves the postsynaptic cell closer to firing an action potential ...
Topic 6
... because the range of different chemicals in the numerous different regions of the brain and spinal cord make isolation very difficult. One technique that can be used to approximate the study of CNS transmitter release to a REGION (not an individual neuron) of the brain or spinal cord involves in vit ...
... because the range of different chemicals in the numerous different regions of the brain and spinal cord make isolation very difficult. One technique that can be used to approximate the study of CNS transmitter release to a REGION (not an individual neuron) of the brain or spinal cord involves in vit ...
Slide 1 - AccessPharmacy
... Two types of ion channels regulated by receptors and drugs. A. Diagram of a voltage-activated Na+ channel with the pore in the open and closed state. The pore-forming P loops are shown in blue, angled into the pore to form the selectivity filter. The S4 helices forming the voltage sensor are shown i ...
... Two types of ion channels regulated by receptors and drugs. A. Diagram of a voltage-activated Na+ channel with the pore in the open and closed state. The pore-forming P loops are shown in blue, angled into the pore to form the selectivity filter. The S4 helices forming the voltage sensor are shown i ...
Neuromuscular junction

A neuromuscular junction (sometimes called a myoneural junction) is a junction between nerve and muscle; it is a chemical synapse formed by the contact between the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron and the postsynaptic membrane of a muscle fiber. It is at the neuromuscular junction that a motor neuron is able to transmit a signal to the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction.Muscles require innervation to function—and even just to maintain muscle tone, avoiding atrophy. Synaptic transmission at the neuromuscular junction begins when an action potential reaches the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron, which activates voltage-dependent calcium channels to allow calcium ions to enter the neuron. Calcium ions bind to sensor proteins (synaptotagmin) on synaptic vesicles, triggering vesicle fusion with the cell membrane and subsequent neurotransmitter release from the motor neuron into the synaptic cleft. In vertebrates, motor neurons release acetylcholine (ACh), a small molecule neurotransmitter, which diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) on the cell membrane of the muscle fiber, also known as the sarcolemma. nAChRs are ionotropic receptors, meaning they serve as ligand-gated ion channels. The binding of ACh to the receptor can depolarize the muscle fiber, causing a cascade that eventually results in muscle contraction.Neuromuscular junction diseases can be of genetic and autoimmune origin. Genetic disorders, such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy, can arise from mutated structural proteins that comprise the neuromuscular junction, whereas autoimmune diseases, such as myasthenia gravis, occur when antibodies are produced against nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on the sarcolemma.