Presentazione di PowerPoint
... Neuronal glutamate (Glu) is synthesized de novo from glucose (not shown) and from glutamine (Gln) supplied by glial cells. Glutamate is then packaged into synaptic vesicles by vesicular glutamate transporters (vGluTs). SNARE complex proteins mediate the interaction and fusion of vesicles with the pr ...
... Neuronal glutamate (Glu) is synthesized de novo from glucose (not shown) and from glutamine (Gln) supplied by glial cells. Glutamate is then packaged into synaptic vesicles by vesicular glutamate transporters (vGluTs). SNARE complex proteins mediate the interaction and fusion of vesicles with the pr ...
Chapter 2 - Biological Basis of Behavior
... BUT cause a depletion over time Acetylcholine triggers muscle contraction important role in arousal and attention Loss = linked to Alzheimer’s Disease ...
... BUT cause a depletion over time Acetylcholine triggers muscle contraction important role in arousal and attention Loss = linked to Alzheimer’s Disease ...
Synapses and Neurotransmitters Notes
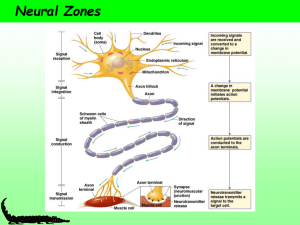
... A neuromuscular junction (NMJ) is a contact between a neuron and a muscle: it is like a synapse in that the action potential stops and the signal is carried by a chemical neurotransmitter released by the neuron. Neurotransmitters Are Made and Stored in the Pre-synaptic Terminal The end of the neuron ...
... A neuromuscular junction (NMJ) is a contact between a neuron and a muscle: it is like a synapse in that the action potential stops and the signal is carried by a chemical neurotransmitter released by the neuron. Neurotransmitters Are Made and Stored in the Pre-synaptic Terminal The end of the neuron ...
Chapter 48 – Nervous System – Homework – Part I
... 1. Describe the basic pathway of information flow through neurons that cause you to turn your head when you hear the sound of your name being called. 2. Compare and contrast sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons 3. Compare and contrast dendrites and axons. 4. Discuss how the following rel ...
... 1. Describe the basic pathway of information flow through neurons that cause you to turn your head when you hear the sound of your name being called. 2. Compare and contrast sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons 3. Compare and contrast dendrites and axons. 4. Discuss how the following rel ...
Presentation Package - faculty.coe.unt.edu
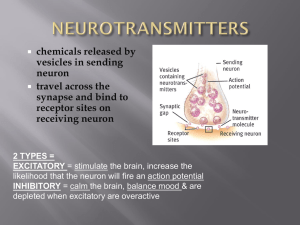
... • Neurons communicate with one another by releasing neurotransmitters across synapses. • Synapses involve a presynaptic axon terminal, a postsynaptic receptor, neurotransmitters, and the space between them. • Neurotransmitters bind to the receptors and cause depolarization (excitation) or hyperpolar ...
... • Neurons communicate with one another by releasing neurotransmitters across synapses. • Synapses involve a presynaptic axon terminal, a postsynaptic receptor, neurotransmitters, and the space between them. • Neurotransmitters bind to the receptors and cause depolarization (excitation) or hyperpolar ...
The motor system Outline Muscles Reflexes Disorders of movement
... Curare Botulinum toxin _________________________ Myasthenia gravis _________________________ disorder Results in the breakdown of _________________________ (ACh) receptors on the muscle fiber Symptoms include extreme weakness, fatigue, droopy eyelids, slurred speech, difficulty _____________________ ...
... Curare Botulinum toxin _________________________ Myasthenia gravis _________________________ disorder Results in the breakdown of _________________________ (ACh) receptors on the muscle fiber Symptoms include extreme weakness, fatigue, droopy eyelids, slurred speech, difficulty _____________________ ...
Nervous System Study Guide
... and potassium amount inside and outside of neuron cell. 6. When a neuron at rest, what is the amount of sodium amount outside and inside the cell? 7. When a neuron at rest, what is the amount of K+ ions inside and outside the neuron cell? 8. Functions of sodium-potassium pumps during action potentia ...
... and potassium amount inside and outside of neuron cell. 6. When a neuron at rest, what is the amount of sodium amount outside and inside the cell? 7. When a neuron at rest, what is the amount of K+ ions inside and outside the neuron cell? 8. Functions of sodium-potassium pumps during action potentia ...
Neurotransmitters - Shifa College of Medicine
... • Degeneration of nigrostriatal dopamine neurons in the brain resulting in a deficiency of Dopamine • Symptoms include trembling of hands, arms, legs, jaw and face; stiffness of the arms, legs and trunk; slowness of movement; poor balance and coordination • Treatment with L-DOPA which enters the bra ...
... • Degeneration of nigrostriatal dopamine neurons in the brain resulting in a deficiency of Dopamine • Symptoms include trembling of hands, arms, legs, jaw and face; stiffness of the arms, legs and trunk; slowness of movement; poor balance and coordination • Treatment with L-DOPA which enters the bra ...
PowerPoint
... • If enough neurotransmitter is released by the axon terminal, so many Na+ ions diffuse into the neuron that the neuron becomes DEPOLARIZED. ...
... • If enough neurotransmitter is released by the axon terminal, so many Na+ ions diffuse into the neuron that the neuron becomes DEPOLARIZED. ...
Neural Anatomy and Function
... twitch and 180 fast twitch) • As the pectoralis major muscle contracts the GTO in the pectoralis major are stimulated • They stimulate a sensory nerve leading to the CNS • In the CNS, the sensory nerve synapses with a motor nerve that will inhibit (relax) the pectoralis major muscle • The man is una ...
... twitch and 180 fast twitch) • As the pectoralis major muscle contracts the GTO in the pectoralis major are stimulated • They stimulate a sensory nerve leading to the CNS • In the CNS, the sensory nerve synapses with a motor nerve that will inhibit (relax) the pectoralis major muscle • The man is una ...
ANP 214 REVIEW QUESTIONS 1
... 4. Which type of parasympathetic receptor relies upon G-protein activity? Several different types of toxins are agonists for these types of receptors, and will therefore bind to the receptor. What types of symptoms might be observed in a patient suffering from poisoning by such a toxin? 5. Given you ...
... 4. Which type of parasympathetic receptor relies upon G-protein activity? Several different types of toxins are agonists for these types of receptors, and will therefore bind to the receptor. What types of symptoms might be observed in a patient suffering from poisoning by such a toxin? 5. Given you ...
ANPS 019 Beneyto-Santonja 11-07
... Superficial cutaneous – highly sensitive fine touch and pressure for specific localization Deep cutaneous – less sensitive crude touch and pressure for less specific localization Barorecptors detect internal pressure (blood vessels, bladder, GI) Proprioceptors/Joint receptors (monitor limb p ...
... Superficial cutaneous – highly sensitive fine touch and pressure for specific localization Deep cutaneous – less sensitive crude touch and pressure for less specific localization Barorecptors detect internal pressure (blood vessels, bladder, GI) Proprioceptors/Joint receptors (monitor limb p ...
Sending Signals Notes
... • If enough neurotransmitter is released by the axon terminal, so many Na+ ions diffuse into the neuron that the neuron becomes DEPOLARIZED. ...
... • If enough neurotransmitter is released by the axon terminal, so many Na+ ions diffuse into the neuron that the neuron becomes DEPOLARIZED. ...
File
... usually (not always) the Axon terminal. The axon terminals are also called the bouton terminaux or synaptic knob. The synaptic knobs have synaptic vesicles that contain the NT (neurotransmitters). The NT are produced in the body & conducted along the axon (anterograde flow). The NT can be inhibitory ...
... usually (not always) the Axon terminal. The axon terminals are also called the bouton terminaux or synaptic knob. The synaptic knobs have synaptic vesicles that contain the NT (neurotransmitters). The NT are produced in the body & conducted along the axon (anterograde flow). The NT can be inhibitory ...
lesson 6
... membrane results in the inside of the neuron being 70 mV less positive than the outside ...
... membrane results in the inside of the neuron being 70 mV less positive than the outside ...
A1981ME66900001
... supplying crustacean limb muscles. Some muscles innervated by two excitatory motor neurons showed, with stimulation of a 'fast' motor neuron, large electrical events in individual muscle fibers, but a small contraction of the entire muscle. Conversely, identical stimulation of the companion 'slow' m ...
... supplying crustacean limb muscles. Some muscles innervated by two excitatory motor neurons showed, with stimulation of a 'fast' motor neuron, large electrical events in individual muscle fibers, but a small contraction of the entire muscle. Conversely, identical stimulation of the companion 'slow' m ...
Neuromuscular junction

A neuromuscular junction (sometimes called a myoneural junction) is a junction between nerve and muscle; it is a chemical synapse formed by the contact between the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron and the postsynaptic membrane of a muscle fiber. It is at the neuromuscular junction that a motor neuron is able to transmit a signal to the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction.Muscles require innervation to function—and even just to maintain muscle tone, avoiding atrophy. Synaptic transmission at the neuromuscular junction begins when an action potential reaches the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron, which activates voltage-dependent calcium channels to allow calcium ions to enter the neuron. Calcium ions bind to sensor proteins (synaptotagmin) on synaptic vesicles, triggering vesicle fusion with the cell membrane and subsequent neurotransmitter release from the motor neuron into the synaptic cleft. In vertebrates, motor neurons release acetylcholine (ACh), a small molecule neurotransmitter, which diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) on the cell membrane of the muscle fiber, also known as the sarcolemma. nAChRs are ionotropic receptors, meaning they serve as ligand-gated ion channels. The binding of ACh to the receptor can depolarize the muscle fiber, causing a cascade that eventually results in muscle contraction.Neuromuscular junction diseases can be of genetic and autoimmune origin. Genetic disorders, such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy, can arise from mutated structural proteins that comprise the neuromuscular junction, whereas autoimmune diseases, such as myasthenia gravis, occur when antibodies are produced against nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on the sarcolemma.