Frequent exchange of the DNA polymerase during bacterial
... been inferred from in vivo experiments that suggest infrequent replication fork collapse during chromosome replication in E. coli (Maisnier-Patin et al., 2001). Chromosomal DNA presents multiple potential obstacles to replisome progression. DNA lesions can result in the stalling of the replisome due ...
... been inferred from in vivo experiments that suggest infrequent replication fork collapse during chromosome replication in E. coli (Maisnier-Patin et al., 2001). Chromosomal DNA presents multiple potential obstacles to replisome progression. DNA lesions can result in the stalling of the replisome due ...
Genes Practice Questions
... 10 A landmark study in DNA replication research by Meselson and Stahl involved growing bacteria including an isotope of nitrogen 15N and then placing these bacteria in a medium containing only 14N. According to the known method of DNA replication, what do you predict the ratio of the two isotopes wo ...
... 10 A landmark study in DNA replication research by Meselson and Stahl involved growing bacteria including an isotope of nitrogen 15N and then placing these bacteria in a medium containing only 14N. According to the known method of DNA replication, what do you predict the ratio of the two isotopes wo ...
Non-destructive DNA extraction methods that yield DNA barcodes in
... In recent years, the importance of DNA barcoding has increased because of the need to make as complete of a phylogenetic tree as possible in order to differentiate species and discover new species (Hebert et al., 2003; Hebert & Gregory, 2005). DNA barcodes are short sequences of nucleotides that dif ...
... In recent years, the importance of DNA barcoding has increased because of the need to make as complete of a phylogenetic tree as possible in order to differentiate species and discover new species (Hebert et al., 2003; Hebert & Gregory, 2005). DNA barcodes are short sequences of nucleotides that dif ...
1 - life.illinois.edu
... were able to form plaques on E. coli K (P1) were destroyed as time passed. What is the explanation for this result? Answer: The vast majority of DNA synthesized during growth in the E. coli K strain is not radioactive because the phages were made in non-radioactive medium. However, a (rare) phage th ...
... were able to form plaques on E. coli K (P1) were destroyed as time passed. What is the explanation for this result? Answer: The vast majority of DNA synthesized during growth in the E. coli K strain is not radioactive because the phages were made in non-radioactive medium. However, a (rare) phage th ...
Electronic Fingerprints of DNA Bases on Graphene
... To achieve this goal, we have carried out extensive DFTbased, first-principles, numerical simulations of the electronic local densities of states (LDOS) of all four DNA bases on graphene. Considering only the short-range interaction between the DNA bases and graphene, the van der Waals interaction w ...
... To achieve this goal, we have carried out extensive DFTbased, first-principles, numerical simulations of the electronic local densities of states (LDOS) of all four DNA bases on graphene. Considering only the short-range interaction between the DNA bases and graphene, the van der Waals interaction w ...
RecA-mediated strand exchange traverses
... However, there should be an efficient strand exchange between homologous DNA regions coding for functional proteins. In individual lines of organisms, their DNA is subject to stochastic mutations wherein base substitutions are the most frequent non-detrimental mutations in protein-coding genes. Thus ...
... However, there should be an efficient strand exchange between homologous DNA regions coding for functional proteins. In individual lines of organisms, their DNA is subject to stochastic mutations wherein base substitutions are the most frequent non-detrimental mutations in protein-coding genes. Thus ...
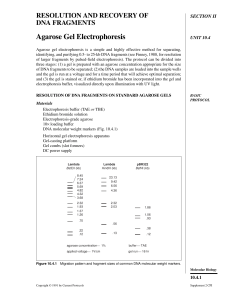
Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
... gradually removed, causing a concomitant decrease in the mobility of the DNA molecule. This occurs until a critical free-dye concentration is reached where no more superhelical turns remain (usually between 0.1 to 0.5 µg/ml). As still more ethidium bromide is bound, positive superhelical turns are g ...
... gradually removed, causing a concomitant decrease in the mobility of the DNA molecule. This occurs until a critical free-dye concentration is reached where no more superhelical turns remain (usually between 0.1 to 0.5 µg/ml). As still more ethidium bromide is bound, positive superhelical turns are g ...
HLA-B27 real-time PCR using TaqMan
... The aim of our study was to adapt our conventional allele specific HLA-B27 protocol to a fluorogenic real time (RT-PCR) method. The allele specific PCR detects the presence of the B*27 genotype by amplifying a region between primer sets that recognise only B*27 specific sequences. The PCR reaction a ...
... The aim of our study was to adapt our conventional allele specific HLA-B27 protocol to a fluorogenic real time (RT-PCR) method. The allele specific PCR detects the presence of the B*27 genotype by amplifying a region between primer sets that recognise only B*27 specific sequences. The PCR reaction a ...
DNA Review Sheet Plus 10 points on the exam tomorrow
... 1. What is the shape of DNA as named by Watson and Crick? Double Helix 2. If one strand of DNA has the bases GGCTAT, what bases does the complementary strand (other side of the DNA) have? CCGATA 3. Name the three parts to a nucleotide: a. deoxyribose sugar b. phosphate c. nitrogenous base 4. The two ...
... 1. What is the shape of DNA as named by Watson and Crick? Double Helix 2. If one strand of DNA has the bases GGCTAT, what bases does the complementary strand (other side of the DNA) have? CCGATA 3. Name the three parts to a nucleotide: a. deoxyribose sugar b. phosphate c. nitrogenous base 4. The two ...
(HPV) L1 gene DNA possibly bound to particulate aluminum
... degenerate primers for initial amplification and the GP5/GP6-based nested PCR primers for the second amplification were used to prepare the template for direct automated cycle DNA sequencing of a hypervariable segment of the HPV L1 gene which is used for manufacturing of the HPV L1 capsid protein by a ...
... degenerate primers for initial amplification and the GP5/GP6-based nested PCR primers for the second amplification were used to prepare the template for direct automated cycle DNA sequencing of a hypervariable segment of the HPV L1 gene which is used for manufacturing of the HPV L1 capsid protein by a ...
Identifying the Genetic Material
... into the bacterial cells, while most of the viral proteins remain outside. The injected DNA molecules causes the bacterial cells to produce more viral DNA and proteins. This meant that the DNA, rather than proteins, is the hereditary material, at least in viruses. These important experiments, and ma ...
... into the bacterial cells, while most of the viral proteins remain outside. The injected DNA molecules causes the bacterial cells to produce more viral DNA and proteins. This meant that the DNA, rather than proteins, is the hereditary material, at least in viruses. These important experiments, and ma ...
Reverse engineering of drug induced DNA damage response
... drug induced inductions as well as of time dependent ATM kinase inhibition on cell survival through further biological experiments. Intermediate and temporal modelling outcomes revealed the distinct signaling profile associated with ATM kinase activity and inhibition and explained the underlying sig ...
... drug induced inductions as well as of time dependent ATM kinase inhibition on cell survival through further biological experiments. Intermediate and temporal modelling outcomes revealed the distinct signaling profile associated with ATM kinase activity and inhibition and explained the underlying sig ...
Combing of Molecules in Microchannels
... solution into square arrays, followed by air-drying; the DNA was stretched as the droplets dried, producing circles approximately 500 µm in diameter.23 In a second example, a microcapillary was used to move a drop of solution containing DNA on a surface and thereby direct the deposition of stretched ...
... solution into square arrays, followed by air-drying; the DNA was stretched as the droplets dried, producing circles approximately 500 µm in diameter.23 In a second example, a microcapillary was used to move a drop of solution containing DNA on a surface and thereby direct the deposition of stretched ...
DNA double-strand break repair by homologous recombination
... yeast, and V(D)J recombination in the vertebrate immune system. The action of restriction endonucleases and topoisomerases also generates DSB [7–11]. Unrepaired DSB can cause loss of chromosomes and/or cell death. If misrepaired, DSB can give rise to mutations [12,13] and chromosomal rearrangements ...
... yeast, and V(D)J recombination in the vertebrate immune system. The action of restriction endonucleases and topoisomerases also generates DSB [7–11]. Unrepaired DSB can cause loss of chromosomes and/or cell death. If misrepaired, DSB can give rise to mutations [12,13] and chromosomal rearrangements ...
Host DNA Replication Is Induced by Geminivirus
... BrdU Can Be Distributed Differentially between TGMV and Host DNA The observation of heterogeneous BrdU labeling patterns prompted us to wonder whether we could distinguish further how BrdU was distributed within nuclei. Laser scanning confocal microscopy was used in addition to normal epifluorescenc ...
... BrdU Can Be Distributed Differentially between TGMV and Host DNA The observation of heterogeneous BrdU labeling patterns prompted us to wonder whether we could distinguish further how BrdU was distributed within nuclei. Laser scanning confocal microscopy was used in addition to normal epifluorescenc ...
Francon et al, 2004
... blotted and RPA was detected using the two specific RPA antibodies. At mitosis, RPA34 is phosphorylated and does not bind to chromatin (Fig. 1B,C). When exit from mitosis is induced, RPA34 is dephosphorylated before entry into S phase (Fig. 1B, mAb, 30 minutes). Dephosphorylated RPA34 starts to accu ...
... blotted and RPA was detected using the two specific RPA antibodies. At mitosis, RPA34 is phosphorylated and does not bind to chromatin (Fig. 1B,C). When exit from mitosis is induced, RPA34 is dephosphorylated before entry into S phase (Fig. 1B, mAb, 30 minutes). Dephosphorylated RPA34 starts to accu ...
Mechanism of high-mobility group protein B enhancement of
... increase the affinity of ER for half-site EREs and for imperfect palindromic EREs, and to promote a greater fold increase for these intrinsically weak EREs than for consensus palindromic EREs (24,39). This may be of biological significance since few steroid receptor target genes contain consensus palin ...
... increase the affinity of ER for half-site EREs and for imperfect palindromic EREs, and to promote a greater fold increase for these intrinsically weak EREs than for consensus palindromic EREs (24,39). This may be of biological significance since few steroid receptor target genes contain consensus palin ...
Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
... gradually removed, causing a concomitant decrease in the mobility of the DNA molecule. This occurs until a critical free-dye concentration is reached where no more superhelical turns remain (usually between 0.1 and 0.5 µg/ml). As still more ethidium bromide is bound, positive superhelical turns are ...
... gradually removed, causing a concomitant decrease in the mobility of the DNA molecule. This occurs until a critical free-dye concentration is reached where no more superhelical turns remain (usually between 0.1 and 0.5 µg/ml). As still more ethidium bromide is bound, positive superhelical turns are ...
Degree Thesis Adoption of EBPP by DNA: Are Customers
... period of one year those two third of the population have bought or ordered something via internet. This statistics explain that citizen of Finland should be capable of handling internet on regular basis. But the problem arise here, what about one third of the citizen who do not use internet? Even ...
... period of one year those two third of the population have bought or ordered something via internet. This statistics explain that citizen of Finland should be capable of handling internet on regular basis. But the problem arise here, what about one third of the citizen who do not use internet? Even ...
Linking abnormal mitosis to the acquisition of DNA damage
... generally speaking, proliferating mammalian somatic cells require 12–30 h to properly prepare for division. By contrast, mitosis itself is relatively rapid, typically lasting only 20–60 min, depending on chromosome number and the efficiency of spindle assembly (Yang et al., 2008). It may seem surpri ...
... generally speaking, proliferating mammalian somatic cells require 12–30 h to properly prepare for division. By contrast, mitosis itself is relatively rapid, typically lasting only 20–60 min, depending on chromosome number and the efficiency of spindle assembly (Yang et al., 2008). It may seem surpri ...
Comparison of DNA Replication in Cells from Prokarya and Eukarya
... It is now supposed that utilization of DNA as genetic material emerged after an RNA world existed (Gesteland and Atkins 1993) and that all contemporary organisms evolved from a common ancestor related to primitive photosynthetic bacteria (Woese and Pace 1993). It is therefore not surprising that cel ...
... It is now supposed that utilization of DNA as genetic material emerged after an RNA world existed (Gesteland and Atkins 1993) and that all contemporary organisms evolved from a common ancestor related to primitive photosynthetic bacteria (Woese and Pace 1993). It is therefore not surprising that cel ...
DNA repair

DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as UV light and radiation can cause DNA damage, resulting in as many as 1 million individual molecular lesions per cell per day. Many of these lesions cause structural damage to the DNA molecule and can alter or eliminate the cell's ability to transcribe the gene that the affected DNA encodes. Other lesions induce potentially harmful mutations in the cell's genome, which affect the survival of its daughter cells after it undergoes mitosis. As a consequence, the DNA repair process is constantly active as it responds to damage in the DNA structure. When normal repair processes fail, and when cellular apoptosis does not occur, irreparable DNA damage may occur, including double-strand breaks and DNA crosslinkages (interstrand crosslinks or ICLs).The rate of DNA repair is dependent on many factors, including the cell type, the age of the cell, and the extracellular environment. A cell that has accumulated a large amount of DNA damage, or one that no longer effectively repairs damage incurred to its DNA, can enter one of three possible states: an irreversible state of dormancy, known as senescence cell suicide, also known as apoptosis or programmed cell death unregulated cell division, which can lead to the formation of a tumor that is cancerousThe DNA repair ability of a cell is vital to the integrity of its genome and thus to the normal functionality of that organism. Many genes that were initially shown to influence life span have turned out to be involved in DNA damage repair and protection.