Gene Section CDT1 (chromatin licensing and DNA replication factor 1)
... expression profile appears to be preserved during human carcinogenesis. Overexpression of CDT1 results in rereplication, a form of endogenous DNA damage. ...
... expression profile appears to be preserved during human carcinogenesis. Overexpression of CDT1 results in rereplication, a form of endogenous DNA damage. ...
Module 7 – Microbial Molecular Biology and Genetics
... the aqueous environment of the cell, the conjugated π bonds of nucleotide bases align perpendicular to the axis of the DNA molecule, minimizing their interaction with the solvation shell and therefore, the Gibbs free energy. The four bases found in DNA are adenine (abbreviated A), cytosine (C), guan ...
... the aqueous environment of the cell, the conjugated π bonds of nucleotide bases align perpendicular to the axis of the DNA molecule, minimizing their interaction with the solvation shell and therefore, the Gibbs free energy. The four bases found in DNA are adenine (abbreviated A), cytosine (C), guan ...
HotStarTaq® Plus DNA Polymerase and Master Mix and
... Purchase of these products is accompanied by a limited license outside the U.S. to use it in the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) amplification process for the purchaser’s own internal research in conjunction with a thermal cycler whose use in the automated performance of the PCR process is covered b ...
... Purchase of these products is accompanied by a limited license outside the U.S. to use it in the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) amplification process for the purchaser’s own internal research in conjunction with a thermal cycler whose use in the automated performance of the PCR process is covered b ...
DNA Translocation and Loop Formation Mechanism of Chromatin
... ATP-dependent chromatin-remodeling complexes (remodelers) modulate gene transcription by regulating the accessibility of highly packaged genomic DNA. However, the molecular mechanisms involved at the nucleosomal level in this process remain controversial. Here, we monitor the real-time activity of s ...
... ATP-dependent chromatin-remodeling complexes (remodelers) modulate gene transcription by regulating the accessibility of highly packaged genomic DNA. However, the molecular mechanisms involved at the nucleosomal level in this process remain controversial. Here, we monitor the real-time activity of s ...
ADVANCING JUSTICE THROUGH DNA TECHNOLOGY
... President Bush believes we must do more to realize the full potential of DNA technology to solve crime and protect the innocent. The President has proposed $232.6 million in federal funding in FY 2004 for his initiative, Advancing Justice Through DNA Technology, and calls for continuing this level o ...
... President Bush believes we must do more to realize the full potential of DNA technology to solve crime and protect the innocent. The President has proposed $232.6 million in federal funding in FY 2004 for his initiative, Advancing Justice Through DNA Technology, and calls for continuing this level o ...
Chapter 12 Recombinant DNA Technology Key Concepts
... autonomously replicating DNA molecules such as bacterial plasmids. These small circular molecules act as carriers, or vectors, for the DNA fragments. The vector molecules with their inserts are called recombinant DNA because they consist of novel combinations of DNA from the donor genome (which can ...
... autonomously replicating DNA molecules such as bacterial plasmids. These small circular molecules act as carriers, or vectors, for the DNA fragments. The vector molecules with their inserts are called recombinant DNA because they consist of novel combinations of DNA from the donor genome (which can ...
Application of a Real Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Method to
... of UV-absorbing contaminants, such as protein. The CTAB extraction method yielded a higher concentration of DNA (22 and 12 ng/µL from milk and egg, respectively), with acceptable DNA purity (A260/A280 was 1.8 for both matrixes) (Table 1). The quantity and quality of DNA was also evaluated via the SY ...
... of UV-absorbing contaminants, such as protein. The CTAB extraction method yielded a higher concentration of DNA (22 and 12 ng/µL from milk and egg, respectively), with acceptable DNA purity (A260/A280 was 1.8 for both matrixes) (Table 1). The quantity and quality of DNA was also evaluated via the SY ...
1 A Single-Molecule Hershey-Chase Experiment
... [7,10]. We also cannot rule out the possibility that SYTOX Orange intermittently interferes with the ejection process. Another possibility is that the DNA in the phages are nicked; however, we never see any pausing in in vitro experiments done from the same phage lysate. We note that our results are ...
... [7,10]. We also cannot rule out the possibility that SYTOX Orange intermittently interferes with the ejection process. Another possibility is that the DNA in the phages are nicked; however, we never see any pausing in in vitro experiments done from the same phage lysate. We note that our results are ...
Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus - Southwest Florida Research and
... was transferred to an Eppendorf tube and incubated at 65°C for 30 min. Subsequently, one-third volume of 5 M potassium acetate was added, mixed thoroughly, and incubated on ice for 20 min. The mixture was centrifuged for 10 min at 13,000 rpm, and DNA was precipitated from 0.4 ml of supernatant by ad ...
... was transferred to an Eppendorf tube and incubated at 65°C for 30 min. Subsequently, one-third volume of 5 M potassium acetate was added, mixed thoroughly, and incubated on ice for 20 min. The mixture was centrifuged for 10 min at 13,000 rpm, and DNA was precipitated from 0.4 ml of supernatant by ad ...
genotyping arabidopsis - STLCC.edu :: Users` Server
... called “Activator” (Ac) is necessary for the transposition of Ds. Ds is believed to be a mutant transposon, lacking the gene for transposase. Ac carries the transposase gene, and no matter where in the genome it is located, it supplies the enzyme for the transposition of Ds. It is possible to cross ...
... called “Activator” (Ac) is necessary for the transposition of Ds. Ds is believed to be a mutant transposon, lacking the gene for transposase. Ac carries the transposase gene, and no matter where in the genome it is located, it supplies the enzyme for the transposition of Ds. It is possible to cross ...
Chapter 20
... on the LB plate, not the plate with ampicillin. What you see on the LB plate is known as a “lawn” of bacteria , which means that so many grew that all the When vector was used (+DNA) bacteria colonies mix together and just cover the that got the vector could grow on the plate. AMP plates and colonie ...
... on the LB plate, not the plate with ampicillin. What you see on the LB plate is known as a “lawn” of bacteria , which means that so many grew that all the When vector was used (+DNA) bacteria colonies mix together and just cover the that got the vector could grow on the plate. AMP plates and colonie ...
Hypercholesterolemia
... Cholesterol is synthesized in the liver and is absorbed in the intesChemical Structure of Cholesterol. tine from ingested food. It is circulated in body fluids in spherical bodies known as lipoprotein particles. These lipoproteins are classified according to their densities determined by gradient cent ...
... Cholesterol is synthesized in the liver and is absorbed in the intesChemical Structure of Cholesterol. tine from ingested food. It is circulated in body fluids in spherical bodies known as lipoprotein particles. These lipoproteins are classified according to their densities determined by gradient cent ...
OsHUS1 Facilitates Accurate Meiotic Recombination in Rice
... recombination (ER, also known as non-allelic homologous recombination). As eukaryotic genomes are rich in repeated DNA sequences, ER can produce chromosomal rearrangements, which in humans result in numerous genomic disorders [9,10]. Despite the adverse impact of ER on genome integrity, ER occurs re ...
... recombination (ER, also known as non-allelic homologous recombination). As eukaryotic genomes are rich in repeated DNA sequences, ER can produce chromosomal rearrangements, which in humans result in numerous genomic disorders [9,10]. Despite the adverse impact of ER on genome integrity, ER occurs re ...
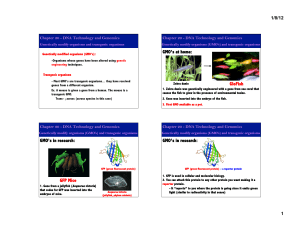
GloFish GMO`s at home: GFP Mice GMO`s in research: GMO`s in
... Combine millions of vector with millions of E.coli and heat shock… One can also use electroporation (forming pores using electricity) to transform as opposed to heat shocking. It involves sending electricity through the vector/bacterial solution, which induces temporary holes in the bacterial membra ...
... Combine millions of vector with millions of E.coli and heat shock… One can also use electroporation (forming pores using electricity) to transform as opposed to heat shocking. It involves sending electricity through the vector/bacterial solution, which induces temporary holes in the bacterial membra ...
Structure of DIG
... First: Incorporate “DIG” (Digoxigenin) into your probe DNA Structure of DIG: ...
... First: Incorporate “DIG” (Digoxigenin) into your probe DNA Structure of DIG: ...
number of fifty human tumours
... The relation between DNA content and chromosome number Considering first the main group of 30 tumours on which substantial numbers of chromosome counts were made, it is evident that except for Tumour No. 29 there is quite good agreement between basic DNA content and chromosome number. For Tumour No. ...
... The relation between DNA content and chromosome number Considering first the main group of 30 tumours on which substantial numbers of chromosome counts were made, it is evident that except for Tumour No. 29 there is quite good agreement between basic DNA content and chromosome number. For Tumour No. ...
DNA/RNA/Transcription/Translation Chapter CHAP 13 all reading
... with cytosine. These base-pairing rules are dictated by the chemical structure of the bases. The structure and size of the nitrogenous bases allow for only these two pair combinations. The base pairs are held together by weak hydrogen bonds. Adenine forms two hydrogen bonds with thymine, while cytos ...
... with cytosine. These base-pairing rules are dictated by the chemical structure of the bases. The structure and size of the nitrogenous bases allow for only these two pair combinations. The base pairs are held together by weak hydrogen bonds. Adenine forms two hydrogen bonds with thymine, while cytos ...
Transcription-associated recombination in eukaryotes: link between
... THO together with certain RNA export factors forms a larger complex called TREX (34). Mutations in these RNA export factors confer a similar transcription-dependent hyperrecombination phenotype and defect in transcription elongation as THO mutations (33,41). In addition, yeast mutants in proteins in ...
... THO together with certain RNA export factors forms a larger complex called TREX (34). Mutations in these RNA export factors confer a similar transcription-dependent hyperrecombination phenotype and defect in transcription elongation as THO mutations (33,41). In addition, yeast mutants in proteins in ...
Deciphering the role of DNA methylation in multiple sclerosis
... described epigenetic mechanisms, first referred to its correlation with cancer, regulating the expression of oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes [20]. However, over the past decade, a huge effort has been made to explain its role in immunity and autoimmunity. To begin with, DNA methylation is an es ...
... described epigenetic mechanisms, first referred to its correlation with cancer, regulating the expression of oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes [20]. However, over the past decade, a huge effort has been made to explain its role in immunity and autoimmunity. To begin with, DNA methylation is an es ...
JOIN2004 Universidade do Minho
... Regular expressions permit you to find and alter many patterns with relative ease. The excellent regular expressions in Perl are a major reason for Perl's success as a bioinformatics programming language. ...
... Regular expressions permit you to find and alter many patterns with relative ease. The excellent regular expressions in Perl are a major reason for Perl's success as a bioinformatics programming language. ...
How dormant origins promote complete genome replication
... With these considerations in mind, we recently modelled the behaviour of origin activation within a single 250 kb origin cluster [41]. Origins were assigned a certain initiation probability per unit time and were then activated stochastically during S phase (Figure 4a). Model parameters (mean origin ...
... With these considerations in mind, we recently modelled the behaviour of origin activation within a single 250 kb origin cluster [41]. Origins were assigned a certain initiation probability per unit time and were then activated stochastically during S phase (Figure 4a). Model parameters (mean origin ...
DNA Fingerprinting by Restriction Enzyme Patterns
... whereby the genomic DNA of an organism is analyzed by examining several specific, variable DNA sequences located throughout the genome. In humans, DNA fingerprinting is now used routinely for identification purposes. Human DNA fingerprinting was pioneered by Dr. Alex Jeffreys at the University of Leices ...
... whereby the genomic DNA of an organism is analyzed by examining several specific, variable DNA sequences located throughout the genome. In humans, DNA fingerprinting is now used routinely for identification purposes. Human DNA fingerprinting was pioneered by Dr. Alex Jeffreys at the University of Leices ...
DNA repair

DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as UV light and radiation can cause DNA damage, resulting in as many as 1 million individual molecular lesions per cell per day. Many of these lesions cause structural damage to the DNA molecule and can alter or eliminate the cell's ability to transcribe the gene that the affected DNA encodes. Other lesions induce potentially harmful mutations in the cell's genome, which affect the survival of its daughter cells after it undergoes mitosis. As a consequence, the DNA repair process is constantly active as it responds to damage in the DNA structure. When normal repair processes fail, and when cellular apoptosis does not occur, irreparable DNA damage may occur, including double-strand breaks and DNA crosslinkages (interstrand crosslinks or ICLs).The rate of DNA repair is dependent on many factors, including the cell type, the age of the cell, and the extracellular environment. A cell that has accumulated a large amount of DNA damage, or one that no longer effectively repairs damage incurred to its DNA, can enter one of three possible states: an irreversible state of dormancy, known as senescence cell suicide, also known as apoptosis or programmed cell death unregulated cell division, which can lead to the formation of a tumor that is cancerousThe DNA repair ability of a cell is vital to the integrity of its genome and thus to the normal functionality of that organism. Many genes that were initially shown to influence life span have turned out to be involved in DNA damage repair and protection.