The National DNA Database
... Act 1994, it has been overseen by a Management Board operated under a Memorandum of Understanding between the Forensic Science Service (FSS) and the Association of Chief Police Officers (ACPO). Recent developments, including the Home Office DNA Expansion Programme, the Review of the Forensic Science ...
... Act 1994, it has been overseen by a Management Board operated under a Memorandum of Understanding between the Forensic Science Service (FSS) and the Association of Chief Police Officers (ACPO). Recent developments, including the Home Office DNA Expansion Programme, the Review of the Forensic Science ...
Impact of Sample Type and DNA Isolation Procedure on
... infectious diseases faster, more precisely, and more sustainably. ...
... infectious diseases faster, more precisely, and more sustainably. ...
Development and Optimization of a DNA extraction
... with proteins. Moreover, DNA is species-specific, allowing the verification of species, and can be found in every cell of plants and animals which are the major constituents of food products (Prado, et al., 2007). The main steps for DNA-based analysis are extraction, amplification and quantification ...
... with proteins. Moreover, DNA is species-specific, allowing the verification of species, and can be found in every cell of plants and animals which are the major constituents of food products (Prado, et al., 2007). The main steps for DNA-based analysis are extraction, amplification and quantification ...
Unit 3 Solutions - Manning`s Science
... strand, DNA synthesis proceeds in the opposite direction to the movement of the replication fork. The lagging strand is synthesized in short fragments called Okazaki fragments. 22. DNA replication requires the use of many enzymes that have specific roles. The presence of numerous specialized enzyme ...
... strand, DNA synthesis proceeds in the opposite direction to the movement of the replication fork. The lagging strand is synthesized in short fragments called Okazaki fragments. 22. DNA replication requires the use of many enzymes that have specific roles. The presence of numerous specialized enzyme ...
3D DNA Crystals and Nanotechnology
... This simplicity is also reflected in the immediately recognizable relationship between the double helical structure and DNA’s role in genetic information storage. The original determination of the double helical DNA structure was itself deeply rooted in the exploration of another class of structures ...
... This simplicity is also reflected in the immediately recognizable relationship between the double helical structure and DNA’s role in genetic information storage. The original determination of the double helical DNA structure was itself deeply rooted in the exploration of another class of structures ...
Incorporation of reporter molecule
... modi®ed dNTP combinations identi®ed and con®rmed with these two model template assay systems were then tested further in the natural DNA template assay with a pUC19-derived template (see Materials and Methods). Evaluation of modi®ed dNTP substrates First, the substrate properties of each modi®ed dNT ...
... modi®ed dNTP combinations identi®ed and con®rmed with these two model template assay systems were then tested further in the natural DNA template assay with a pUC19-derived template (see Materials and Methods). Evaluation of modi®ed dNTP substrates First, the substrate properties of each modi®ed dNT ...
Cloning methods
... supercoils by creating single stranded DNA breaks and re-ligating them. Type I Topoisomerases, also known as nicking – closing enzymes, are monomeric proteins with a molecular weight of approximately 100 kD. They are found in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. In prokaryotes, they form a phosphotyrosine di ...
... supercoils by creating single stranded DNA breaks and re-ligating them. Type I Topoisomerases, also known as nicking – closing enzymes, are monomeric proteins with a molecular weight of approximately 100 kD. They are found in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. In prokaryotes, they form a phosphotyrosine di ...
Analysis of Guanine Oxidation Products in Double
... single-stranded DNA. Therefore, the hotooxidation products of double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) may also differ from that of quadruplex or single-stranded DNA, with the difference likely explaining the influence of DNA structures on guanine oxidation pathways. In this study, the guanine oxidation products ...
... single-stranded DNA. Therefore, the hotooxidation products of double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) may also differ from that of quadruplex or single-stranded DNA, with the difference likely explaining the influence of DNA structures on guanine oxidation pathways. In this study, the guanine oxidation products ...
Complete Laboratory PDF
... another on a chromosome, the greater the chance that they will be inherited together as a unit (linked). Conversely, locations farther apart on the chromosome are more likely to be separated by chromosome recombination during meiosis. Thus, the frequency of recombination with previously mapped genes ...
... another on a chromosome, the greater the chance that they will be inherited together as a unit (linked). Conversely, locations farther apart on the chromosome are more likely to be separated by chromosome recombination during meiosis. Thus, the frequency of recombination with previously mapped genes ...
G-quadruplexes and helicases
... genetically unstable in yeast growing exponentially, leading to a 100-fold increase in gross chromosomal rearrangements at the repeated locus (48,49). A mutated version of this array, unable to form G4 structures, was much less sensitive to the absence of the helicase in the nucleus. By melting expe ...
... genetically unstable in yeast growing exponentially, leading to a 100-fold increase in gross chromosomal rearrangements at the repeated locus (48,49). A mutated version of this array, unable to form G4 structures, was much less sensitive to the absence of the helicase in the nucleus. By melting expe ...
The Master Molecule of Life
... proteins and 30% nucleic acids. But which was the genetic molecule? The big debate was between those who favored proteins as the genetic molecule and those who favored nucleic acids. The first major breakthrough came in 1928. British scientist, Fred Griffith, learned that genetic material could be t ...
... proteins and 30% nucleic acids. But which was the genetic molecule? The big debate was between those who favored proteins as the genetic molecule and those who favored nucleic acids. The first major breakthrough came in 1928. British scientist, Fred Griffith, learned that genetic material could be t ...
Chapter 7: Chromatin Assembly, Cohesion, and
... DNA is protected by methylation at these sites. These restriction-modification systems constitute a barrier to horizontal gene transfer that plays a role in bacterial speciation. However, for this system to operate efficiently, DNA methylation also must be linked closely to DNA replication. Some mul ...
... DNA is protected by methylation at these sites. These restriction-modification systems constitute a barrier to horizontal gene transfer that plays a role in bacterial speciation. However, for this system to operate efficiently, DNA methylation also must be linked closely to DNA replication. Some mul ...
Accepted Version - CSIRO Research Publications Repository
... studies are reporting heritable variation caused by epigenetic variation [27,28]. These epigenetic variations were categorized “obligatory”, “facilitated”, or “pure epialleles” by Richards [27]. “Obligatory” epigenetic variation is entirely dependent on DNA sequence changes, “facilitated” epigenetic ...
... studies are reporting heritable variation caused by epigenetic variation [27,28]. These epigenetic variations were categorized “obligatory”, “facilitated”, or “pure epialleles” by Richards [27]. “Obligatory” epigenetic variation is entirely dependent on DNA sequence changes, “facilitated” epigenetic ...
Generalized Transduction by Phage P22 in Salmonella typhimurium. II. Mechanisms of Integration of Transducing DNA.
... greater than 2 to 4 x IO8daltons but substantially less than 27 x lo6 daltons, the molecularweightof the transducingDNA injectedinto the bacteria.The integrated largedouble strandfragmentsof transducingDNA can be detected in DNA isolated soon after transduction, but not in DNA isolated late after tr ...
... greater than 2 to 4 x IO8daltons but substantially less than 27 x lo6 daltons, the molecularweightof the transducingDNA injectedinto the bacteria.The integrated largedouble strandfragmentsof transducingDNA can be detected in DNA isolated soon after transduction, but not in DNA isolated late after tr ...
Quick Ligation™ Kit
... The overall concentration of vector + insert should be between 1– 10 µg/ml for efficient ligation. Insert:vector ratios between 2 and 6 are optimal for single insertions. Ratios below 2:1 result in lower ligation efficiency. Ratios above 6:1 promote multiple inserts. If you are unsure of your DNA co ...
... The overall concentration of vector + insert should be between 1– 10 µg/ml for efficient ligation. Insert:vector ratios between 2 and 6 are optimal for single insertions. Ratios below 2:1 result in lower ligation efficiency. Ratios above 6:1 promote multiple inserts. If you are unsure of your DNA co ...
Phage Isolation and Investigation
... resistance and have undergone homologous recombination, but then they also will have been subsequently infected by a wild-type phage that inserted its own DNA into the host. These cells that were infected twice are not useful because they are immune to further phage infection. While testing for biof ...
... resistance and have undergone homologous recombination, but then they also will have been subsequently infected by a wild-type phage that inserted its own DNA into the host. These cells that were infected twice are not useful because they are immune to further phage infection. While testing for biof ...
Detection method - Gmoinfo
... modified carnation line 26407 (Unique identifier: IFD-26407-2). In this context, the European Union Reference Laboratory for GM Food and Feed (EU-RL GMFF) was asked to carry out a singlelaboratory validation of the performance of a polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based method for detecting and ident ...
... modified carnation line 26407 (Unique identifier: IFD-26407-2). In this context, the European Union Reference Laboratory for GM Food and Feed (EU-RL GMFF) was asked to carry out a singlelaboratory validation of the performance of a polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based method for detecting and ident ...
Product Information: Phusion U Green Multiplex PCR Master
... The recommended final primer concentration is 0.3 µM of each primer. If required, the primer concentration may be optimized in the range between 0.2 µM and 0.4 µM. Special attention to primer design parameters is critical for a successful multiplex PCR. Usually, primers of 21-34 nt length are used. ...
... The recommended final primer concentration is 0.3 µM of each primer. If required, the primer concentration may be optimized in the range between 0.2 µM and 0.4 µM. Special attention to primer design parameters is critical for a successful multiplex PCR. Usually, primers of 21-34 nt length are used. ...
Diversity of DNA methyltransferases that recognize asymmetric
... palindromic DNA sequences and add a methyl group to the target base (either adenine or cytosine) on both strands. However, there are a number of MTases that recognize asymmetric target sequences and differ in their subunit organization. In a bacterial cell, after each round of replication, the subst ...
... palindromic DNA sequences and add a methyl group to the target base (either adenine or cytosine) on both strands. However, there are a number of MTases that recognize asymmetric target sequences and differ in their subunit organization. In a bacterial cell, after each round of replication, the subst ...
Peanuts - Zymo Research
... The newly developed ZymoPURE™ Plasmid kits feature state-of-the-art technology for the simplest large-scale purification of transfection-grade plasmid DNA. Streamlined methodology avoids time-consuming steps and enables highly-concentrated plasmid DNA to be eluted directly from a microcentrifuge col ...
... The newly developed ZymoPURE™ Plasmid kits feature state-of-the-art technology for the simplest large-scale purification of transfection-grade plasmid DNA. Streamlined methodology avoids time-consuming steps and enables highly-concentrated plasmid DNA to be eluted directly from a microcentrifuge col ...
Electrophoresis Revised
... Liquid is never drawn into the barrel of the micropipette itself. An appropriate tip should always be placed firmly on the end. Since the principle by which the micropipette works is the creation of a vacuum in the tip, causing liquid to be drawn up, it is critical that the tip be on tight enough to ...
... Liquid is never drawn into the barrel of the micropipette itself. An appropriate tip should always be placed firmly on the end. Since the principle by which the micropipette works is the creation of a vacuum in the tip, causing liquid to be drawn up, it is critical that the tip be on tight enough to ...
lect 5- Cloning Vectors
... • Some plasmids encode resistance to antibiotics and are called as R plasmids. ...
... • Some plasmids encode resistance to antibiotics and are called as R plasmids. ...
Tissue-preserving approach to extracting DNA from paraffin
... extracted from tissue stored for many years. Previous approaches to DNA extraction from paraffinembedded tissue have employed either scalpel microdissection of tissue or laser capture microdissection (LCM) for very small specimens.1–6 Both techniques have the advantage of being able to separate tumo ...
... extracted from tissue stored for many years. Previous approaches to DNA extraction from paraffinembedded tissue have employed either scalpel microdissection of tissue or laser capture microdissection (LCM) for very small specimens.1–6 Both techniques have the advantage of being able to separate tumo ...
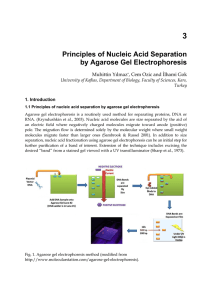
Principles of Nucleic Acid Separation by Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
... cyanol and Bromophenol blue are the two common dyes used as loading buffers and they run about the same speed as DNA fragments that are 5000 bp and 300 bp respectively. The other less frequently used progress markers are Cresol Red and Orange G which run at about 125 bp and 50 bp, respectively. If s ...
... cyanol and Bromophenol blue are the two common dyes used as loading buffers and they run about the same speed as DNA fragments that are 5000 bp and 300 bp respectively. The other less frequently used progress markers are Cresol Red and Orange G which run at about 125 bp and 50 bp, respectively. If s ...
From Gene to Protein—A Historical Perspective - AP Central
... life, and the storage and transfer of this information are necessary for life to continue. In most cases, this information is passed from parent to offspring via deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA. This double-stranded molecule provides a simple and elegant solution for the transmission of heritable info ...
... life, and the storage and transfer of this information are necessary for life to continue. In most cases, this information is passed from parent to offspring via deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA. This double-stranded molecule provides a simple and elegant solution for the transmission of heritable info ...
DNA repair

DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as UV light and radiation can cause DNA damage, resulting in as many as 1 million individual molecular lesions per cell per day. Many of these lesions cause structural damage to the DNA molecule and can alter or eliminate the cell's ability to transcribe the gene that the affected DNA encodes. Other lesions induce potentially harmful mutations in the cell's genome, which affect the survival of its daughter cells after it undergoes mitosis. As a consequence, the DNA repair process is constantly active as it responds to damage in the DNA structure. When normal repair processes fail, and when cellular apoptosis does not occur, irreparable DNA damage may occur, including double-strand breaks and DNA crosslinkages (interstrand crosslinks or ICLs).The rate of DNA repair is dependent on many factors, including the cell type, the age of the cell, and the extracellular environment. A cell that has accumulated a large amount of DNA damage, or one that no longer effectively repairs damage incurred to its DNA, can enter one of three possible states: an irreversible state of dormancy, known as senescence cell suicide, also known as apoptosis or programmed cell death unregulated cell division, which can lead to the formation of a tumor that is cancerousThe DNA repair ability of a cell is vital to the integrity of its genome and thus to the normal functionality of that organism. Many genes that were initially shown to influence life span have turned out to be involved in DNA damage repair and protection.