Gene Section RAD52 (RAD52 homolog (S. cerevisiae)) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... protects them from exonuclease resection, and facilitates end-to-end interaction (Van Dyck et al., 1999). Furthermore, capture of the second DNA end in homologous recombination appears to involve RAD52-mediated annealing of RPAssDNA strands in biochemical reactions (Sugiyama et al., 2006). Although, ...
... protects them from exonuclease resection, and facilitates end-to-end interaction (Van Dyck et al., 1999). Furthermore, capture of the second DNA end in homologous recombination appears to involve RAD52-mediated annealing of RPAssDNA strands in biochemical reactions (Sugiyama et al., 2006). Although, ...
ISOLATE II PCR and Gel Kit
... DNA fragments. The ISOLATE II PCR and Gel Kit is recommended for DNA up to 10–15kb. Longer fragments can be purified but recovery may be low and above 20kb they may be damaged by centrifugation (mechanical shearing through the membrane). Agarose gel extraction Although TBE agarose gels can be used w ...
... DNA fragments. The ISOLATE II PCR and Gel Kit is recommended for DNA up to 10–15kb. Longer fragments can be purified but recovery may be low and above 20kb they may be damaged by centrifugation (mechanical shearing through the membrane). Agarose gel extraction Although TBE agarose gels can be used w ...
Using a Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism to Predict
... Bitter-tasting compounds are recognized by receptor proteins on the surface of taste cells. There are approximately 30 genes for different bitter taste receptors in mammals. The gene for the PTC taste receptor, TAS2R38, was identified in 2003. Sequencing identified three nucleotide ...
... Bitter-tasting compounds are recognized by receptor proteins on the surface of taste cells. There are approximately 30 genes for different bitter taste receptors in mammals. The gene for the PTC taste receptor, TAS2R38, was identified in 2003. Sequencing identified three nucleotide ...
A novel DNA modification by sulphur
... phosphoadenosine phosphosulphate (PAPS) reductaserelated protein in Pyrococcus abyssi and the same family of proteins from many other bacteria. Both enzymes are involved in sulphate reduction for the biosynthesis of sulphur-containing compounds such as cysteine by many microorganisms. ATP sulphuryla ...
... phosphoadenosine phosphosulphate (PAPS) reductaserelated protein in Pyrococcus abyssi and the same family of proteins from many other bacteria. Both enzymes are involved in sulphate reduction for the biosynthesis of sulphur-containing compounds such as cysteine by many microorganisms. ATP sulphuryla ...
The legal, social and ethical controversy of the collection and
... gain employment such as in early childhood [4, p.5], or during the process of adoption or other security clearance requirements. ...
... gain employment such as in early childhood [4, p.5], or during the process of adoption or other security clearance requirements. ...
A-2015A: Amplified Fragment Length
... 0.625 µM of each primer was the optimum concentration (Figure 2). Varying the amount of MseI primer appeared to have no effect on fragment numbers, size, or distribution (Figure 3). When the D4 (Beckman Coulter, Inc.) dye-labeled EcoRI primer was held at a constant concentration and the unlabeled Ms ...
... 0.625 µM of each primer was the optimum concentration (Figure 2). Varying the amount of MseI primer appeared to have no effect on fragment numbers, size, or distribution (Figure 3). When the D4 (Beckman Coulter, Inc.) dye-labeled EcoRI primer was held at a constant concentration and the unlabeled Ms ...
Chapter 2 - Institut Montefiore
... DNA: the master molecule of every cell It contains vital information that gets passed on to each successive generation. It coordinates the making of itself as well as other molecules (proteins). If it is changed slightly, serious consequences may result. If it is destroyed beyond repair, the cell ...
... DNA: the master molecule of every cell It contains vital information that gets passed on to each successive generation. It coordinates the making of itself as well as other molecules (proteins). If it is changed slightly, serious consequences may result. If it is destroyed beyond repair, the cell ...
Genetic dissection of Helicobacter pylori AddAB role in homologous
... of the damage, they could partially complement each other. Unlike what was shown for E. coli (Lloyd et al., 1988), the inactivation of RecOR in H. pylori has a more dramatic effect on UV survival than the inactivation of AddAB (RecBCD in E. coli). A different picture emerges from the analysis of the ...
... of the damage, they could partially complement each other. Unlike what was shown for E. coli (Lloyd et al., 1988), the inactivation of RecOR in H. pylori has a more dramatic effect on UV survival than the inactivation of AddAB (RecBCD in E. coli). A different picture emerges from the analysis of the ...
molecular biology
... always an integer. It is positive for right handed DNA and negative for left handed DNA. Linking number does not vary when double stranded DNA is twisted or deformed in any way as long as both DNA strands remain intact. The linking number can be changed by ±1 by breaking one DNA strand, rotating one ...
... always an integer. It is positive for right handed DNA and negative for left handed DNA. Linking number does not vary when double stranded DNA is twisted or deformed in any way as long as both DNA strands remain intact. The linking number can be changed by ±1 by breaking one DNA strand, rotating one ...
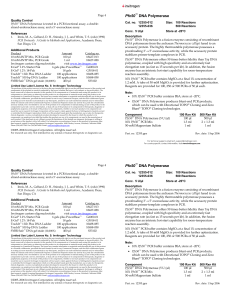
Pfx50™ DNA Polymerase - Thermo Fisher Scientific
... DNA polymerase from the archaean Thermococcus zilligii fused to an accessory protein. The highly thermostable polymerase possesses a proofreading 3’→ 5’ exonuclease activity, while the accessory protein stabilizes primer-template complexes in PCR. Pfx50™ DNA Polymerase offers 50 times better fidelit ...
... DNA polymerase from the archaean Thermococcus zilligii fused to an accessory protein. The highly thermostable polymerase possesses a proofreading 3’→ 5’ exonuclease activity, while the accessory protein stabilizes primer-template complexes in PCR. Pfx50™ DNA Polymerase offers 50 times better fidelit ...
RecA maintains the integrity of chloroplast DNA molecules in
... Fig. 2. The effect of a T-DNA insertion in cpRecA on cpDNA amount and structure. (A) PFGE of cpDNA obtained from an equal volume of pelleted chloroplasts from wt and cprecA mutant plants after staining with ethidium bromide. (B) Blot hybridization of the gel in (A) with a petA probe. Immature, entir ...
... Fig. 2. The effect of a T-DNA insertion in cpRecA on cpDNA amount and structure. (A) PFGE of cpDNA obtained from an equal volume of pelleted chloroplasts from wt and cprecA mutant plants after staining with ethidium bromide. (B) Blot hybridization of the gel in (A) with a petA probe. Immature, entir ...
A novel assay for examining the molecular
... continued elongation. In rolling circle replication, the normal mechanism for termination of SV40 replication does not occur and the elongation phase of replication is prolonged. Thus, using this assay system, elongation phase reactions can be examined in the absence of initiation or termination. We ...
... continued elongation. In rolling circle replication, the normal mechanism for termination of SV40 replication does not occur and the elongation phase of replication is prolonged. Thus, using this assay system, elongation phase reactions can be examined in the absence of initiation or termination. We ...
DNA SEQUENCING (using a Li
... If the fragment is short, and the sequence desired is close to the 5' end of that fragment, then the run time will be short (1-2 h). If the fragment is long, and the desired sequence is closer to the 3' end, then the run time will be longer (2-5 h). The other method of sequencing DNA (Sanger 1977) u ...
... If the fragment is short, and the sequence desired is close to the 5' end of that fragment, then the run time will be short (1-2 h). If the fragment is long, and the desired sequence is closer to the 3' end, then the run time will be longer (2-5 h). The other method of sequencing DNA (Sanger 1977) u ...
The Mechanism of Insertion of a Segment of
... Haldenwang et al. (1980) constructed the plasmid p1949 in three stages, the net result being the union of pMB9 (TcR, 3.55 MDal) that had been linearized with HpaI, and pC194 (CmR, 2-0 MDal) that had been linearized with HpaII. As expected, the resultant chimaera is unable to transform B. subtilis to ...
... Haldenwang et al. (1980) constructed the plasmid p1949 in three stages, the net result being the union of pMB9 (TcR, 3.55 MDal) that had been linearized with HpaI, and pC194 (CmR, 2-0 MDal) that had been linearized with HpaII. As expected, the resultant chimaera is unable to transform B. subtilis to ...
Extraction of DNA from soil
... Ecological and molecular PCR-based studies require extensive purification of nucleic acids extracts in order to remove humic acids and other contaminants. DNA losses during extensive purification may compromise the detection of rare DNA sequences. Jacobsen [27] successfully removed the PCR-inhibitor ...
... Ecological and molecular PCR-based studies require extensive purification of nucleic acids extracts in order to remove humic acids and other contaminants. DNA losses during extensive purification may compromise the detection of rare DNA sequences. Jacobsen [27] successfully removed the PCR-inhibitor ...
Bacterial Systems for Testing Spontaneous and
... (Wójcik et al., 1996; Wójcik & Janion, unpublished data; Nowosielska & Grzesiuk, 2000) or dnaQ (Nowosielska et al. 2004a; 2004b). MutT, MutY and Fpg (MutM), proteins belonging to the GO system, defend bacteria against the mutagenic action of 8-oxoG in DNA. MutT is a pyrophosphatase that hydrolyses 8 ...
... (Wójcik et al., 1996; Wójcik & Janion, unpublished data; Nowosielska & Grzesiuk, 2000) or dnaQ (Nowosielska et al. 2004a; 2004b). MutT, MutY and Fpg (MutM), proteins belonging to the GO system, defend bacteria against the mutagenic action of 8-oxoG in DNA. MutT is a pyrophosphatase that hydrolyses 8 ...
Drug-specific Sites of Topoisomerase II DNA
... satellite III DNA and the histone gene cluster) since their chromatin structures have been well characterized (see below); thus, the results may provide significant information on enzyme and drug activities also in human malignant cells. Our analysis has been focused on VM-26, dh-EPI (a potent doxor ...
... satellite III DNA and the histone gene cluster) since their chromatin structures have been well characterized (see below); thus, the results may provide significant information on enzyme and drug activities also in human malignant cells. Our analysis has been focused on VM-26, dh-EPI (a potent doxor ...
Chapter 6: DNA Replication and Telomere Maintenance I
... 1. It is important before cell division that the whole genome (all DNA) is replicated ...
... 1. It is important before cell division that the whole genome (all DNA) is replicated ...
Lecture 19 POWERPOINT here
... • One can use the techniques of cell biology to manufacture artificial and real products, be they genes, proteins, or organisms • If you want to insert some DNA into another molecule then the best place to start is to use the same restriction enzyme to cut both - so they have the same ends. ...
... • One can use the techniques of cell biology to manufacture artificial and real products, be they genes, proteins, or organisms • If you want to insert some DNA into another molecule then the best place to start is to use the same restriction enzyme to cut both - so they have the same ends. ...
DNA repair pathways and the effect of radiotherapy in breast cancer
... factors have been identified. A major risk factor is the cumulative exposure of breast tissue to ovarian hormones such as oestrogens. Early age at menarche, high age at menopause, and hormone-replacement therapy (HRT) in postmenopausal women, all increase the risk of breast cancer by prolonging the ...
... factors have been identified. A major risk factor is the cumulative exposure of breast tissue to ovarian hormones such as oestrogens. Early age at menarche, high age at menopause, and hormone-replacement therapy (HRT) in postmenopausal women, all increase the risk of breast cancer by prolonging the ...
Articles (Danaher) ) , short, fluorescently
... one TPLFN reaction mixture was introduced to the sample. We loaded 1-µm polystyrene beads into some of the microreactors (not visible in the fluorescence images) each with ~5,000 copies of immobilized DNA template. Each of the beads was decorated with one of four different DNA oligo test sequences ( ...
... one TPLFN reaction mixture was introduced to the sample. We loaded 1-µm polystyrene beads into some of the microreactors (not visible in the fluorescence images) each with ~5,000 copies of immobilized DNA template. Each of the beads was decorated with one of four different DNA oligo test sequences ( ...
PcrA Helicase Tightly Couples ATP Hydrolysis to Unwinding Double
... the duplex separation around the plasmid. In contrast, the lagging strand synthesis is initiated from a separate singlestranded origin, which only becomes available once the duplex separation has gone past this origin (12). The plasmid dso sequence has several inverted complementary repeats (ICRs) i ...
... the duplex separation around the plasmid. In contrast, the lagging strand synthesis is initiated from a separate singlestranded origin, which only becomes available once the duplex separation has gone past this origin (12). The plasmid dso sequence has several inverted complementary repeats (ICRs) i ...
Chpt2_Struc_Nucleic_Acids.doc
... mice (Fig. 2.1.A.). Smooth (S) strains produce a capsular polysaccharide on their surface, which allow the Pneumococi to escape destruction by the mouse, and the infection proceeds, i.e. they are virulent. This polysaccaride can be type I, II, or III. Virulent S strains can be killed by heat (i.e., ...
... mice (Fig. 2.1.A.). Smooth (S) strains produce a capsular polysaccharide on their surface, which allow the Pneumococi to escape destruction by the mouse, and the infection proceeds, i.e. they are virulent. This polysaccaride can be type I, II, or III. Virulent S strains can be killed by heat (i.e., ...
A simplified subtractive hybridization protocol used to isolate DNA
... were designated citrus variegated chlorosis (CVC) and coffee leaf scald, respectively. A rapid dissemination of CVC is occurring in the major citrus-growing areas in Brazil, with associated large economic losses. The extent of the damage in coffee plants is still undetermined. Highly sensitive and r ...
... were designated citrus variegated chlorosis (CVC) and coffee leaf scald, respectively. A rapid dissemination of CVC is occurring in the major citrus-growing areas in Brazil, with associated large economic losses. The extent of the damage in coffee plants is still undetermined. Highly sensitive and r ...
DNA repair

DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as UV light and radiation can cause DNA damage, resulting in as many as 1 million individual molecular lesions per cell per day. Many of these lesions cause structural damage to the DNA molecule and can alter or eliminate the cell's ability to transcribe the gene that the affected DNA encodes. Other lesions induce potentially harmful mutations in the cell's genome, which affect the survival of its daughter cells after it undergoes mitosis. As a consequence, the DNA repair process is constantly active as it responds to damage in the DNA structure. When normal repair processes fail, and when cellular apoptosis does not occur, irreparable DNA damage may occur, including double-strand breaks and DNA crosslinkages (interstrand crosslinks or ICLs).The rate of DNA repair is dependent on many factors, including the cell type, the age of the cell, and the extracellular environment. A cell that has accumulated a large amount of DNA damage, or one that no longer effectively repairs damage incurred to its DNA, can enter one of three possible states: an irreversible state of dormancy, known as senescence cell suicide, also known as apoptosis or programmed cell death unregulated cell division, which can lead to the formation of a tumor that is cancerousThe DNA repair ability of a cell is vital to the integrity of its genome and thus to the normal functionality of that organism. Many genes that were initially shown to influence life span have turned out to be involved in DNA damage repair and protection.