Document
... 2. You are hired as a scientific consultant for a popular television show about forensic analysis of crime scene evidence. You are told that in an upcoming scene, investigators will compare the DNA profiles of a known suspect and an unknown biological sample collected from the victim. You are asked ...
... 2. You are hired as a scientific consultant for a popular television show about forensic analysis of crime scene evidence. You are told that in an upcoming scene, investigators will compare the DNA profiles of a known suspect and an unknown biological sample collected from the victim. You are asked ...
Answers
... transcriptase surrounded by a bilayer envelope made from host membranes (EX: HIV) Viral DNA that is incorporated into host DNA during the lysogenic life cycle Enzyme found in RNA viruses that catalyzes the production of DNA from an RNA template Small pieces complementary to DNA used to start the str ...
... transcriptase surrounded by a bilayer envelope made from host membranes (EX: HIV) Viral DNA that is incorporated into host DNA during the lysogenic life cycle Enzyme found in RNA viruses that catalyzes the production of DNA from an RNA template Small pieces complementary to DNA used to start the str ...
DNA Lecture #1: DNA Structure and Proof That DNA Controls Traits
... amount of Adenine = Thymine Cytosine = Guanine 1953: Watson and Crick discover the double helix structure of DNA, where 2 strands wind around each other ...
... amount of Adenine = Thymine Cytosine = Guanine 1953: Watson and Crick discover the double helix structure of DNA, where 2 strands wind around each other ...
Word document
... What are the uses of DNA profiling ? What are the conditions under which genetic markers are most useful in determining a suspect’s guilt ? Clue: the relative frequency of the genetic markers in the suspect is important here. Does the state of Arizona produce DNA data from suspects that can be uplo ...
... What are the uses of DNA profiling ? What are the conditions under which genetic markers are most useful in determining a suspect’s guilt ? Clue: the relative frequency of the genetic markers in the suspect is important here. Does the state of Arizona produce DNA data from suspects that can be uplo ...
DNA
... *NEVER leaves the nucleus. *is passed from one generation to the next in chromosomes. *looks like a ladder, twisted around itself, called a double helix DNA Timeline Facts… Early 1950’s o 1st picture of DNA taken by Rosalind Franklin using an X-ray machine. ...
... *NEVER leaves the nucleus. *is passed from one generation to the next in chromosomes. *looks like a ladder, twisted around itself, called a double helix DNA Timeline Facts… Early 1950’s o 1st picture of DNA taken by Rosalind Franklin using an X-ray machine. ...
DNA Modeling
... a. separate the left and right sides leaving a space of about 6-8 inches between. b. use the remaining nucleotides to complete the molecule using the left side as the base to match with. c. build a second DNA model by adding new nucleotides to the right half of the original piece of the molecule. d. ...
... a. separate the left and right sides leaving a space of about 6-8 inches between. b. use the remaining nucleotides to complete the molecule using the left side as the base to match with. c. build a second DNA model by adding new nucleotides to the right half of the original piece of the molecule. d. ...
18 Things You Should Know About Genetics
... (6)The STEPS of the DNA ladder are made from 4 chemical bases; adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine. (7)The particular ORDER of the bases determines the species of the organism as well as its characteristics. (8)The SIDES of the DNA ladder are composed of alternating sugar and phosphate groups. ( ...
... (6)The STEPS of the DNA ladder are made from 4 chemical bases; adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine. (7)The particular ORDER of the bases determines the species of the organism as well as its characteristics. (8)The SIDES of the DNA ladder are composed of alternating sugar and phosphate groups. ( ...
Unit 8 Test Review Answers do not have to be in complete
... Unit 8 Test Review Answers do not have to be in complete sentences but must be complete. 1. What is transformation as it relates to Griffith’s experiment? 2. What were Avery’s findings? 3. What is a bacteriophage? 4. How did radioactive markers prove that DNA was the genetic material in Hershey and ...
... Unit 8 Test Review Answers do not have to be in complete sentences but must be complete. 1. What is transformation as it relates to Griffith’s experiment? 2. What were Avery’s findings? 3. What is a bacteriophage? 4. How did radioactive markers prove that DNA was the genetic material in Hershey and ...
Name Ch 12 Study Guide
... 10) Assume that the two parent strands of DNA have been separated and that the base sequence on one parent strand is A-T-T-C-G-C; the base sequence that will complement that parent strand is __________________________________________ 11) Who was Rosalind Franklin? 12) What was her contribution to th ...
... 10) Assume that the two parent strands of DNA have been separated and that the base sequence on one parent strand is A-T-T-C-G-C; the base sequence that will complement that parent strand is __________________________________________ 11) Who was Rosalind Franklin? 12) What was her contribution to th ...
nitrogen bases
... 1. Label boxes a-d using the terms: Nitrogen base, Nucleotide, Deoxyribose (sugar), and Phosphate. Use your DNA Guided Notes. c. Deoxyribose (Sugar) a. Nitrogen base ...
... 1. Label boxes a-d using the terms: Nitrogen base, Nucleotide, Deoxyribose (sugar), and Phosphate. Use your DNA Guided Notes. c. Deoxyribose (Sugar) a. Nitrogen base ...
Test Study Guide
... 4. What are the 3 essential functions of DNA (In the text, they compared this to a book)? 5. DNA is a _________________________ made up of many small repeating units called ________________________. ...
... 4. What are the 3 essential functions of DNA (In the text, they compared this to a book)? 5. DNA is a _________________________ made up of many small repeating units called ________________________. ...
L16.3 Assessment
... b. A guanine DNA nucleotide to a cytosine DNA nucleotide c. A cytosine DNA nucleotide to an adenine DNA nucleotide Which of the following is NOT part of a DNA molecule? a. Nitrogen base b. Deoxyribose sugar c. Phosphate group d. Ribose sugar DNA replication results in two DNA molecules, a. Each with ...
... b. A guanine DNA nucleotide to a cytosine DNA nucleotide c. A cytosine DNA nucleotide to an adenine DNA nucleotide Which of the following is NOT part of a DNA molecule? a. Nitrogen base b. Deoxyribose sugar c. Phosphate group d. Ribose sugar DNA replication results in two DNA molecules, a. Each with ...
dna-discovery - WordPress.com
... • scientists worked for over 100 years before DNA was confirmed to be the hereditary material for all life Late 1869 • Fredrich Miescher isolated nonprotein substance from the nucleus of pus cells • he noted that a phosphorus rich substance was present and it did not behave like a protein (at the ti ...
... • scientists worked for over 100 years before DNA was confirmed to be the hereditary material for all life Late 1869 • Fredrich Miescher isolated nonprotein substance from the nucleus of pus cells • he noted that a phosphorus rich substance was present and it did not behave like a protein (at the ti ...
DNA Pre-Test
... specifies its traits, that this hereditary information (DNA) contains genes located in the chromosomes of each cell, and that heredity is the passage of these instructions from one generation to another. 1. Chromosomes are located in the _________ of the cell. A. Cell wall B. Cytoplasm C. Mitoch ...
... specifies its traits, that this hereditary information (DNA) contains genes located in the chromosomes of each cell, and that heredity is the passage of these instructions from one generation to another. 1. Chromosomes are located in the _________ of the cell. A. Cell wall B. Cytoplasm C. Mitoch ...
DNA Quiz Review
... DNA Quiz Review 1. Write out the full name for DNA. 2. What is a gene? 3. Where in the cell are chromosomes located? 4. DNA can be found in what organelles in the cell? 5. What two scientists established the structure of DNA? Word Bank ...
... DNA Quiz Review 1. Write out the full name for DNA. 2. What is a gene? 3. Where in the cell are chromosomes located? 4. DNA can be found in what organelles in the cell? 5. What two scientists established the structure of DNA? Word Bank ...
Visualizing DNA
... moving through the gel than smaller fragments. Thus, larger fragments will move slower than smaller fragments. This allows separation of all different sizes of DNA fragments. ...
... moving through the gel than smaller fragments. Thus, larger fragments will move slower than smaller fragments. This allows separation of all different sizes of DNA fragments. ...
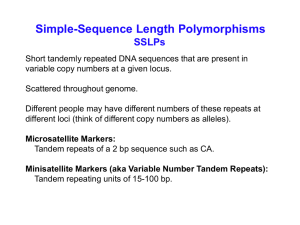
Using microsatellites as molecular markers
... Depending on number of microsatellite repeats, will get different lengths PCR products (many different possible alleles, not just two) ...
... Depending on number of microsatellite repeats, will get different lengths PCR products (many different possible alleles, not just two) ...
DNA notes
... proteins and is the blueprint for life. • The same DNA is found in all cells in your body (sex cells have half of the DNA)! • Only certain parts of the DNA molecule are read and used in each cell type. ...
... proteins and is the blueprint for life. • The same DNA is found in all cells in your body (sex cells have half of the DNA)! • Only certain parts of the DNA molecule are read and used in each cell type. ...
ap: chapter 16: the molecular basis of inheritance
... 1. After Morgan and fellow scientists developed the Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance, the search was on for the chemical mechanism of inheritance. What are the two components of the chromosome? __________________________________________________________________________ 2. From initial logic, which c ...
... 1. After Morgan and fellow scientists developed the Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance, the search was on for the chemical mechanism of inheritance. What are the two components of the chromosome? __________________________________________________________________________ 2. From initial logic, which c ...
DNA profiling

DNA profiling (also called DNA fingerprinting, DNA testing, or DNA typing) is a forensic technique used to identify individuals by characteristics of their DNA. A DNA profile is a small set of DNA variations that is very likely to be different in all unrelated individuals, thereby being as unique to individuals as are fingerprints (hence the alternate name for the technique). DNA profiling should not be confused with full genome sequencing. First developed and used in 1985, DNA profiling is used in, for example, parentage testing and criminal investigation, to identify a person or to place a person at a crime scene, techniques which are now employed globally in forensic science to facilitate police detective work and help clarify paternity and immigration disputes.Although 99.9% of human DNA sequences are the same in every person, enough of the DNA is different that it is possible to distinguish one individual from another, unless they are monozygotic (""identical"") twins. DNA profiling uses repetitive (""repeat"") sequences that are highly variable, called variable number tandem repeats (VNTRs), in particular short tandem repeats (STRs). VNTR loci are very similar between closely related humans, but are so variable that unrelated individuals are extremely unlikely to have the same VNTRs.The DNA profiling technique nowadays used is based on technology developed in 1988.