Mighty Miniscule DNA
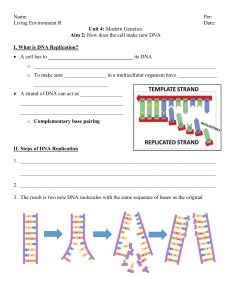
... cell contains a nucleus which is filled with the directions for cell function, called DNA. ...
... cell contains a nucleus which is filled with the directions for cell function, called DNA. ...
Activity 3.1
... 3.1.1 What is DNA? There are a lot of sources on DNA to find on the internet. An important source for information is a guide developed by the European Initiative for Biotechnology Education. Your teacher can give you (part of) the guide that this organization has developed. You can also download it ...
... 3.1.1 What is DNA? There are a lot of sources on DNA to find on the internet. An important source for information is a guide developed by the European Initiative for Biotechnology Education. Your teacher can give you (part of) the guide that this organization has developed. You can also download it ...
Genetic Engineering - Duplin County Schools
... Applications of Genetic Engineering • Transgenic Organisms – Contain genes from other organisms – Usually bacteria because they reproduce rapidly and are easy to grow. ...
... Applications of Genetic Engineering • Transgenic Organisms – Contain genes from other organisms – Usually bacteria because they reproduce rapidly and are easy to grow. ...
No Slide Title
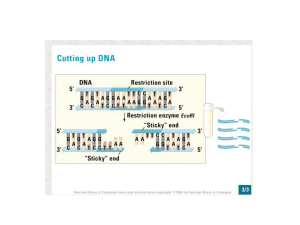
... Restriction Enzymes • Restriction enzymes cut DNA from any source into fragments • Sticky ends can pair up with complementary DNA with the help of ligase producing recombinant DNA • Example: EcoRI, HindII ...
... Restriction Enzymes • Restriction enzymes cut DNA from any source into fragments • Sticky ends can pair up with complementary DNA with the help of ligase producing recombinant DNA • Example: EcoRI, HindII ...
3.5 Genetic Modification and Biotechnology
... Gene transfer to bacteria using plasmids makes use of restriction endonucleases and DNA ligase. Assessment of the potential risks and benefits associated with genetic modification of crops. Analysis of data on risks to monarch butterflies of Bt crops. ...
... Gene transfer to bacteria using plasmids makes use of restriction endonucleases and DNA ligase. Assessment of the potential risks and benefits associated with genetic modification of crops. Analysis of data on risks to monarch butterflies of Bt crops. ...
DNA, Genes and Chromosomes
... is all the genetic information inside humans and almost all other organisms. ...
... is all the genetic information inside humans and almost all other organisms. ...
12.1 Identifying the Substance of Genes
... Chapter 12 Section 1: Identifying the Substance of Genes ...
... Chapter 12 Section 1: Identifying the Substance of Genes ...
DNA Fingerprinting
... III. Why isn’t it used in all cases? A. Sometimes no DNA is found at the scene B. Suspects are starting to take steps to prevent leaving any C. DNA can be washed away or ...
... III. Why isn’t it used in all cases? A. Sometimes no DNA is found at the scene B. Suspects are starting to take steps to prevent leaving any C. DNA can be washed away or ...
DNA profiling

DNA profiling (also called DNA fingerprinting, DNA testing, or DNA typing) is a forensic technique used to identify individuals by characteristics of their DNA. A DNA profile is a small set of DNA variations that is very likely to be different in all unrelated individuals, thereby being as unique to individuals as are fingerprints (hence the alternate name for the technique). DNA profiling should not be confused with full genome sequencing. First developed and used in 1985, DNA profiling is used in, for example, parentage testing and criminal investigation, to identify a person or to place a person at a crime scene, techniques which are now employed globally in forensic science to facilitate police detective work and help clarify paternity and immigration disputes.Although 99.9% of human DNA sequences are the same in every person, enough of the DNA is different that it is possible to distinguish one individual from another, unless they are monozygotic (""identical"") twins. DNA profiling uses repetitive (""repeat"") sequences that are highly variable, called variable number tandem repeats (VNTRs), in particular short tandem repeats (STRs). VNTR loci are very similar between closely related humans, but are so variable that unrelated individuals are extremely unlikely to have the same VNTRs.The DNA profiling technique nowadays used is based on technology developed in 1988.