DOC
... 6. What is the specific role of exonuclease-1 in this type of DNA repair? That is, which step does it accomplish? After a mismatch is identified and a nick introduced, EXO1 cuts out a section of the DNA strand containing the mismatched base. 7. How do E. coli distinguish between parental and newly r ...
... 6. What is the specific role of exonuclease-1 in this type of DNA repair? That is, which step does it accomplish? After a mismatch is identified and a nick introduced, EXO1 cuts out a section of the DNA strand containing the mismatched base. 7. How do E. coli distinguish between parental and newly r ...
Conservative replication
... 2. The 15N become integrated into the bases, making the DNA in the bacteria heavier. 3. The bacteria grown with 15N was then moved into a medium with 14N. 4. Samples of bacteria were periodically taken out. 5. The DNA in these samples was extracted. ...
... 2. The 15N become integrated into the bases, making the DNA in the bacteria heavier. 3. The bacteria grown with 15N was then moved into a medium with 14N. 4. Samples of bacteria were periodically taken out. 5. The DNA in these samples was extracted. ...
Biology 101 Lecture Quiz #12 Name
... Note: Lettered selections on the right side might be used more than one time (or not at all) as answers for questions or descriptions on the left. ...
... Note: Lettered selections on the right side might be used more than one time (or not at all) as answers for questions or descriptions on the left. ...
AP Bio Ch 17 The Molecular Basis of Disease This chapter is only
... to know about finding out DNA is the molecule of heredity and how it replicates. p.294 1. Give the proper definition of transformation –this is the term used when a plasmid is put into a bacteria. p.295 2. What kind of microscope got the shot in Figure 16-3? p.296 3.What do the 5’ ( 5 prime) and 3’ ...
... to know about finding out DNA is the molecule of heredity and how it replicates. p.294 1. Give the proper definition of transformation –this is the term used when a plasmid is put into a bacteria. p.295 2. What kind of microscope got the shot in Figure 16-3? p.296 3.What do the 5’ ( 5 prime) and 3’ ...
Genetics - California Science Teacher
... 16. Process in which naked DNA is taken up by bacterial or yeast cell 17. Process in which RNA is produced by using a DNA template. 18. Process that results in the production of cDNA from an RNA molecule. 19. Process in which DNA is produced by using a DNA template ...
... 16. Process in which naked DNA is taken up by bacterial or yeast cell 17. Process in which RNA is produced by using a DNA template. 18. Process that results in the production of cDNA from an RNA molecule. 19. Process in which DNA is produced by using a DNA template ...
Practice Question for Replication, Genetics and Biotechnology
... 32. codominant or incomplete dominance._______________ 33. A cross that studies the inheritance of two traits is known as ...
... 32. codominant or incomplete dominance._______________ 33. A cross that studies the inheritance of two traits is known as ...
IV.D.3 ISOLATION OF DNA FRAGMENTS FROM
... ISOLATION OF DNA FRAGMENTS FROM POLYACRYLAMIDE GELS "crush and soak" method ...
... ISOLATION OF DNA FRAGMENTS FROM POLYACRYLAMIDE GELS "crush and soak" method ...
Prepare for gel electrophoresis
... from your mother! Many studies use this DNA to determine how closely related different species of organisms are! ...
... from your mother! Many studies use this DNA to determine how closely related different species of organisms are! ...
Gel Electrophoresis DNA Fingerprinting
... • How are DNA molecules analyzed. • Restriction enzyme digestion of DNA molecules. • Gel electrophoresis to separate DNA fragments of different sizes. ...
... • How are DNA molecules analyzed. • Restriction enzyme digestion of DNA molecules. • Gel electrophoresis to separate DNA fragments of different sizes. ...
Topic 12 DNA - Ms. Mogck`s Classroom
... • Maurice Wilkins showed her work to Watson and Crick without her knowledge ...
... • Maurice Wilkins showed her work to Watson and Crick without her knowledge ...
Coloring DNA
... 9. What sugar is found in DNA? _______________________ In RNA? ____________________ 10. How do the bases bond together? A bonds with _____ ...
... 9. What sugar is found in DNA? _______________________ In RNA? ____________________ 10. How do the bases bond together? A bonds with _____ ...
Genetic Engineering Paper Exercise
... Genetic Engineering Paper Exercise You are provided with 2 DNA ‘samples’ Yellow = Human DNA Cut out the two strips that make up the human DNA and stick them together to make linear ‘DNA’. Stick tabs 1 and 2 together using the sticky labels. Green = Bacterial plasmid DNA. Join the tabs using the stic ...
... Genetic Engineering Paper Exercise You are provided with 2 DNA ‘samples’ Yellow = Human DNA Cut out the two strips that make up the human DNA and stick them together to make linear ‘DNA’. Stick tabs 1 and 2 together using the sticky labels. Green = Bacterial plasmid DNA. Join the tabs using the stic ...
DNA structure and function
... DNA Structure and Purpose • In simplest terms, DNA is a blueprint for life. • It is made up of genes which hold the information for making proteins within the cell – Proteins in turn help make up everything in your body! ...
... DNA Structure and Purpose • In simplest terms, DNA is a blueprint for life. • It is made up of genes which hold the information for making proteins within the cell – Proteins in turn help make up everything in your body! ...
How hair can reveal a history
... technique and I’ve got a cold case from 1976. Do you think it will help?’” says Isoforensics President Lesley Chesson. ■ ...
... technique and I’ve got a cold case from 1976. Do you think it will help?’” says Isoforensics President Lesley Chesson. ■ ...
Study Guide Chap 6: DNA
... constructed models of the structure of DNA and used Franklin’s data to correctly identify the structure of DNA as a double helix.___________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 2. _DNA_____ has a ...
... constructed models of the structure of DNA and used Franklin’s data to correctly identify the structure of DNA as a double helix.___________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 2. _DNA_____ has a ...
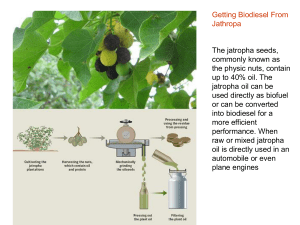
Jatropha genotyping In Gh Pu QR In Gh Pu QR 13 primer pairs
... commonly known as the physic nuts, contain up to 40% oil. The jatropha oil can be used directly as biofuel or can be converted into biodiesel for a more efficient performance. When raw or mixed jatropha oil is directly used in an automobile or even plane engines ...
... commonly known as the physic nuts, contain up to 40% oil. The jatropha oil can be used directly as biofuel or can be converted into biodiesel for a more efficient performance. When raw or mixed jatropha oil is directly used in an automobile or even plane engines ...
Genetic Engineering Guied Notes
... 3. If host and foreign DNA have been cleaved by the same restriction enzyme, the ends can _ join_ together. 4. Gene cloning occurs- this cell continues to divide by __mitosis___ and __meiosis_____ this new foreign DNA (gene) as if it were its own ...
... 3. If host and foreign DNA have been cleaved by the same restriction enzyme, the ends can _ join_ together. 4. Gene cloning occurs- this cell continues to divide by __mitosis___ and __meiosis_____ this new foreign DNA (gene) as if it were its own ...
Genetic Engineering (and other cool molecular biology techniques)
... PCR (polymerase chain reaction) • Specific sequence of DNA is amplified (copied many times) • Requires: – DNA template (contains your gene of interest) – Tac polymerase (a DNA polymerase that can work at high temperatures) – Nucleotides (to synthesize new DNA) – Primers (specific to the gene of int ...
... PCR (polymerase chain reaction) • Specific sequence of DNA is amplified (copied many times) • Requires: – DNA template (contains your gene of interest) – Tac polymerase (a DNA polymerase that can work at high temperatures) – Nucleotides (to synthesize new DNA) – Primers (specific to the gene of int ...
Human Energy - The Assumptions
... of the most important lectures you attend all year. Namaste, James Taylor ...
... of the most important lectures you attend all year. Namaste, James Taylor ...
molecular genetics unit review
... iii. DNA mRNA polypeptide/protein (know how to transcribe DNA and translate mRNA if given a sequence) What are the four ways gene expression is controlled? What is an operon? Describe/explain the 2 main operons (lac, trp) in prokaryotic cells. a) What are mutations? b) What are the different typ ...
... iii. DNA mRNA polypeptide/protein (know how to transcribe DNA and translate mRNA if given a sequence) What are the four ways gene expression is controlled? What is an operon? Describe/explain the 2 main operons (lac, trp) in prokaryotic cells. a) What are mutations? b) What are the different typ ...
LEQ: How do we splice new genes into DNA?
... end of the gel; apply current; negative DNA is pulled to the positive end; smaller pieces travel farther faster; DNA fragments are separated based on the size of the fragment (# of base pairs). ...
... end of the gel; apply current; negative DNA is pulled to the positive end; smaller pieces travel farther faster; DNA fragments are separated based on the size of the fragment (# of base pairs). ...
25/100 bp Mixed DNA Ladder DNA Molecular Weight Markers
... ● Description : 25/100 bp Mixed DNA Ladder is specially designed for determining the size of double strand DNA from 25 to 2,000 base pairs. The DNA Ladder consists of 17 double strand DNA fragments ranging in size from 25 to 200 bp in 25 bp increments, and additional fragments of 300, 400, 500, 600, ...
... ● Description : 25/100 bp Mixed DNA Ladder is specially designed for determining the size of double strand DNA from 25 to 2,000 base pairs. The DNA Ladder consists of 17 double strand DNA fragments ranging in size from 25 to 200 bp in 25 bp increments, and additional fragments of 300, 400, 500, 600, ...
DNA profiling

DNA profiling (also called DNA fingerprinting, DNA testing, or DNA typing) is a forensic technique used to identify individuals by characteristics of their DNA. A DNA profile is a small set of DNA variations that is very likely to be different in all unrelated individuals, thereby being as unique to individuals as are fingerprints (hence the alternate name for the technique). DNA profiling should not be confused with full genome sequencing. First developed and used in 1985, DNA profiling is used in, for example, parentage testing and criminal investigation, to identify a person or to place a person at a crime scene, techniques which are now employed globally in forensic science to facilitate police detective work and help clarify paternity and immigration disputes.Although 99.9% of human DNA sequences are the same in every person, enough of the DNA is different that it is possible to distinguish one individual from another, unless they are monozygotic (""identical"") twins. DNA profiling uses repetitive (""repeat"") sequences that are highly variable, called variable number tandem repeats (VNTRs), in particular short tandem repeats (STRs). VNTR loci are very similar between closely related humans, but are so variable that unrelated individuals are extremely unlikely to have the same VNTRs.The DNA profiling technique nowadays used is based on technology developed in 1988.