Lecture 1 Introduction to recombinant DNA Technology
... What is a genetic engineering? • Set of techniques by which one can deliberately insert new piece/s of DNA into the existing DNA piece to modify the characters of an organism. ...
... What is a genetic engineering? • Set of techniques by which one can deliberately insert new piece/s of DNA into the existing DNA piece to modify the characters of an organism. ...
InfoTrac
... Retinome predicts eye cooler if the sample is 50 percent or greater European ancestry as to whether eye color is blue, mostly blue, brown or mostly brown. A representative eye photo database is also provided along with relevant photo database pictures of the individual references. STR-Witness(tm) -- ...
... Retinome predicts eye cooler if the sample is 50 percent or greater European ancestry as to whether eye color is blue, mostly blue, brown or mostly brown. A representative eye photo database is also provided along with relevant photo database pictures of the individual references. STR-Witness(tm) -- ...
File
... 3. The subunits that make up DNA are called a. phosphates. c. amino acids. b. nucleotides. d. bases. 4. What two things must DNA be able to do? __________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________ ...
... 3. The subunits that make up DNA are called a. phosphates. c. amino acids. b. nucleotides. d. bases. 4. What two things must DNA be able to do? __________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________ ...
Document
... • two strands of nucleotides, coiled into a double helix • Each nucleotide has – A five-carbon sugar (deoxyribose) – A phosphate group – A nitrogen-containing base (adenine, thymine, guanine, or cytosine ...
... • two strands of nucleotides, coiled into a double helix • Each nucleotide has – A five-carbon sugar (deoxyribose) – A phosphate group – A nitrogen-containing base (adenine, thymine, guanine, or cytosine ...
Microarray Cancer Lab - Madison West High School
... Probe DNA - short pieces of single stranded DNA attached to glass Target DNA - cDNA from cells grown under different conditions Floating in solution on top of probe DNA example: cDNA from seedlings grown in light vs. dark ...
... Probe DNA - short pieces of single stranded DNA attached to glass Target DNA - cDNA from cells grown under different conditions Floating in solution on top of probe DNA example: cDNA from seedlings grown in light vs. dark ...
DNA Paper Model Activity Try to attach and mode the Gene Reading
... DNA ribbon that is not spooled around a histone or covered by a methyl. Can the machinery read any significant stretch of DNA? No, it cannot. 2. Refer to question 1, would this be an active or inactive gene? Explain. It’s inactive, because the methyl groups make the DNA inaccessible. 3. Try to attac ...
... DNA ribbon that is not spooled around a histone or covered by a methyl. Can the machinery read any significant stretch of DNA? No, it cannot. 2. Refer to question 1, would this be an active or inactive gene? Explain. It’s inactive, because the methyl groups make the DNA inaccessible. 3. Try to attac ...
DNA Discovery - Biology Junction
... Replication in small pieces (Okazaki fragments) Enzyme stitches pieces together later ...
... Replication in small pieces (Okazaki fragments) Enzyme stitches pieces together later ...
DNA Vocabulary Study Option
... Carbohydrate, Lipid and Protein unit for Biology. The unit is one of the larger units and contains a lot of vocabulary to keep straight. In order the help the students I have created this study option for home. ...
... Carbohydrate, Lipid and Protein unit for Biology. The unit is one of the larger units and contains a lot of vocabulary to keep straight. In order the help the students I have created this study option for home. ...
Who`s the daddy practice
... Exercise 1: A Mix-Up at the Hospital The DNA sequence contains much more variety than is seen at the phenotypic level (outward traits ). This variety can be detected by restriction length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis, by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) with variable tandem repeat regions (VNTR), or ...
... Exercise 1: A Mix-Up at the Hospital The DNA sequence contains much more variety than is seen at the phenotypic level (outward traits ). This variety can be detected by restriction length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis, by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) with variable tandem repeat regions (VNTR), or ...
Chapter 14
... helical structure of DNA. The elongated horizontal patterns at the top and bottom indicate that the purine and pyrimidine bases are stacked 0.34 nm apart and are perpendicular to the axis of the DNA molecule. ...
... helical structure of DNA. The elongated horizontal patterns at the top and bottom indicate that the purine and pyrimidine bases are stacked 0.34 nm apart and are perpendicular to the axis of the DNA molecule. ...
Problem Set 3A
... paper to the other. Show both replication forks and a bit of DNA at each end that has not yet been replicated. Use single long arrows for each of the original DNA strands, being sure with all DNA and RNA strands that the arrows are oriented correctly to signify the 5’ and 3’ ends of the molecules. I ...
... paper to the other. Show both replication forks and a bit of DNA at each end that has not yet been replicated. Use single long arrows for each of the original DNA strands, being sure with all DNA and RNA strands that the arrows are oriented correctly to signify the 5’ and 3’ ends of the molecules. I ...
Italian Association for Cancer Research NETWORK OF
... The overall goals of the Network are: (a) to create a network of researchers involved in the identification of relevant interactions between genes and the environment through studies of molecular epidemiology in Italy; (b) to rationalize and improve the quality of laboratory measurements by referrin ...
... The overall goals of the Network are: (a) to create a network of researchers involved in the identification of relevant interactions between genes and the environment through studies of molecular epidemiology in Italy; (b) to rationalize and improve the quality of laboratory measurements by referrin ...
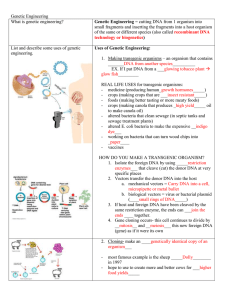
Genetic Engineering
... small fragments and inserting the fragments into a host organism of the same or different species (also called recombinant DNA technology or biogenetics) Uses of Genetic Engineering: 1. Making transgenic organisms – an organism that contains _______DNA from another species__________ EX. If I put DNA ...
... small fragments and inserting the fragments into a host organism of the same or different species (also called recombinant DNA technology or biogenetics) Uses of Genetic Engineering: 1. Making transgenic organisms – an organism that contains _______DNA from another species__________ EX. If I put DNA ...
... dna replication is necessary for the transmission of genetic information and thus such a process must achieve accurate copying of the genome. Since the last century the replicon model has been proposed in order to explain the general mechanism of genome duplication in bacteria. Later work in yeast l ...
Carbohydrate Tutorial
... Role of DNA 3. While you are growing you need DNA to produce more _____________. 4. As an adult you also need DNA to : a. b. c. The Cell 5. DNA directs the entire operation by issuing instructions to make things you need such as __________________. 6. DNA allows organisms to make _______________ of ...
... Role of DNA 3. While you are growing you need DNA to produce more _____________. 4. As an adult you also need DNA to : a. b. c. The Cell 5. DNA directs the entire operation by issuing instructions to make things you need such as __________________. 6. DNA allows organisms to make _______________ of ...
which together form the gene "stories" NOTE
... contained in the chromosomes humans have 46, dogs78, mice40, some bacteriaonly one DNA gives the cells specific instructions to create protiens for the organism they belong to ...
... contained in the chromosomes humans have 46, dogs78, mice40, some bacteriaonly one DNA gives the cells specific instructions to create protiens for the organism they belong to ...
DNA/Strawberry Lab Write the question and answers on your own
... because they have 8 copies of each type of chromosomes. This large number of chromosomes will filter out of your solution and you will actually see DNA. Write a brief description of what you think the DNA will look like. _____________________________________________________________________________ A ...
... because they have 8 copies of each type of chromosomes. This large number of chromosomes will filter out of your solution and you will actually see DNA. Write a brief description of what you think the DNA will look like. _____________________________________________________________________________ A ...
DNA Typing
... Chemical strung together=DNA code Some sections of DNA vary from individual to individual Scientists can link a strand of DNA to a given individual ...
... Chemical strung together=DNA code Some sections of DNA vary from individual to individual Scientists can link a strand of DNA to a given individual ...
DNA Unit Study Guide 2017 - Liberty Union High School District
... 5. How many bonds are there between A/T? __________ G/C? _________ 6. What are the chemicals that make up the backbone? ______________ & ___________________. 7. What is the enzyme responsible for unwinding the DNA so it can replicate? _____________________ 8. What is the enzyme responsible for makin ...
... 5. How many bonds are there between A/T? __________ G/C? _________ 6. What are the chemicals that make up the backbone? ______________ & ___________________. 7. What is the enzyme responsible for unwinding the DNA so it can replicate? _____________________ 8. What is the enzyme responsible for makin ...
REVIEW OF MOLECULAR GENETICS - Pascack Valley Regional
... TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
... TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
DNA Workshop - Lapeer High School
... First click the button in the upper left that says “DNA Replication.” Follow the prompts and go through the animation. You can repeat if necessary. a. What kind of protein unzips the DNA to start the process? b. Which bases always pair with each other? c. Where in the cell does replication take plac ...
... First click the button in the upper left that says “DNA Replication.” Follow the prompts and go through the animation. You can repeat if necessary. a. What kind of protein unzips the DNA to start the process? b. Which bases always pair with each other? c. Where in the cell does replication take plac ...
1928: Frederick Griffith
... Oswald Avery & other scientists concluded ______ was the “transforming factor.” Avery and other scientists discovered DNA __________________________ genetic information from one generation to the next. Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase studied viruses grown in cultures ________________ _______________ ...
... Oswald Avery & other scientists concluded ______ was the “transforming factor.” Avery and other scientists discovered DNA __________________________ genetic information from one generation to the next. Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase studied viruses grown in cultures ________________ _______________ ...
Document
... 1. Below is a sequence of bases along one side of a DNA molecule. Write out the sequence of DNA bases that would pair with the ones shown. DNA- ...
... 1. Below is a sequence of bases along one side of a DNA molecule. Write out the sequence of DNA bases that would pair with the ones shown. DNA- ...
DNA profiling

DNA profiling (also called DNA fingerprinting, DNA testing, or DNA typing) is a forensic technique used to identify individuals by characteristics of their DNA. A DNA profile is a small set of DNA variations that is very likely to be different in all unrelated individuals, thereby being as unique to individuals as are fingerprints (hence the alternate name for the technique). DNA profiling should not be confused with full genome sequencing. First developed and used in 1985, DNA profiling is used in, for example, parentage testing and criminal investigation, to identify a person or to place a person at a crime scene, techniques which are now employed globally in forensic science to facilitate police detective work and help clarify paternity and immigration disputes.Although 99.9% of human DNA sequences are the same in every person, enough of the DNA is different that it is possible to distinguish one individual from another, unless they are monozygotic (""identical"") twins. DNA profiling uses repetitive (""repeat"") sequences that are highly variable, called variable number tandem repeats (VNTRs), in particular short tandem repeats (STRs). VNTR loci are very similar between closely related humans, but are so variable that unrelated individuals are extremely unlikely to have the same VNTRs.The DNA profiling technique nowadays used is based on technology developed in 1988.