Q on Genetic Control of Protein Structure and function – Chapter 5
... Draw a diagram of a single DNA nucleotide. Which enzyme turns DNA nucleotides into a polynucleotide? Explain what is meant by “complementary base pairing”. What type of bond holds the two DNA strands together? What are the 2 essential functions of DNA? What are the 2 main types of RNA and what are t ...
... Draw a diagram of a single DNA nucleotide. Which enzyme turns DNA nucleotides into a polynucleotide? Explain what is meant by “complementary base pairing”. What type of bond holds the two DNA strands together? What are the 2 essential functions of DNA? What are the 2 main types of RNA and what are t ...
DNA & DNA Replication
... Each strand of the parent DNA is used as a template to make the new daughter strand DNA replication makes 2 new complete double helices each with 1 old and 1 new strand ...
... Each strand of the parent DNA is used as a template to make the new daughter strand DNA replication makes 2 new complete double helices each with 1 old and 1 new strand ...
Name Period
... 10)What is meant by 5’ and 3’ carbons? What attached to each in DNA? 11)Why is DNA said to have an intrinsic polarity? 12)What are Chargaff’s rules 13)What technique did Franklin use to study DNA, what shape did she find? 14)What specific structure did Watson and Crick discover DNA to have? 15)What ...
... 10)What is meant by 5’ and 3’ carbons? What attached to each in DNA? 11)Why is DNA said to have an intrinsic polarity? 12)What are Chargaff’s rules 13)What technique did Franklin use to study DNA, what shape did she find? 14)What specific structure did Watson and Crick discover DNA to have? 15)What ...
Study Guide Unit 4 - Mrs. Wolodkowicz`s Biological Realm
... write the definitions for DNA & RNA, transcription & translation, autosome, & sex linkage. the components of DNA the nitrogen bases & their complementary base pairs in DNA & RNA functions of tRNA & mRNA the laws of segregation & independent assortment the terms: dominant, recessive, geno ...
... write the definitions for DNA & RNA, transcription & translation, autosome, & sex linkage. the components of DNA the nitrogen bases & their complementary base pairs in DNA & RNA functions of tRNA & mRNA the laws of segregation & independent assortment the terms: dominant, recessive, geno ...
Chapter 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
... 11. What does “semi-conservative” replication mean? 12. What are the functions of primase? DNA polymerase? Ligase? 13. What is the difference between the 5’ and 3’ ends of the DNA molecule? Where are the 5’ and 3’ ends on opposite strands of the double helix? 14. What is the difference between the l ...
... 11. What does “semi-conservative” replication mean? 12. What are the functions of primase? DNA polymerase? Ligase? 13. What is the difference between the 5’ and 3’ ends of the DNA molecule? Where are the 5’ and 3’ ends on opposite strands of the double helix? 14. What is the difference between the l ...
DNA - Southington Public Schools
... Almost all functions of living things including growing, reproducing, digesting food, moving, fighting disease, even thinking rely on the production of various proteins. Without DNA, living things would not exist very long. Parts of DNA DNA is very complex and long (almost 1m in each human cell!), b ...
... Almost all functions of living things including growing, reproducing, digesting food, moving, fighting disease, even thinking rely on the production of various proteins. Without DNA, living things would not exist very long. Parts of DNA DNA is very complex and long (almost 1m in each human cell!), b ...
HRW BIO CRF Ch 09_p01-58
... a phosphate group, a five-carbon sugar molecule, and a nitrogen base It stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. a ...
... a phosphate group, a five-carbon sugar molecule, and a nitrogen base It stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. a ...
Biology Chapter 12 Review 5-6
... 5. Identify the 4 different types of nitrogenous bases? 6. Nitrogenous bases can be sorted into two groups. Name the groups and explain how they are classified. 7. What units make up the backbone of DNA? 8. Explain how the information Watson and Crick acquired from Rosalind Franklin and Chargaff was ...
... 5. Identify the 4 different types of nitrogenous bases? 6. Nitrogenous bases can be sorted into two groups. Name the groups and explain how they are classified. 7. What units make up the backbone of DNA? 8. Explain how the information Watson and Crick acquired from Rosalind Franklin and Chargaff was ...
Biology 202
... b. Why must primase create a primer for DNA synthesis? 1 pt DNA polymerases require a polynucleotide primer with a free 3’ OH. c. Which enzyme (in E. coli) removes the primer after synthesis is completed? 0.5 pts DNA Polymerase I 3. Why do mutations that inactivate the 3'-5' exonuclease activity of ...
... b. Why must primase create a primer for DNA synthesis? 1 pt DNA polymerases require a polynucleotide primer with a free 3’ OH. c. Which enzyme (in E. coli) removes the primer after synthesis is completed? 0.5 pts DNA Polymerase I 3. Why do mutations that inactivate the 3'-5' exonuclease activity of ...
DNA Structure quick review/quiz
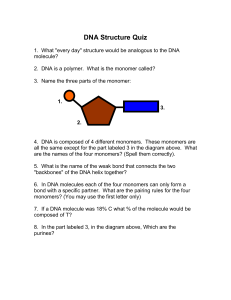
... DNA Structure Quiz 1. What "every day" structure would be analogous to the DNA molecule? 2. DNA is a polymer. What is the monomer called? 3. Name the three parts of the monomer: ...
... DNA Structure Quiz 1. What "every day" structure would be analogous to the DNA molecule? 2. DNA is a polymer. What is the monomer called? 3. Name the three parts of the monomer: ...
Lecture #7 Date - Helena High School
... Griffith: bacterial work; transformation: change in genotype and phenotype due to assimilation of external substance (DNA) by a cell Avery: transformation agent was DNA ...
... Griffith: bacterial work; transformation: change in genotype and phenotype due to assimilation of external substance (DNA) by a cell Avery: transformation agent was DNA ...
Study Guide: The Cell
... 14. Describe the function(s) of DNA polymerase in replication. 15. Explain the involvement of DNA helicase and DNA ligase in replication. 16. What is the center of the chromosome called? 17. What are the tips of a chromosome called? 18. What problem occurs at the tips of chromosomes during replicati ...
... 14. Describe the function(s) of DNA polymerase in replication. 15. Explain the involvement of DNA helicase and DNA ligase in replication. 16. What is the center of the chromosome called? 17. What are the tips of a chromosome called? 18. What problem occurs at the tips of chromosomes during replicati ...
SBI3U - misshoughton.net
... A gene is composed of a specific sequence of nucleotides (bases) that codes for a specific amino acid sequence specific protein A chromosome is composed of hundreds to thousands of genes ...
... A gene is composed of a specific sequence of nucleotides (bases) that codes for a specific amino acid sequence specific protein A chromosome is composed of hundreds to thousands of genes ...
Secret of Photo 51
... Mr. Kent, JFK High School Secret of Photo 51 1. Why is DNA called the blueprint for all life on earth? 2. Who are Francis Crick a. James Watson b. Rosalind Franklin c. Maurice Wilkins 3. How did Rosalind Franklin’s remarkable X-ray image of DNA lead to one of the greatest discoveries in science, and ...
... Mr. Kent, JFK High School Secret of Photo 51 1. Why is DNA called the blueprint for all life on earth? 2. Who are Francis Crick a. James Watson b. Rosalind Franklin c. Maurice Wilkins 3. How did Rosalind Franklin’s remarkable X-ray image of DNA lead to one of the greatest discoveries in science, and ...
genetics science learning center – internet lesson
... 8. If our cells were as large as an aspirin, how long would the DNA be? 9. How many chromosomes does a mosquito have? _________ an onion?____________ a carp? _____________ What is HEREDITY? 10. Why aren’t children identical to their parents? ...
... 8. If our cells were as large as an aspirin, how long would the DNA be? 9. How many chromosomes does a mosquito have? _________ an onion?____________ a carp? _____________ What is HEREDITY? 10. Why aren’t children identical to their parents? ...
DNA Modeling
... 2. Draw a picture of each of the matching bases that paired together during this lab. ...
... 2. Draw a picture of each of the matching bases that paired together during this lab. ...
Ch 11 homework
... 8. Outline the 4 ways genes expression can be regulated after mRNA has been processed and transported to the cytoplasm. (2) ...
... 8. Outline the 4 ways genes expression can be regulated after mRNA has been processed and transported to the cytoplasm. (2) ...
Recombinant DNA Technologies
... d. T- Thymine -put together in a double-helical molecule with A-T & C-G as the “rungs” -form GENES e. We have about 30,000 genes and they are mapped by location on each chromosome -”Human Genome Project” f. We are 99.9% identical; .1% makes us unique and different from Rob Marder (thank heaven!) a. ...
... d. T- Thymine -put together in a double-helical molecule with A-T & C-G as the “rungs” -form GENES e. We have about 30,000 genes and they are mapped by location on each chromosome -”Human Genome Project” f. We are 99.9% identical; .1% makes us unique and different from Rob Marder (thank heaven!) a. ...
2nd Semester Review The second semester test covers Meiosis
... General process and function Define gamete chromosome homologous chromosomes (homologous pair) haploid/diploid 2. DNA: General process of replication General idea of protein synthesis: Transcription- where it occurs, what is produced Translation- role of mRNA, tRNA and rRNA Define- gene codon nucleo ...
... General process and function Define gamete chromosome homologous chromosomes (homologous pair) haploid/diploid 2. DNA: General process of replication General idea of protein synthesis: Transcription- where it occurs, what is produced Translation- role of mRNA, tRNA and rRNA Define- gene codon nucleo ...
Introduction to Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources
... DNA bases always combine as follows: • Cytosine (C) combines with Guanine (G) • Adenine (A) combines with Thymine (T) ...
... DNA bases always combine as follows: • Cytosine (C) combines with Guanine (G) • Adenine (A) combines with Thymine (T) ...
DNA polymerase

The DNA polymerases are enzymes that create DNA molecules by assembling nucleotides, the building blocks of DNA. These enzymes are essential to DNA replication and usually work in pairs to create two identical DNA strands from a single original DNA molecule. During this process, DNA polymerase “reads” the existing DNA strands to create two new strands that match the existing ones.Every time a cell divides, DNA polymerase is required to help duplicate the cell’s DNA, so that a copy of the original DNA molecule can be passed to each of the daughter cells. In this way, genetic information is transmitted from generation to generation.Before replication can take place, an enzyme called helicase unwinds the DNA molecule from its tightly woven form. This opens up or “unzips” the double-stranded DNA to give two single strands of DNA that can be used as templates for replication.