WS 12 Notes - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State University
... Between the two DNA strands (in an intact double helix), A bonds with T, and C bonds with G. This is due to hydrogen bonding. A and T form 2 hydrogen bonds, C and G form 3 hydrogen bonds. This "lock-and-key" model is due to hydrogen bonding and shape. ...
... Between the two DNA strands (in an intact double helix), A bonds with T, and C bonds with G. This is due to hydrogen bonding. A and T form 2 hydrogen bonds, C and G form 3 hydrogen bonds. This "lock-and-key" model is due to hydrogen bonding and shape. ...
AP Biology Chapter 5 Notes
... DNA: Explain the importance of 3’ and 5’ and how it relates to anti-parallel. DNA: How big is the human Genome? DNA Replication: How did the structure of DNA relate to its function? ...
... DNA: Explain the importance of 3’ and 5’ and how it relates to anti-parallel. DNA: How big is the human Genome? DNA Replication: How did the structure of DNA relate to its function? ...
which together form the gene "stories" NOTE
... humans have 46, dogs78, mice40, some bacteriaonly one DNA gives the cells specific instructions to create protiens for the organism they belong to ...
... humans have 46, dogs78, mice40, some bacteriaonly one DNA gives the cells specific instructions to create protiens for the organism they belong to ...
DNA info
... chromosomes which are made up of DNA, histones, and other support proteins. Therefore genes are found on DNA. All of the hereditary material could be called ‘instructions for making a living thing’! A gene is a specific segment of DNA that has a specific location on a chromosome. Humans have 23 pair ...
... chromosomes which are made up of DNA, histones, and other support proteins. Therefore genes are found on DNA. All of the hereditary material could be called ‘instructions for making a living thing’! A gene is a specific segment of DNA that has a specific location on a chromosome. Humans have 23 pair ...
DNA - TeacherWeb
... Is it DNA? In 1928, Griffith found out that the information carried in the cell could be transferred to another cell. He called this transfer “transformation”. He did not yet know about DNA and the prevailing thought of the time was that protein was the more likely culprit. ...
... Is it DNA? In 1928, Griffith found out that the information carried in the cell could be transferred to another cell. He called this transfer “transformation”. He did not yet know about DNA and the prevailing thought of the time was that protein was the more likely culprit. ...
File - Ms. Breeze Biology
... 2. In DNA, ___________________ always forms ________________________ bonds with guanine (G). 3. The sequence of ________________________ carries the genetic information of an organism. 4. The process of ____________________________ produces a new copy of an organism’s genetic information, which is p ...
... 2. In DNA, ___________________ always forms ________________________ bonds with guanine (G). 3. The sequence of ________________________ carries the genetic information of an organism. 4. The process of ____________________________ produces a new copy of an organism’s genetic information, which is p ...
DNA REPLICATION Review of DNA Structure
... complementary to the DNA templates • After formation of the primer, DNA polymerase III – elongates the new strand by adding nucleotides to the 3’end (~50 per second) • DNA polymerase I – later replaces RNA primers with DNA nucleotides ...
... complementary to the DNA templates • After formation of the primer, DNA polymerase III – elongates the new strand by adding nucleotides to the 3’end (~50 per second) • DNA polymerase I – later replaces RNA primers with DNA nucleotides ...
AP BIO Unit 6 Review Ch. 14,15,16,18,19 Westbrook Gene
... Lung cancers caused by smoking have been shown to be due to what kind of mutation? Cells that leave a tumor and spread throughout the body, forming new tumors at distant sites, are called what? DNA can be cleaved at a specific site, generating in most cases two fragments with short single-stranded e ...
... Lung cancers caused by smoking have been shown to be due to what kind of mutation? Cells that leave a tumor and spread throughout the body, forming new tumors at distant sites, are called what? DNA can be cleaved at a specific site, generating in most cases two fragments with short single-stranded e ...
Slide 1
... If RT-PCR was performed with sequence-specific primers, then the trimmed fragment of interest can be inserted directly into an expression vector. If RT-PCR was done with generic (non-specific) primers, then a cDNA library can be created and probed against known or predicted sequences. ...
... If RT-PCR was performed with sequence-specific primers, then the trimmed fragment of interest can be inserted directly into an expression vector. If RT-PCR was done with generic (non-specific) primers, then a cDNA library can be created and probed against known or predicted sequences. ...
12.1 Notes - West Branch Schools
... basic building blocks of proteins, must be established for genes to be successfully translated into functional proteins. The correspondence between codons (3 base code of ...
... basic building blocks of proteins, must be established for genes to be successfully translated into functional proteins. The correspondence between codons (3 base code of ...
Topic 2 – DNA structure According to Watson and Crick, DNA
... The sequence of base pairs along the DNA molecule determine the genetic code. ...
... The sequence of base pairs along the DNA molecule determine the genetic code. ...
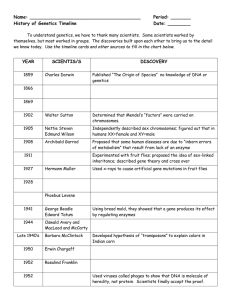
Name
... Proposed that some human diseases are due to “inborn errors of metabolism” that result from lack of an enzyme ...
... Proposed that some human diseases are due to “inborn errors of metabolism” that result from lack of an enzyme ...
Objectives 10 - u.arizona.edu
... 6) State the function of telomerase and describe its probable mechanism. Telomerase replicates chromosomal tips by extending the 3’ ends of a chromosome by adding numerous repeats of a six base pair sequence, which is primed by primase and extended by polymerase. The telomerase recognizes the tips ...
... 6) State the function of telomerase and describe its probable mechanism. Telomerase replicates chromosomal tips by extending the 3’ ends of a chromosome by adding numerous repeats of a six base pair sequence, which is primed by primase and extended by polymerase. The telomerase recognizes the tips ...
CST Review PowerPoint
... used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and some viruses. -The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in regulating the use of this genetic information. ...
... used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and some viruses. -The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in regulating the use of this genetic information. ...
DNA Nucleotide Chargaff`s Rule Double
... The principal enzyme involved in DNA replication. The enzyme that unwinds or unzips a double-stranded DNA molecule. A single-stranded nucleic acid that contains the sugar ribose. A type of RNA that carries copies of instructions for the assembly of amino acids into proteins from DNA. A type of RNA t ...
... The principal enzyme involved in DNA replication. The enzyme that unwinds or unzips a double-stranded DNA molecule. A single-stranded nucleic acid that contains the sugar ribose. A type of RNA that carries copies of instructions for the assembly of amino acids into proteins from DNA. A type of RNA t ...
Researchers ACT on DNA Storage
... Unlike many forms of information storage, DNA is extremely long-lasting and does not require constant electrical power. Plus, it's tiny—a small cup of DNA can store one hundred million hours of high-quality video. But until now, this storage method has faced too many obstacles: DNA synthesis is expe ...
... Unlike many forms of information storage, DNA is extremely long-lasting and does not require constant electrical power. Plus, it's tiny—a small cup of DNA can store one hundred million hours of high-quality video. But until now, this storage method has faced too many obstacles: DNA synthesis is expe ...
Chapter 12 DNA Analysis Checkpoint Answers In the nucleus of the
... identify and determine the sequence of all genes found on the human chromosome. 5. The nucleus 6. Adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine 7. The phosphate groups give DNA its acidic properties. 8. Blood, semen, saliva, hair follicular tissue, bone 9. Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism ...
... identify and determine the sequence of all genes found on the human chromosome. 5. The nucleus 6. Adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine 7. The phosphate groups give DNA its acidic properties. 8. Blood, semen, saliva, hair follicular tissue, bone 9. Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism ...
Mutations Can Change the Meaning of Genes
... How Mutations Affect Genes Mutation: any change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA Types of Mutations: Base substitutions: replacement of one nucleotide w/ another. May or may not affect protein Base deletions & Base insertions: May be more harmful b/c all subsequent codons will be altered ...
... How Mutations Affect Genes Mutation: any change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA Types of Mutations: Base substitutions: replacement of one nucleotide w/ another. May or may not affect protein Base deletions & Base insertions: May be more harmful b/c all subsequent codons will be altered ...
AP BIOLOGY MOLECULAR GENETICS QUESTIONS
... 14. What is DNA "proofreading"? Does it work very well or are there alot of misteaks that creap throug? ...
... 14. What is DNA "proofreading"? Does it work very well or are there alot of misteaks that creap throug? ...
Study Guide: Chapter 2
... 16. What two types of molecules make up a nucleosome: lipids, proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids? 17. Why would it be advantageous to the cell to have its DNA molecules tightly condensed into nucleosomes during mitosis? 18. What does it mean for a DNA strand to be complementary? 19. What is the ...
... 16. What two types of molecules make up a nucleosome: lipids, proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids? 17. Why would it be advantageous to the cell to have its DNA molecules tightly condensed into nucleosomes during mitosis? 18. What does it mean for a DNA strand to be complementary? 19. What is the ...
Molecular Genetics Outcome Checklist
... _____ I can describe the contributions that were made by James Watson and Francis Crick to the field of genetics. _____ I can describe the contributions that Rosalind Franklin made to the field of genetics. _____ I can describe the structure of DNA, including the three components of nucleotides, the ...
... _____ I can describe the contributions that were made by James Watson and Francis Crick to the field of genetics. _____ I can describe the contributions that Rosalind Franklin made to the field of genetics. _____ I can describe the structure of DNA, including the three components of nucleotides, the ...
DNA polymerase

The DNA polymerases are enzymes that create DNA molecules by assembling nucleotides, the building blocks of DNA. These enzymes are essential to DNA replication and usually work in pairs to create two identical DNA strands from a single original DNA molecule. During this process, DNA polymerase “reads” the existing DNA strands to create two new strands that match the existing ones.Every time a cell divides, DNA polymerase is required to help duplicate the cell’s DNA, so that a copy of the original DNA molecule can be passed to each of the daughter cells. In this way, genetic information is transmitted from generation to generation.Before replication can take place, an enzyme called helicase unwinds the DNA molecule from its tightly woven form. This opens up or “unzips” the double-stranded DNA to give two single strands of DNA that can be used as templates for replication.