organization homeostasis study guide, answers
... form of heat) in order to keep the organs warm. Hypothermia is a condition in which the body temperature drops to dangerously low levels—too low to maintain normal metabolism or other body functions. A person who is exposed to cold temperatures for too long will start to shiver. That's the beginning ...
... form of heat) in order to keep the organs warm. Hypothermia is a condition in which the body temperature drops to dangerously low levels—too low to maintain normal metabolism or other body functions. A person who is exposed to cold temperatures for too long will start to shiver. That's the beginning ...
Organs, Tissues and All Living Systems Long Answer
... cells, tissues, organs, and systems in plants and animals (e.g., muscle cells and nerve cells form the tissue found in the heart, which is a component of the circulatory system; granum and thylakoid structures act as solar collectors in the chloroplast to produce carbohydrates for plant growth) ...
... cells, tissues, organs, and systems in plants and animals (e.g., muscle cells and nerve cells form the tissue found in the heart, which is a component of the circulatory system; granum and thylakoid structures act as solar collectors in the chloroplast to produce carbohydrates for plant growth) ...
Organs, Tissues and All Living Systems Long Answer Rubric
... cells, tissues, organs, and systems in plants and animals (e.g., muscle cells and nerve cells form the tissue found in the heart, which is a component of the circulatory system; granum and thylakoid structures act as solar collectors in the chloroplast to produce carbohydrates for plant growth) ...
... cells, tissues, organs, and systems in plants and animals (e.g., muscle cells and nerve cells form the tissue found in the heart, which is a component of the circulatory system; granum and thylakoid structures act as solar collectors in the chloroplast to produce carbohydrates for plant growth) ...
Hierarchy of Life
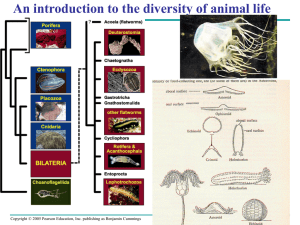
... 5. Gastrovascular cavity (Functions in digestion and food distribution.) (Possesses one mouth/anus opening.) 6. Sexual (medusa stage)and asexual (Polyp stage) reproduction is performed. IV. Bilateral Eumetazoa A. Phylum: Platyhelminthes (Flatworms) 1. Triplobastic (three germ layers) – ectoderm, mes ...
... 5. Gastrovascular cavity (Functions in digestion and food distribution.) (Possesses one mouth/anus opening.) 6. Sexual (medusa stage)and asexual (Polyp stage) reproduction is performed. IV. Bilateral Eumetazoa A. Phylum: Platyhelminthes (Flatworms) 1. Triplobastic (three germ layers) – ectoderm, mes ...
Prediction of Blastulation
... Cultured an additional set of human embryos from the zygote to approximately the four-cell stage and monitored embryonic development by time-lapse imaging. The cell cycle parameter values were determined for each embryo Embryos were then immunostained for LAMIN-B1 Blinded results were then scored fo ...
... Cultured an additional set of human embryos from the zygote to approximately the four-cell stage and monitored embryonic development by time-lapse imaging. The cell cycle parameter values were determined for each embryo Embryos were then immunostained for LAMIN-B1 Blinded results were then scored fo ...
File - SCIENTIST CINDY
... through urine, sweat, and vapor in breath. Lastly, ATP is used to store energy for the body. Cellular respiration is the process in which the food you eat is broken down to release energy in the form of ATP. ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is a molecule that delivers energy around your body so your ...
... through urine, sweat, and vapor in breath. Lastly, ATP is used to store energy for the body. Cellular respiration is the process in which the food you eat is broken down to release energy in the form of ATP. ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is a molecule that delivers energy around your body so your ...
HST 071 IN SUMMARY NORMAL MENSTRUAL CYCLE
... 1. What is the arcuate nucleus and what does it produce? 2. Describe the wave form of GnRH? LH? 3. What does inhibin do and where does it come from? 4. What is a dominant follicle? 5. How many follicles attempt maturation each month? 6. What is produced by the corpus luteum? 7. What is a basa ...
... 1. What is the arcuate nucleus and what does it produce? 2. Describe the wave form of GnRH? LH? 3. What does inhibin do and where does it come from? 4. What is a dominant follicle? 5. How many follicles attempt maturation each month? 6. What is produced by the corpus luteum? 7. What is a basa ...
Intermediate 2 Biology Revision
... 5. The type of nerve cell that is found in the CNS connecting sensory neurones to other neurons of the body. 6. The nerve cell that carries information to effectors from the CNS 12.4 Nervous system in action 1. Term given to the cells that pick up information detected by sense organs ...
... 5. The type of nerve cell that is found in the CNS connecting sensory neurones to other neurons of the body. 6. The nerve cell that carries information to effectors from the CNS 12.4 Nervous system in action 1. Term given to the cells that pick up information detected by sense organs ...
BIOLOGY REVISION Levels of Organisation: LEVEL 1 – Cells Are
... cell membrane from a lower to a higher concentration. In active transport, particles move against the concentration gradient - and therefore require an input of energy from the cell. Sometimes dissolved molecules are at a higher concentration inside the cell than outside, but, because the organism n ...
... cell membrane from a lower to a higher concentration. In active transport, particles move against the concentration gradient - and therefore require an input of energy from the cell. Sometimes dissolved molecules are at a higher concentration inside the cell than outside, but, because the organism n ...
video slide
... These are essentially colonial protozoa, whose colonies are reinforced with solid spicules of various shapes and composition. Silica SiO2 and Calcite CaCO3 are the commonest. They are exclusively aquatic, mainly marine, and live by filter feeding. The feeding cells are called choanocytes, which inco ...
... These are essentially colonial protozoa, whose colonies are reinforced with solid spicules of various shapes and composition. Silica SiO2 and Calcite CaCO3 are the commonest. They are exclusively aquatic, mainly marine, and live by filter feeding. The feeding cells are called choanocytes, which inco ...
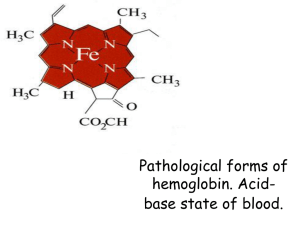
Pathological forms of hemoglobin. Acid
... balance between acids and bases, in other words, the pH. The body is very sensitive to its pH level, so strong mechanisms exist to maintain it. Outside the acceptable range of pH, proteins are denatured and digested, enzymes lose their ability to function, and death may occur. ...
... balance between acids and bases, in other words, the pH. The body is very sensitive to its pH level, so strong mechanisms exist to maintain it. Outside the acceptable range of pH, proteins are denatured and digested, enzymes lose their ability to function, and death may occur. ...
human embryonic stem cell therapy
... second stage will be to discover the correct mode of delivery of the specialized cells to the part of the body that is diseased or injured. A third stage will be to determine if such specialized cells enter the body, become part of it, and begin functioning to replace the injured cells; this is the ...
... second stage will be to discover the correct mode of delivery of the specialized cells to the part of the body that is diseased or injured. A third stage will be to determine if such specialized cells enter the body, become part of it, and begin functioning to replace the injured cells; this is the ...
The Respiratory System
... Lungs - 2 large, capillary lined sacks into which air is drawn. The capillaries absorb oxygen into the blood, where it is then delivered to all cells Diaphragm - an involuntary muscle that controls breathing ...
... Lungs - 2 large, capillary lined sacks into which air is drawn. The capillaries absorb oxygen into the blood, where it is then delivered to all cells Diaphragm - an involuntary muscle that controls breathing ...
epithelial tissue - wlhs.wlwv.k12.or.us
... Tissues are groups of cells with specialized structural and functional roles. Intercellular materials, varying from solid to liquid, separate cells. (also known as MATRIX) ...
... Tissues are groups of cells with specialized structural and functional roles. Intercellular materials, varying from solid to liquid, separate cells. (also known as MATRIX) ...
Turn in Body system story/brochure
... ROUND 1 – 5 POINTS EACH ROUND 2 – 10 POINTS EACH ROUND 3 - 15 POINTS EACH ...
... ROUND 1 – 5 POINTS EACH ROUND 2 – 10 POINTS EACH ROUND 3 - 15 POINTS EACH ...
March presentation
... This system provides protection for organs, support for movement There are three different types of muscles • Smooth muscle – found in organs (involuntary) • Skeletal – used for movement (voluntary) • Cardiac – the special muscle of the heart (involuntary) ...
... This system provides protection for organs, support for movement There are three different types of muscles • Smooth muscle – found in organs (involuntary) • Skeletal – used for movement (voluntary) • Cardiac – the special muscle of the heart (involuntary) ...
Unit 5, Module 14 Animals
... C. Excretion – how organisms get rid of their waste and balance their fluids (pH, salt concentration, water). Excretory structures help animals to perform these functions. 1. Invertebrate animals may have specialized excretory structures in some body segments to filter nitrogenous waste from the bl ...
... C. Excretion – how organisms get rid of their waste and balance their fluids (pH, salt concentration, water). Excretory structures help animals to perform these functions. 1. Invertebrate animals may have specialized excretory structures in some body segments to filter nitrogenous waste from the bl ...
Characteristics of Living Things
... – You perspire to release excess heat from your body – A rabbit grows a thick coat of fur in preparation for winter All living things are made up of cells that contain DNA – You are made of trillions of cells; some are blood cells, nerve cells, skin cells…etc – A bacteria is uni-cellular and microsc ...
... – You perspire to release excess heat from your body – A rabbit grows a thick coat of fur in preparation for winter All living things are made up of cells that contain DNA – You are made of trillions of cells; some are blood cells, nerve cells, skin cells…etc – A bacteria is uni-cellular and microsc ...
Regents Biology
... Egg-laying land animals no place to get rid of waste while in egg needs waste that doesn’t dissolve in water inside egg ...
... Egg-laying land animals no place to get rid of waste while in egg needs waste that doesn’t dissolve in water inside egg ...
Study Guide
... band of connective tissue that attaches a muscle to a bone , ligament – a tough band of connective tissue that connects bones or cartilage at a joint or supports an organ, muscle, or other body part. Ossification (also described above) - In the second month of fetal development, much of the skeleton ...
... band of connective tissue that attaches a muscle to a bone , ligament – a tough band of connective tissue that connects bones or cartilage at a joint or supports an organ, muscle, or other body part. Ossification (also described above) - In the second month of fetal development, much of the skeleton ...
Regents Biology - Explore Biology
... Egg-laying land animals no place to get rid of waste while in egg needs waste that doesn’t dissolve in water inside egg ...
... Egg-laying land animals no place to get rid of waste while in egg needs waste that doesn’t dissolve in water inside egg ...
Chapter 7 Study Guide
... adolescence – stage during which children start to become adults physically and mentally, also known as “going through puberty” puberty – period of physical sexual development that usually leads to the ability to reproduce 4.Adulthood-stage after adolescence; marked by continued mental, emotional, a ...
... adolescence – stage during which children start to become adults physically and mentally, also known as “going through puberty” puberty – period of physical sexual development that usually leads to the ability to reproduce 4.Adulthood-stage after adolescence; marked by continued mental, emotional, a ...
Developmental biology

Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop, and is synonymous with ontogeny. In animals most development occurs in embryonic life, but it is also found in regeneration, asexual reproduction and metamorphosis, and in the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. In plants, development occurs in embryos, during vegetative reproduction, and in the normal outgrowth of roots, shoots and flowers.Practical outcomes from the study of animal developmental biology have included in vitro fertilization, now widely used in fertility treatment, the understanding of risks from substances that can damage the fetus (teratogens), and the creation of various animal models for human disease which are useful in research. Developmental Biology has also help to generate modern stem cell biology which promises a number of important practical benefits for human health.Many of the processes of development are now well understood, and some major textbooks of the subject are