* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Respiratory System
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
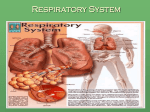
The Respiratory System Breathe in… Breathe out… Good! Functions To bring in oxygen to the lungs/cells To take away Co2 and wastes from cells/lungs Ext. respiration-the exchange of oxygen/waste between the lungs and outside world Int. respiration-the exchange of oxygen, Co2 and waste between the blood and cells components Lungs - 2 large, capillary lined sacks into which air is drawn. The capillaries absorb oxygen into the blood, where it is then delivered to all cells Diaphragm - an involuntary muscle that controls breathing The process of breathing Inspiration - or inhalation/breathing in the diaphragm contracts (gets smaller) allowing for the ribs to open and the lungs to open, thereby pulling air in (a pressurized system) * Exhalation - or breathing out, the process is reversed: diaphragm relaxes, ribs and lungs close, forcing air out Interesting Facts You can live with only one lung, and often that lung will develop and get stronger When you smoke ANYTHING, you are coating the lining of your lungs with tar and other substances that block/prevent oxygen from getting to the blood/body Pneumonia - build up of fluid in the lungs, thereby prevent oxygen transfer Lung Cancer - #1 cancer killer, 85% of lung cancer cases are related to smoking, either first hand or second hand smoke