Human Body Systems
... • 85% of body heat from muscles • There are nearly 600 skeletal muscles that make up nearly half of the total body weight in the human. • Muscles can only pull – they cannot push. • Energy is stored in the muscles in a chemical called ATP. • Lactic acid is released when the muscles are overworked an ...
... • 85% of body heat from muscles • There are nearly 600 skeletal muscles that make up nearly half of the total body weight in the human. • Muscles can only pull – they cannot push. • Energy is stored in the muscles in a chemical called ATP. • Lactic acid is released when the muscles are overworked an ...
ANIMAL KINGDOM 1 EVOLUTIONARY TRENDS and PHYLUM
... The behaviour of the hydra is much more varied and complex than that of the uncoordinated sponge. The many celled hydra has a network of nerve cells extending throughout the entire animal. This nerve net is slightly more concentrated around the mouth than elsewhere. There is no brain controlling the ...
... The behaviour of the hydra is much more varied and complex than that of the uncoordinated sponge. The many celled hydra has a network of nerve cells extending throughout the entire animal. This nerve net is slightly more concentrated around the mouth than elsewhere. There is no brain controlling the ...
BioInquiry Micromodule Worksheet
... Use the “Hints” or search on your own to help answer the following inquiries. Use this worksheet to record your answers or attach your own report. Enjoy your search. 1. What are some of the advantages to being multicellular as opposed to unicellular? ...
... Use the “Hints” or search on your own to help answer the following inquiries. Use this worksheet to record your answers or attach your own report. Enjoy your search. 1. What are some of the advantages to being multicellular as opposed to unicellular? ...
File - This area is password protected
... new species, unable to reproduce successfully with individuals of the original species. Individuals with the most favourable genes for the environment they live in are selected over time: this is natural selection Selective breeding is a process used to produce different breeds of animals or varieti ...
... new species, unable to reproduce successfully with individuals of the original species. Individuals with the most favourable genes for the environment they live in are selected over time: this is natural selection Selective breeding is a process used to produce different breeds of animals or varieti ...
Tissue
... Substitution of viable cells for dead cells Regeneration = same type of cells takes place of previous cells; same function Replacement = different type of tissue develops; forms scars; loss of some function Fibroclast lays down fibrin and forms scar tissue Type of tissue repair is determined b ...
... Substitution of viable cells for dead cells Regeneration = same type of cells takes place of previous cells; same function Replacement = different type of tissue develops; forms scars; loss of some function Fibroclast lays down fibrin and forms scar tissue Type of tissue repair is determined b ...
The respiratory system
... b. Type II pneumocytes (type II alveolar cells; great alveolar cells; granular pneumocytes; septal cells) (1) are cuboidal and are most often found near septal intersections. (2) bulge into the alveolus and have a free surface that contains short microvilli around their peripheral borders. (3) are a ...
... b. Type II pneumocytes (type II alveolar cells; great alveolar cells; granular pneumocytes; septal cells) (1) are cuboidal and are most often found near septal intersections. (2) bulge into the alveolus and have a free surface that contains short microvilli around their peripheral borders. (3) are a ...
File
... – It also carries waste products such as carbon dioxide away from the cells. – The circulatory system transports chemical messages between cells and different parts of the body. – It also carries cells and substances that fight disease. ...
... – It also carries waste products such as carbon dioxide away from the cells. – The circulatory system transports chemical messages between cells and different parts of the body. – It also carries cells and substances that fight disease. ...
Anatomy and Physiology I BY 30
... • When the body temperature is higher than the set point the blood vessels dilate bring the blood closer to the skin. Evaporated sweat cools the body • When the body is cold blood is shunted toward the internal organs way from the skin to minimize heat lose. Shivering creates heat as a byproduct of ...
... • When the body temperature is higher than the set point the blood vessels dilate bring the blood closer to the skin. Evaporated sweat cools the body • When the body is cold blood is shunted toward the internal organs way from the skin to minimize heat lose. Shivering creates heat as a byproduct of ...
Science Study Guide
... 10. voluntary muscles – the kind of muscle that a person can control 11. involuntary muscles – the kind of muscle that works without a person’s control B. Know these facts for the test: 1. To see a cell, you must look through a microscope like the one on this page. 2. Muscle cells form muscle tissue ...
... 10. voluntary muscles – the kind of muscle that a person can control 11. involuntary muscles – the kind of muscle that works without a person’s control B. Know these facts for the test: 1. To see a cell, you must look through a microscope like the one on this page. 2. Muscle cells form muscle tissue ...
disease - Alevelsolutions
... that causes tetanus produces a toxin that blocks the function of certain nerve cells, causing muscle spasms. 2. Cell damage – Pathogens can physically damage host cells by • Rupturing them to release nutrients (proteins etc.) inside them • Replicating inside the cells and bursting them when they are ...
... that causes tetanus produces a toxin that blocks the function of certain nerve cells, causing muscle spasms. 2. Cell damage – Pathogens can physically damage host cells by • Rupturing them to release nutrients (proteins etc.) inside them • Replicating inside the cells and bursting them when they are ...
BIO 262 Unit 3 Review Sheet
... 3. Fluid loss can be described as fluid leaking out of the capillaries into the surrounding connective tissue, or it may involve blood loss. Explain briefly how plasma proteins protect us from each. ...
... 3. Fluid loss can be described as fluid leaking out of the capillaries into the surrounding connective tissue, or it may involve blood loss. Explain briefly how plasma proteins protect us from each. ...
key words/concepts
... PRODUCED ALSO IN BONE M,ARROW THYMUS GLAND TO BECOME SPECIALIZED: ATTACK VIRUSES HIDING INSIDE CELLS; VIRUS ATTACK COORDINATED BY HELPER T CELLS (CD4 CELLS); AIDS, HIV: ATTACKS CD4 CELLS; WEAKENED IMMUNE SYSTEM; PERSON SUSCEPTIBLE TO OTHER VIRUSES, BACTERIA, FUNGI, PARASITES, PNEUMONIA, CANCER; H ...
... PRODUCED ALSO IN BONE M,ARROW THYMUS GLAND TO BECOME SPECIALIZED: ATTACK VIRUSES HIDING INSIDE CELLS; VIRUS ATTACK COORDINATED BY HELPER T CELLS (CD4 CELLS); AIDS, HIV: ATTACKS CD4 CELLS; WEAKENED IMMUNE SYSTEM; PERSON SUSCEPTIBLE TO OTHER VIRUSES, BACTERIA, FUNGI, PARASITES, PNEUMONIA, CANCER; H ...
2014 Biology STAAR EOC Review
... together to form: Biological Molecules. Biological molecules join together to form cells. Cells join together to form tissues. Tissues join together to form organs. Organs join together to form organ systems. Organ systems join together to form an organism. The following systems will be discussed la ...
... together to form: Biological Molecules. Biological molecules join together to form cells. Cells join together to form tissues. Tissues join together to form organs. Organs join together to form organ systems. Organ systems join together to form an organism. The following systems will be discussed la ...
File - Down the Rabbit Hole
... fingerprints. They play an important role in organ transplants. • If the marker proteins on a transplanted organ are different from those of the original organ the body will reject it as a foreign invader ...
... fingerprints. They play an important role in organ transplants. • If the marker proteins on a transplanted organ are different from those of the original organ the body will reject it as a foreign invader ...
1 - Quia
... methane gas. Vitamins K and some B are synthesized by bacterial action and absorbed. 7) Define the following terms: a) anabolism- Constructive metabolism characterized by the conversion of simple substances into more complex compounds of living matter. b) catabolism- A complex, metabolic process in ...
... methane gas. Vitamins K and some B are synthesized by bacterial action and absorbed. 7) Define the following terms: a) anabolism- Constructive metabolism characterized by the conversion of simple substances into more complex compounds of living matter. b) catabolism- A complex, metabolic process in ...
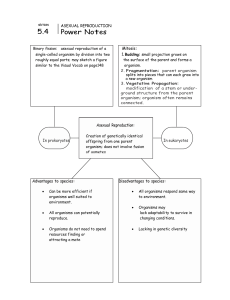
Print Preview - D:\Temp\e3temp_3492\.aptcache\aea03492/tfa03492
... Binary fission: asexual reproduction of a single-celled organism by division into two roughly equal parts; may sketch a figure similar to the Visual Vocab on page148 ...
... Binary fission: asexual reproduction of a single-celled organism by division into two roughly equal parts; may sketch a figure similar to the Visual Vocab on page148 ...
www.sasd.us
... directly in an open circulatory system There is no distinction between blood and interstitial fluid, and this general body fluid is more correctly called ...
... directly in an open circulatory system There is no distinction between blood and interstitial fluid, and this general body fluid is more correctly called ...
Basic Theories for Introductory Biology
... The sperm and eggs of sexually reproducing organisms are produced by meiosis; hence they contain only half of the normal number of chromosomes. ...
... The sperm and eggs of sexually reproducing organisms are produced by meiosis; hence they contain only half of the normal number of chromosomes. ...
Leaving Cert Biology Notes - Learning Outcomes 2014
... Heredity : Define as passing on of genetically controlled characteristics from parents to offspring e.g. blood type Gene expression: Define as when a gene is switched on and produces its characteristic e.g. the insulin producing gene only works in cells of the Islets of Langerhans in the pancreas o ...
... Heredity : Define as passing on of genetically controlled characteristics from parents to offspring e.g. blood type Gene expression: Define as when a gene is switched on and produces its characteristic e.g. the insulin producing gene only works in cells of the Islets of Langerhans in the pancreas o ...
Pathogen
... antibodies and memory cells. Passive immunity results from the individual receiving antibodies. ...
... antibodies and memory cells. Passive immunity results from the individual receiving antibodies. ...
Topic 9 LIFE FUNCTIONS COMMON TO LIVING THINGS In this
... In Chapter 8, you learned that cells, tissues, organs, and systems work together to keep an organism ____________. Each cell, tissue, organ, and system is built in a special way to help it perform its function. Cells, tissues, organs, and systems are all designed for their special ___________. They ...
... In Chapter 8, you learned that cells, tissues, organs, and systems work together to keep an organism ____________. Each cell, tissue, organ, and system is built in a special way to help it perform its function. Cells, tissues, organs, and systems are all designed for their special ___________. They ...
Unit VII: Animal Structure and Function, Part I
... - come from stem cells in bone marrow + mature in different locations before moving on to lymphoid tissue (lymph nodes, spleen, blood, lymph) - respond to specific antigens + clonal selection - effector cells and memory cells + primary and secondary immune response • self vs. non-self + autoimmune d ...
... - come from stem cells in bone marrow + mature in different locations before moving on to lymphoid tissue (lymph nodes, spleen, blood, lymph) - respond to specific antigens + clonal selection - effector cells and memory cells + primary and secondary immune response • self vs. non-self + autoimmune d ...
Anatomy Test - Cobra Invitational ANSWERS
... B) responds to internal and external changes by activating appropriate muscles and glands C) secretes hormones that regulate processes such as growth, reproduction, and nutrient use (metabolism) by body cells D) picks up fluid leaked from blood vessels and returns it to the blood E) produces heat 2. ...
... B) responds to internal and external changes by activating appropriate muscles and glands C) secretes hormones that regulate processes such as growth, reproduction, and nutrient use (metabolism) by body cells D) picks up fluid leaked from blood vessels and returns it to the blood E) produces heat 2. ...
Developmental biology

Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop, and is synonymous with ontogeny. In animals most development occurs in embryonic life, but it is also found in regeneration, asexual reproduction and metamorphosis, and in the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. In plants, development occurs in embryos, during vegetative reproduction, and in the normal outgrowth of roots, shoots and flowers.Practical outcomes from the study of animal developmental biology have included in vitro fertilization, now widely used in fertility treatment, the understanding of risks from substances that can damage the fetus (teratogens), and the creation of various animal models for human disease which are useful in research. Developmental Biology has also help to generate modern stem cell biology which promises a number of important practical benefits for human health.Many of the processes of development are now well understood, and some major textbooks of the subject are