* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - This area is password protected
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
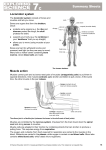
Inheritance & Health Key Notes Inherited Features Offspring get half of their inherited features from each parent. During fertilisation, the nucleus from the sperm cell joins with the nucleus in the egg cell, and a new nucleus is formed with all the genetic information needed The sperm cell is extremely streamlined, with a powerful tail for swimming. It also has special chemicals in its head to help it penetrate the egg cell. The egg cell is full of cytoplasm, used as an energy store for when fertilisation occurs. It also has a special barrier, which only allows one sperm to penetrate and fertilise it. Both contain a nucleus, containing genes… Some variations are inherited, whilst other variations are due to environmental factors Inherited variation is a characteristic you have got from your parents what can you inherit? Gender Eye colour Hair colour Skin colour Lobed or lobeless ears During fertilisation half the genes are transferred from the male (sperm), and half from the female (egg) This is why you inherit characteristics from both your mum and your dad (half from each) Likewise, your siblings (brothers and sisters) also have half the genes of your mum, and half of your dad (but your are not identical to them because the genes can mix slightly) Environmental Variation Characteristics of animals and plants can be affected by factors such as climate, diet, accidents, culture and lifestyle If you eat too much you will become heavier, and if you eat too little you will become lighter A plant in the shade of a big tree will not be able to photosynthesise as quickly as one in the sunshine, so it will be smaller Variation in a feature as a result of the surroundings, is called environmental variation Variation can occur within a species (i.e. some people have blue eyes, others have brown eyes) A great amount of variation also occurs between species (i.e. guerrillas are generally hairier than fish)! Selective Breeding; cloning; & genetic engineering Species gradually evolve by a process of natural selection - individuals in a species show a wide variation (due to gene differences) Individuals with inherited features best suited to their environment are most likely to survive and reproduce: passing on their genetic information to their offspring Over time, a species can change its appearance, and may even become a new species, unable to reproduce successfully with individuals of the original species. Individuals with the most favourable genes for the environment they live in are selected over time: this is natural selection Selective breeding is a process used to produce different breeds of animals or varieties of plants that have useful characteristics Using selective breeding you can produce a specific offspring with useful characteristics of both parents Exact copies of organisms are called clones - they have identical genetic information as the organism they were cloned from. Cloning is the production of genetically identical copies Clones frequently occur naturally, but they can also be produced artificially. Cloning is an example of asexual reproduction (where genetic information comes from just one parent) Clones can also be produced artificially - you can take a small number of cells from a 'parent' plant and ‘grow’ them in a medium rich in nutrients and plant growth hormones Genetic engineering takes genes from one organism, and places them into the chromosomes of another organism. It alters an organism's genetic code, and works because there is only one code for life Genetic modification can be used to help many people - e.g. people suffering from diabetes can get their insulin from genetically modified bacteria, rather than having to extract it from other humans / animals Some people believe growing and eating genetically modified plants could be dangerous because they contain genes, which are not natural Fitness & organ systems Being fit means your body is able to do the activities your lifestyle demands - e.g. being able to run; get upstairs without getting out of breathe; being strong enough to lift things etc… Fitness is different for each person, but is made up of: Strength Speed Stamina Suppleness When you exercise your muscles work harder - using up more oxygen To compensate, your heart beats quicker pumping more blood around your body. Your breathing rate also increases, allowing you to get more oxygen into your body (and expel more carbon dioxide) Fit people (who exercise a lot) have stronger heart muscles, so their heart pumps more blood with each beat. This means it can beat less than an unfit person’s and still pump the same amount of blood Fit people usually have slower resting heart beat rates. After exercise a fit person’s heart rate usually returns to its resting rate quicker than an unfit persons. This is also true of their breathing rate Respiration takes place in the cells (it is not “breathing in and out”) Respiration is the release of energy (from glucose) in our cells Animals and plants respire. In the light plants respire, but produce the oxygen for this to occur by photosynthesis - the carbon dioxide they produce via respiration is used for photosynthesis. In the dark plants respire, producing carbon dioxide glucose + oxygen carbon dioxide + water + (energy) C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + (energy) Respiratory (breathing) system (lungs; trachea; alveoli) - helps with absorbing oxygen from the air, and removing the waste carbon dioxide Circulatory system (heart; veins; arteries; capillaries) - helps transport materials necessary for respiration Digestive system (stomach; small intestine; oesophagus) - helps digest and absorb food for respiration Skeletal system - helps support parts of the body Breathing: Breathing in (inhale) - ribs move up and out, diaphragm contracts (pulled down) Breathing out (exhale) - ribs move down and in, diaphragm relaxes (moves upward) For respiration to occur, we need to get oxygen from the air to the blood, and remove waste carbon dioxide from the blood Alveoli in the lungs are adapted to make gas exchange happen easily and efficiently: they cause the lungs to have a very large surface area; are moist with thin walls; and have many capillaries Smoking is extremely bad for your health, containing: Carbon monoxide – a poisonous gas that reduces the amount of oxygen that red blood cells carry around the body Tar – a brown, sticky substance that consists of tiny particles and is formed when tobacco smoke condenses. Deposited in the lungs, it coats the surface of the alveoli Nicotine – an addictive drug that affects the central nervous system, increasing the heart rate and narrowing the blood vessels, causing high blood pressure Circulation & diet The circulatory system is the body's main transport system, carrying food and oxygen to the cells and taking waste products (carbon dioxide) away. It consists of the heart; arteries; veins; and capillaries The heart pumps blood around the body – in humans this is a four chambered pump. The right side of the heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs to pick up oxygen. The left side of the heart pumps the oxygenated blood from the lungs around the rest of the body (which is why it is more muscular) Arteries are thick-walled muscular tubes which carry blood away from the heart - fast flowing! Veins are thin walled tubes which carry blood back to the heart – they have a large diameter and valves as the blood flows slower Capillaries are extremely narrow tubes which carry blood through our tissues: their walls are just one cell thick - so thin that oxygen, food and waste products can easily pass through them Heart disease occurs when some of the heart muscle cells die. It is often caused by a build up of fatty substances inside the arteries (arteriosclerosis). This fatty material reduces the amount of blood which can get to the heart muscle tissue Smoking, drinking, lack of exercise and poor diet can all increase the likelihood of heart disease: a complete blockage leads to a heart attack (smoking constricts the blood vessels) Exercise can help - it strengthens the heart muscle tissue and improves circulation and blood flow. If a person is unfit their heart is not as muscular as a fit persons - this means it needs to work harder to pump blood around the body After exercise the heart will be working very hard, but if the arteries are clogged with excess cholesterol then not enough blood (containing oxygen) can get around the body This means the person’s cells will not be getting enough oxygen to function - which can be life threatening (hence if you are unfit you breathe harder and faster than a fit person after some exercise) If you have too little of a particular nutrient, we say that you have a deficiency in that nutrient, e.g. fibre deficiency can lead to constipation Alcohol & drugs Alcohol is a recreational drug that has short term and long term effects on the body Alcohol is a depressant that works by slowing down the nervous system and relaxing the brain - it can reach the brain in <1 minute The liver breaks down alcohol to remove this toxic drug from the body too much alcohol can damage the liver and brain Alcohol can result in some serious behavioural changes in people - it’s a depressant (slows the nerve impulses) which can make people feel relaxed and happy, but also severely slows their reaction times But it is different for different people - some people can become aggressive, confused and loud! These include brain damage - from brain cells being destroyed The liver is also extremely vulnerable - the liver breaks the toxic alcohol down, but too much of it slowly kills of the liver cells leading to cirrhosis and possibly cancer Alcohol also stops some vitamins being absorbed into the body - heavy drinkers will suffer vitamin deficiencies. And if you’re pregnant, all the poisonous alcohol in your blood will pass to the foetus - severely affecting its development A drug is any substance that changes the way the body or mind works. Drugs are substances that have effects on the body Medicines are drugs that help people suffering from pain or disease, such as aspirin or penicillin Other drugs, often called recreational drugs, are taken for pleasure. Some recreational drugs are legal, such as tobacco, alcohol and caffeine. Most other recreational drugs are illegal, such as cannabis, ecstasy and heroin. Recreational drugs are addictive, and they may be depressants or stimulants. Stimulants - increase the speed at which nerves carry messages (they make you feel more alert) Caffeine (legal) Cocaine Ecstasy Amphetamines They make you feel more energetic and confident, but they can damage the liver and heart. They can also cause loss of memory and concentration, and bring an increased risk of mental illness. Depressants - slow down messages in the brain and along the nerves (they make you feel more relaxed, happy, distorted view of surroundings) Alcohol (legal) Cannabis Solvents Heroin Some of the long-term effects of depressants on the body include damage to the liver, brain and heart Alcohol can cause weight gain; solvent abuse causes a rash around the nose and mouth; cannabis causes loss of memory and concentration, as well as an increased risk of mental illness. Antagonistic Muscles The skeleton has three main functions: Supporting the body Protecting some of the vital organs Helping the body move Muscles can only pull, and they work by getting shorter (contract) As muscles can only pull, each joint is moved by a pair of muscles - an antagonistic pair Muscles are attached to bones by strong tendons - when a muscle contracts, it pulls on the bone, and the bone can move if it is part of a joint The elbow joint lets our forearm move up or down, controlled by two muscles, the biceps on the front of the upper arm, and the triceps on the back of the upper arm: When the biceps muscle contracts, the forearm moves up When the triceps muscle contracts, the forearm moves down Pulled muscles - muscle fibres (linking muscle cells together) are stretched or torn Sprains - ligaments in a joint are torn (ligaments are cords which attach the bones together) Cartilage injuries - cartilage at the end of the bone gets torn Dislocations - bones in a joint move apart or out of line