Life Science: Cells
... Context: Hemoglobin is what gives red blood cells their color. mitosis Definition: Cell division Context: Cells reproduce by mitosis, a process in which a cell’s nucleus and other parts split into two new cells. nucleus Definition: The control center of a cell, which contains DNA and regulates the c ...
... Context: Hemoglobin is what gives red blood cells their color. mitosis Definition: Cell division Context: Cells reproduce by mitosis, a process in which a cell’s nucleus and other parts split into two new cells. nucleus Definition: The control center of a cell, which contains DNA and regulates the c ...
3) ALL LIVING THINGS RESPOND TO A STIMULUS
... To grow means to get bigger and to get bigger; more cells must be added. To increase numbers of cells, cell division must occur. Develop means to change into an adult ...
... To grow means to get bigger and to get bigger; more cells must be added. To increase numbers of cells, cell division must occur. Develop means to change into an adult ...
Study Guide for Life Systems Test
... #5 Cells are specialized to perform specific functions. Groups of similar cells join together to form ____________________________________. ...
... #5 Cells are specialized to perform specific functions. Groups of similar cells join together to form ____________________________________. ...
7th Grade Life Science Mid
... An element is a substance that cannot be broken down into any simpler substance by any typical means. Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen are the elements that make up the bulk of living things. Remember: CHON. A compound is a chemical combination of two or more elements. Elements come together t ...
... An element is a substance that cannot be broken down into any simpler substance by any typical means. Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen are the elements that make up the bulk of living things. Remember: CHON. A compound is a chemical combination of two or more elements. Elements come together t ...
Animal Systems and Specialized Cells Scavenger Hunt
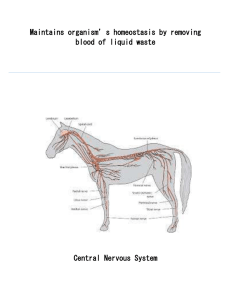
... system and carries impulses away from the CNS. ...
... system and carries impulses away from the CNS. ...
Cells, Tissues, Organs and Systems
... •Generalization: A group of cells working together make up tissues, a group of tissues working together make up organs, a group of organs working together make up an organ system, and a group of organ systems working together make up an organism. ...
... •Generalization: A group of cells working together make up tissues, a group of tissues working together make up organs, a group of organs working together make up an organ system, and a group of organ systems working together make up an organism. ...
Lec. No.10 Centrosome In cell biology, the centrosome is an
... the main microtubules organizing center ( MTOC) of the animal cell ,it is duplicated during S phase of the cell cycle . Centerioles , found only in animal cells, these paired organelles are located together near the nucleus. Each centerioles is made of nine bundles of microtubules (three per bundle) ...
... the main microtubules organizing center ( MTOC) of the animal cell ,it is duplicated during S phase of the cell cycle . Centerioles , found only in animal cells, these paired organelles are located together near the nucleus. Each centerioles is made of nine bundles of microtubules (three per bundle) ...
Image-conscious biology
... The way that we investigate these is primarily using high content screening. High content screening is image-based screening. What a person can do on a microscope, we can now do in small microtitre plates, which enable us to look at hundreds of thousands of images in a very short period of time. We ...
... The way that we investigate these is primarily using high content screening. High content screening is image-based screening. What a person can do on a microscope, we can now do in small microtitre plates, which enable us to look at hundreds of thousands of images in a very short period of time. We ...
Cells - Biloxi Public Schools
... called these structures 'cells' only saw the outer walls (cell walls) because cork cells are not alive ...
... called these structures 'cells' only saw the outer walls (cell walls) because cork cells are not alive ...
CENTRO ESCOLAR UNIVERSITY Biological Sciences Department
... interactions; structures of the cells and their functions; cell growth and oncogenic transformation transport and cell signaling and communications; cytoskeleton and the extracellular matrix; chromatin structure and RNA synthesis; genetic mechanisms of heritability of characteristics; and cell movem ...
... interactions; structures of the cells and their functions; cell growth and oncogenic transformation transport and cell signaling and communications; cytoskeleton and the extracellular matrix; chromatin structure and RNA synthesis; genetic mechanisms of heritability of characteristics; and cell movem ...
Stem cells
... • All animal cells originate from embryo stem cells. During the development of an embryo, most of these cells become specialised. They cannot later change to become a different type of cell. This process is called cell differentiation. • Adult stem cells can grow into any type of cell found in the b ...
... • All animal cells originate from embryo stem cells. During the development of an embryo, most of these cells become specialised. They cannot later change to become a different type of cell. This process is called cell differentiation. • Adult stem cells can grow into any type of cell found in the b ...
How does the food you eat provide energy to cells in
... think they have, compared With muulticellular organisms? In the last chapter, you learned of one disadvantage. Unicellular organisms cannot grow very lark. Also, because they must take in all the materials they need through their cell membranes, most unicellular organisms can only live in watery, ...
... think they have, compared With muulticellular organisms? In the last chapter, you learned of one disadvantage. Unicellular organisms cannot grow very lark. Also, because they must take in all the materials they need through their cell membranes, most unicellular organisms can only live in watery, ...
Grade 10 Academic Science – Biology
... across the cell membrane and veins are thin-walled with “doorways” to only permit blood flow in one direction. The respiratory system includes the lungs and other organs. Oxygen enters the body through lung tissues called alveoli. As well, the waste by-product of cellular respiration, carbon dioxide ...
... across the cell membrane and veins are thin-walled with “doorways” to only permit blood flow in one direction. The respiratory system includes the lungs and other organs. Oxygen enters the body through lung tissues called alveoli. As well, the waste by-product of cellular respiration, carbon dioxide ...
I`m Bigger Than You
... An organ, such as the heart, is made up of groups of tissues that work together to perform a specific function. The heart is a pump that keeps blood flowing throughout the body. The heart is primarily made up of muscle tissue, but also contains connective and nerve tissue. However, each of these ind ...
... An organ, such as the heart, is made up of groups of tissues that work together to perform a specific function. The heart is a pump that keeps blood flowing throughout the body. The heart is primarily made up of muscle tissue, but also contains connective and nerve tissue. However, each of these ind ...
Biology CPA Cell Organelles and Features J.Dolce
... 9. Describe the different types of plasma membrane proteins, with regard to structure, location and function. ...
... 9. Describe the different types of plasma membrane proteins, with regard to structure, location and function. ...
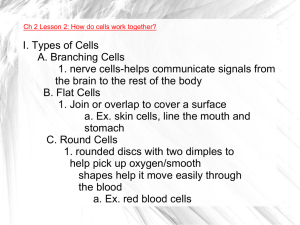
I. Types of Cells A. Branching Cells 1. nerve cells
... 1. Join or overlap to cover a surface a. Ex. skin cells, line the mouth and stomach C. Round Cells 1. rounded discs with two dimples to help pick up oxygen/smooth shapes help it move easily through the blood a. Ex. red blood cells ...
... 1. Join or overlap to cover a surface a. Ex. skin cells, line the mouth and stomach C. Round Cells 1. rounded discs with two dimples to help pick up oxygen/smooth shapes help it move easily through the blood a. Ex. red blood cells ...
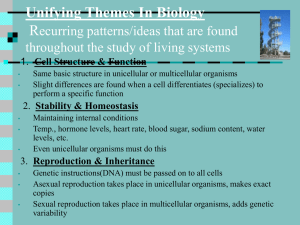
Unifying Themes in Biology Represent recurring patterns
... Temp., hormone levels, heart rate, blood sugar, sodium content, water levels, etc. Even unicellular organisms must do this ...
... Temp., hormone levels, heart rate, blood sugar, sodium content, water levels, etc. Even unicellular organisms must do this ...
Study
... molecules and waste products in the cell into smaller molecules is the lysosome. The organelle in which photosynthesis takes place is the chloroplast. It captures the energy from sunlight and uses it to make food. The organelle responsible for turning food and oxygen into energy is the mitochondrion ...
... molecules and waste products in the cell into smaller molecules is the lysosome. The organelle in which photosynthesis takes place is the chloroplast. It captures the energy from sunlight and uses it to make food. The organelle responsible for turning food and oxygen into energy is the mitochondrion ...
Partnering with God
... Intelligent Design – The Amazing Human Body 630 muscles and 206 bones 100 trillion cells – Each with a unique blueprint. Same with fingerprints, grass, snowflakes and water. Brain transmits 1,000 impulses every second Each brain cell can hold the equivalent information of five encyclopedias Heart pu ...
... Intelligent Design – The Amazing Human Body 630 muscles and 206 bones 100 trillion cells – Each with a unique blueprint. Same with fingerprints, grass, snowflakes and water. Brain transmits 1,000 impulses every second Each brain cell can hold the equivalent information of five encyclopedias Heart pu ...
Goal 6: Cell Theory Review Guide
... 2. Cells are too _small__ to be seen with the naked eye. What important “tool” or instrument needed to be discovered/invented before we could learn what we know about cells so far? microscope 3. Summarize the three statements of the Cell Theory. a. All living things _are composed of one or more cell ...
... 2. Cells are too _small__ to be seen with the naked eye. What important “tool” or instrument needed to be discovered/invented before we could learn what we know about cells so far? microscope 3. Summarize the three statements of the Cell Theory. a. All living things _are composed of one or more cell ...
Grade 7: A re-introduction to Biology - gillammscience
... Use your books and the internet to complete the following tasks. When you are finished go back to www.gillammscience.pbworks.com go to your class page, then to cell respiration activities. Insert your name in the table, upload the document into the column next to your name. ...
... Use your books and the internet to complete the following tasks. When you are finished go back to www.gillammscience.pbworks.com go to your class page, then to cell respiration activities. Insert your name in the table, upload the document into the column next to your name. ...
I. Circulatory System
... A) Can be repeated the same way and get the same results. B) Have large sample size/many test subjects. C) Are performed over longer periods of time. D) Test only one independent variable. All other characteristics of the tested groups should be the same. E) Are peer reviewed – examined by other sci ...
... A) Can be repeated the same way and get the same results. B) Have large sample size/many test subjects. C) Are performed over longer periods of time. D) Test only one independent variable. All other characteristics of the tested groups should be the same. E) Are peer reviewed – examined by other sci ...
./ ` . `.`4 Body Tissues 13. Figure 3-6: A. Simple squamous epLthelium
... portion; the lipid portion is indicated as the major part of the membrane composed o f small spheres, each w ith two "tai]s." Amino adds and glucose also e nter the cell from dle exterior but do so by auaching to a p rotein carrier (ind icated as large, solid, irregLl larl y shaped strucmres extendi ...
... portion; the lipid portion is indicated as the major part of the membrane composed o f small spheres, each w ith two "tai]s." Amino adds and glucose also e nter the cell from dle exterior but do so by auaching to a p rotein carrier (ind icated as large, solid, irregLl larl y shaped strucmres extendi ...
1 Unit 1: The Body as a Whole
... Examples: ethanol (alcohol, contains both polar and non-polar regions); also fatty acids, glycerol, steroids, etc & nonpolar gases like O2) ii) Facilitated diffusion – large, polar molecules such as simple sugars - Combine with protein carriers (i.e. protein-mediated transport) • Osmosis ...
... Examples: ethanol (alcohol, contains both polar and non-polar regions); also fatty acids, glycerol, steroids, etc & nonpolar gases like O2) ii) Facilitated diffusion – large, polar molecules such as simple sugars - Combine with protein carriers (i.e. protein-mediated transport) • Osmosis ...
Cell theory

In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory which describes the properties of cells. These cells are the basic unit of structure in all organisms and also the basic unit of reproduction. With continual improvements made to microscopes over time, magnification technology advanced enough to discover cells in the 17th century. This discovery is largely attributed to Robert Hooke, and began the scientific study of cells, also known as cell biology. Over a century later, many debates about cells began amongst scientists. Most of these debates involved the nature of cellular regeneration, and the idea of cells as a fundamental unit of life. Cell theory was eventually formulated in 1838. This is usually credited to Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, many other scientists like Rudolf Virchow contributed to the theory. Cell theory has become the foundation of biology and is the most widely accepted explanation of the function of cells.The three tenets to the cell theory are as described below: All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells arise from pre-existing, living cells, by biogenesis.