Vocabulary for Chapter 4 Skeletal and Muscular Systems
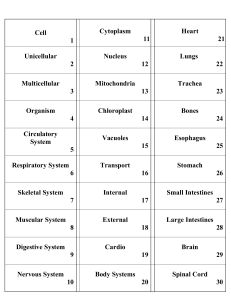
... Vocabulary for Chapter 4 Skeletal and Muscular Systems - Part 1 Levels of Organization: ...
... Vocabulary for Chapter 4 Skeletal and Muscular Systems - Part 1 Levels of Organization: ...
5th Grade Science Human Body Vocabulary Cards
... The central part of the cell containing DNA responsible for growth and development ...
... The central part of the cell containing DNA responsible for growth and development ...
Dev Biol L1
... multicellular organism, with hundreds of different cell types, all formed at the correct time and in the correct place to build a functioning body and perform all the individual functions of life. ...
... multicellular organism, with hundreds of different cell types, all formed at the correct time and in the correct place to build a functioning body and perform all the individual functions of life. ...
Homework Exercise 1 - Cells, Tissues and Organs 1. Place the
... Job Vacancies for Specialised Cells ...
... Job Vacancies for Specialised Cells ...
Cell Transport graphic organizer
... _______________ keep plants from wilting because it causes _________ to flow into the cell. ...
... _______________ keep plants from wilting because it causes _________ to flow into the cell. ...
Diffusion and Osmosis in plant and animal cells
... of cells. • Explain what a selectively permeable membrane is. • Explain what is meant by a concentration gradient. • Define osmosis using the terms selectively permeable membrane and concentration gradient. • Identify water concentration gradients when given percentage solute concentrations. • Predi ...
... of cells. • Explain what a selectively permeable membrane is. • Explain what is meant by a concentration gradient. • Define osmosis using the terms selectively permeable membrane and concentration gradient. • Identify water concentration gradients when given percentage solute concentrations. • Predi ...
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 - Organization - mics-bio2
... same osmotic pressure as cell hypotonic solution = less than the cell hypertonic solution = more than the cell ...
... same osmotic pressure as cell hypotonic solution = less than the cell hypertonic solution = more than the cell ...
Cells - Effingham County Schools
... water to pass, but not the solutes in the water; keeps water inside the cells ...
... water to pass, but not the solutes in the water; keeps water inside the cells ...
Cells
... -In Unicellular organisms one cell must carry out all the functions needed to keep it alive. -It must be able to move, obtain food, reproduce, and respond to the environment -Unicellular organisms cannot grow very large. Also, because they must take in all the materials that they need through their ...
... -In Unicellular organisms one cell must carry out all the functions needed to keep it alive. -It must be able to move, obtain food, reproduce, and respond to the environment -Unicellular organisms cannot grow very large. Also, because they must take in all the materials that they need through their ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI
... 02. Give the principle of dark field microscope. 03. What are polysomes? 04. Pinocytosis – Explain. 05. What are SAT chromosomes? 06. Define karyotype. 07. Briefly explain amitosis. 08. What happens during G1 phase of Cell Cycle? 09. What is mutation theory? 10. What is molecular evolution? PART – B ...
... 02. Give the principle of dark field microscope. 03. What are polysomes? 04. Pinocytosis – Explain. 05. What are SAT chromosomes? 06. Define karyotype. 07. Briefly explain amitosis. 08. What happens during G1 phase of Cell Cycle? 09. What is mutation theory? 10. What is molecular evolution? PART – B ...
100 living environment regents facts
... 61. Hormones are specific chemical messenger molecules that travel though the blood and attach to receptor proteins on the surface of target cells. 62. The hormone insulin is secreted from the pancreas and lowers the glucose level in the blood. 63. Hormonal feedback mechanisms maintain homeostasis i ...
... 61. Hormones are specific chemical messenger molecules that travel though the blood and attach to receptor proteins on the surface of target cells. 62. The hormone insulin is secreted from the pancreas and lowers the glucose level in the blood. 63. Hormonal feedback mechanisms maintain homeostasis i ...
Study Guide Cells Unit Test
... 41. Besides osmosis and diffusion, what are 2 other ways that cells can move materials in and out of the cell? Cells could use energy during active transport to move particles against the norm (moving from low to high) or to move molecule that are a little too big. The cell can use endocytosis and e ...
... 41. Besides osmosis and diffusion, what are 2 other ways that cells can move materials in and out of the cell? Cells could use energy during active transport to move particles against the norm (moving from low to high) or to move molecule that are a little too big. The cell can use endocytosis and e ...
Cells: Beyond the Membrane
... Form cell skeleton that supports cellular structure & allows for cell movement (like skeletal & muscular systems in humans) ...
... Form cell skeleton that supports cellular structure & allows for cell movement (like skeletal & muscular systems in humans) ...
Transport Phenomena in Cell Biology - Thermal
... molecular interactions store and process information • Transcription networks regulate the production of proteins at longer timescales • Signaling networks process information from the environment at shorter timescales Ben-Schorr et al, Nature Genetics 31564 ...
... molecular interactions store and process information • Transcription networks regulate the production of proteins at longer timescales • Signaling networks process information from the environment at shorter timescales Ben-Schorr et al, Nature Genetics 31564 ...
CH 5 – THE FUNDAMENTAL UNIT OF LIFE
... Ans- A cell is defined a sthe structural unit of life or the basic unit of life. 2. White the name of the scientist and the year in which the cell was observed. Ans – Robert Hooke in the year 1665 while observing cork, cell from the bark of the tree with the help of a self-designed primitive microsc ...
... Ans- A cell is defined a sthe structural unit of life or the basic unit of life. 2. White the name of the scientist and the year in which the cell was observed. Ans – Robert Hooke in the year 1665 while observing cork, cell from the bark of the tree with the help of a self-designed primitive microsc ...
Unit 1 Test Review Guide: 5 pts Extra Credit on Summative Category
... Organization of the Human Body 23. How is the human body organized? How are a cell, tissue, organ, and organ system related? ...
... Organization of the Human Body 23. How is the human body organized? How are a cell, tissue, organ, and organ system related? ...
Cells and Systems Quiz – Section 1 and 2 – Study Guide
... Know the major parts/organs of each system. Describe the function of villa. What is the difference between the small and large intestine. Know where gas exchange occurs. How does oxygen get into our circulatory system? Explain two ways in which veins and arteries are different. List four parts of bl ...
... Know the major parts/organs of each system. Describe the function of villa. What is the difference between the small and large intestine. Know where gas exchange occurs. How does oxygen get into our circulatory system? Explain two ways in which veins and arteries are different. List four parts of bl ...
Biology 2011-2012
... Proteins – Amino acids are building blocks. All of your genetics are codes for the many different proteins, including the group of catalysts called enzymes. PEPTIDE BONDS OR POLYPEPTIDE BONDS! d. Nucleic Acids – monomers are nucleotides. Found in DNA and RNA Water is one of most important compounds ...
... Proteins – Amino acids are building blocks. All of your genetics are codes for the many different proteins, including the group of catalysts called enzymes. PEPTIDE BONDS OR POLYPEPTIDE BONDS! d. Nucleic Acids – monomers are nucleotides. Found in DNA and RNA Water is one of most important compounds ...
115 things you should know for the living environment
... 19. New individuals of an existing species are produced through the process of reproduction. 20. Asexual reproduction produces offspring that are genetically identical to the parent organism. 21. Modern cell biology techniques allow complex organisms such as mammals to be clones. 22. DNA mutations ...
... 19. New individuals of an existing species are produced through the process of reproduction. 20. Asexual reproduction produces offspring that are genetically identical to the parent organism. 21. Modern cell biology techniques allow complex organisms such as mammals to be clones. 22. DNA mutations ...
Cells and Cellular Organization
... plants as “cells” (cork cells) Mattias Schleiden: cells make up every part of plants Theordar Schwann: animal tissues were also made of cells Robert Brown: discovers the nucleus Schleiden: nucleus plays a role in cell division A. All living things are made of a single cell (bacteria) or many cells ( ...
... plants as “cells” (cork cells) Mattias Schleiden: cells make up every part of plants Theordar Schwann: animal tissues were also made of cells Robert Brown: discovers the nucleus Schleiden: nucleus plays a role in cell division A. All living things are made of a single cell (bacteria) or many cells ( ...
Homeostasis (Active and Passive Transport)
... This doesn’t often happen because cells in the body of multicellular organisms are protected from fresh water, and are instead bathed in isotonic fluids such as blood In plants, the cell wall surrounds the cell membrane: so even when the cell swells, the walls prevent it from bursting/expanding too ...
... This doesn’t often happen because cells in the body of multicellular organisms are protected from fresh water, and are instead bathed in isotonic fluids such as blood In plants, the cell wall surrounds the cell membrane: so even when the cell swells, the walls prevent it from bursting/expanding too ...
115 things you should know for the living environment regents exam
... 85. An increase in human population has caused a depletion of the world finite resources and an increase in environmental damage. 86. Pollution by humans has disrupted the balance in many ecosystems and subsequently has endangered many species. 87. Acid rain is a major environmental problem caused ...
... 85. An increase in human population has caused a depletion of the world finite resources and an increase in environmental damage. 86. Pollution by humans has disrupted the balance in many ecosystems and subsequently has endangered many species. 87. Acid rain is a major environmental problem caused ...
Cells Alive - Net Start Class
... c. What is the size relationship between ragweed pollen and Staphylococcus bacteria? ____________________________________________________________________________________ d. What is the size relationship between lymphocytes (white blood cells) and the Ebola virus? ____________________________________ ...
... c. What is the size relationship between ragweed pollen and Staphylococcus bacteria? ____________________________________________________________________________________ d. What is the size relationship between lymphocytes (white blood cells) and the Ebola virus? ____________________________________ ...
Cell theory

In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory which describes the properties of cells. These cells are the basic unit of structure in all organisms and also the basic unit of reproduction. With continual improvements made to microscopes over time, magnification technology advanced enough to discover cells in the 17th century. This discovery is largely attributed to Robert Hooke, and began the scientific study of cells, also known as cell biology. Over a century later, many debates about cells began amongst scientists. Most of these debates involved the nature of cellular regeneration, and the idea of cells as a fundamental unit of life. Cell theory was eventually formulated in 1838. This is usually credited to Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, many other scientists like Rudolf Virchow contributed to the theory. Cell theory has become the foundation of biology and is the most widely accepted explanation of the function of cells.The three tenets to the cell theory are as described below: All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells arise from pre-existing, living cells, by biogenesis.