The Cell
... contain organelles that perform the functions needed for life. All cells must maintain homeostasis (balance). They function in a very narrow range of temperature, pH, O2, CO2, food and waste. ...
... contain organelles that perform the functions needed for life. All cells must maintain homeostasis (balance). They function in a very narrow range of temperature, pH, O2, CO2, food and waste. ...
The Basic Structure of Cells
... Discovery of cells Robert Hooke: • A British scientist in the seventeenth century • He observed a thin piece of cork under the microscope that he made on his own • He saw the structures that look like “little rooms” & gave the name “cells” ...
... Discovery of cells Robert Hooke: • A British scientist in the seventeenth century • He observed a thin piece of cork under the microscope that he made on his own • He saw the structures that look like “little rooms” & gave the name “cells” ...
AP Biology Body System Test Review Test on April 19th!!! Chapter
... 9. A marine sea star was mistakenly placed in freshwater and it died. What is the most likely explanation for its death? A) The sea star was stressed and needed more time to acclimate to new conditions. B) The sea star is hyperosmotic to the freshwater, and it could not osmoregulate. C) The osmoreg ...
... 9. A marine sea star was mistakenly placed in freshwater and it died. What is the most likely explanation for its death? A) The sea star was stressed and needed more time to acclimate to new conditions. B) The sea star is hyperosmotic to the freshwater, and it could not osmoregulate. C) The osmoreg ...
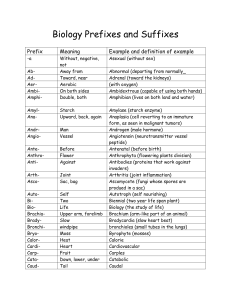
Biology Prefixes and Suffixes
... internally to maintain a constant body temperature) Epiphyte (A plant that grows on the surface of another plant for support) Erythrocyte (red blood cell) Eukaryote (Organism whose cells contains a “true” membrane bound nucleus) Exoskeleton (hard outer surface that provides support or protection for ...
... internally to maintain a constant body temperature) Epiphyte (A plant that grows on the surface of another plant for support) Erythrocyte (red blood cell) Eukaryote (Organism whose cells contains a “true” membrane bound nucleus) Exoskeleton (hard outer surface that provides support or protection for ...
Immune System
... Vaccines (Active immunity)– viral protein without genetic Info. (either from outside of envelope or the capsid protein itself) Prepares immune system for future Attacks, gives time to build up defense (helps Acquired Immunity) ...
... Vaccines (Active immunity)– viral protein without genetic Info. (either from outside of envelope or the capsid protein itself) Prepares immune system for future Attacks, gives time to build up defense (helps Acquired Immunity) ...
B cells
... permits recognition of specific antigen recognizes Ag presented on surface of host cells T cell clones differentiate into effector T cells second signal provided by dendritic cells some T cells form memory cells ...
... permits recognition of specific antigen recognizes Ag presented on surface of host cells T cell clones differentiate into effector T cells second signal provided by dendritic cells some T cells form memory cells ...
Chapter 3b
... diminished, mucous starts to build up in the small airways making it harder for the smoker to breathe and causing the characteristic smokers cough in order to clear out the airways. Eventually though, the ciliated columnar cells are totally displaced. As can be seen below ominous changes have taken ...
... diminished, mucous starts to build up in the small airways making it harder for the smoker to breathe and causing the characteristic smokers cough in order to clear out the airways. Eventually though, the ciliated columnar cells are totally displaced. As can be seen below ominous changes have taken ...
carson and gavy doc
... can influence human behavior. The human organism is so complex, because it is doing many of these things at one time. It’s a good thing cells know what to do in order to keep us going. The next type of organism is plants. They are much less complex than humans. Even still, it is estimated that there ...
... can influence human behavior. The human organism is so complex, because it is doing many of these things at one time. It’s a good thing cells know what to do in order to keep us going. The next type of organism is plants. They are much less complex than humans. Even still, it is estimated that there ...
Week 2 Lecture Summarys copy
... - all major organs are constructed in this time period;at the end of this stage the cells look like a human being - nutrients are pumped to differentiating cells to nourish the fetus (by third week the circulatory system forms and the heart starts to beat - at about the same time (start of week 3) t ...
... - all major organs are constructed in this time period;at the end of this stage the cells look like a human being - nutrients are pumped to differentiating cells to nourish the fetus (by third week the circulatory system forms and the heart starts to beat - at about the same time (start of week 3) t ...
Cell Unit
... Kingdom. Monerans are considered by many scientists to be the oldest life forms on Earth, and the ancestors of all the other types of life that have since evolved. ...
... Kingdom. Monerans are considered by many scientists to be the oldest life forms on Earth, and the ancestors of all the other types of life that have since evolved. ...
The Ever-Spreading Molecular World In Living Organisms Diffusion
... Spreading of molecules or tiny particles of materials in all directions, moving from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration, until uniformly distributed; occurs in gas, liquids or solids, allowing diffusing particles to gradually mix with surrounding molecules. Open the gates ...
... Spreading of molecules or tiny particles of materials in all directions, moving from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration, until uniformly distributed; occurs in gas, liquids or solids, allowing diffusing particles to gradually mix with surrounding molecules. Open the gates ...
6.1.01a - UC CEAS
... a) Organs are made from one type of tissue. b) Tissues are made from one type of organ. c) Tissues are made from one different types of organs. d) Organs are made from different types of tissues. 4) Which is an example of a group of cells with a common structure and function? a) Kidney b) Kidney tis ...
... a) Organs are made from one type of tissue. b) Tissues are made from one type of organ. c) Tissues are made from one different types of organs. d) Organs are made from different types of tissues. 4) Which is an example of a group of cells with a common structure and function? a) Kidney b) Kidney tis ...
National 5 Biology Unit 1 cell Biology – Homework 2
... National 5 Biology Unit 1 cell Biology – Homework 2 ...
... National 5 Biology Unit 1 cell Biology – Homework 2 ...
Chapter 15: The Cell - Heritage Christian School
... Cellular Transport: Moving materials in and out In plants the tough cellulose cell wall is really full of holes and will allow almost anything in and out. The cell membrane however, is a very complex structure made of lipids and specialized proteins. The membrane is thin and flexible but is selecti ...
... Cellular Transport: Moving materials in and out In plants the tough cellulose cell wall is really full of holes and will allow almost anything in and out. The cell membrane however, is a very complex structure made of lipids and specialized proteins. The membrane is thin and flexible but is selecti ...
MTC31 - Plasma Membranes and Permeability
... o Transcellular fluid which is trapped within spaces between epithelial cells The ICF and ECF have equal osmolality values of 290mosmol/Kg Cells are contained by a plasma membrane which is a fatty film based on a lipid bi-layer 5nm thick Molecules within the bi-layer are mobile – mostly lipids and ( ...
... o Transcellular fluid which is trapped within spaces between epithelial cells The ICF and ECF have equal osmolality values of 290mosmol/Kg Cells are contained by a plasma membrane which is a fatty film based on a lipid bi-layer 5nm thick Molecules within the bi-layer are mobile – mostly lipids and ( ...
Unit C: Cell Structure and Function
... The microscope is a vital scientific tool that aids in scientific advancement. All living organisms are made of cells with specialized parts and functions. ...
... The microscope is a vital scientific tool that aids in scientific advancement. All living organisms are made of cells with specialized parts and functions. ...
CRCT Review PPT
... Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Which of the following is an example of diffusion? A. Open a gate to allow horses to pass ...
... Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Which of the following is an example of diffusion? A. Open a gate to allow horses to pass ...
Chapter3 - sshsanatomy
... Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. New cells are produced from existing cells. ...
... Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. New cells are produced from existing cells. ...
SMK CONVENT BUKIT NANAS, KUALA LUMPUR
... A student is able to: structure and function compare the epidermal cells of • draw and label an onion or cells of Hydrilla leaf animal cell. with human cheek cells. • draw and label a Study electron micrographs of plant cell animal cells and plant cells to • identify the cellular identify cellular c ...
... A student is able to: structure and function compare the epidermal cells of • draw and label an onion or cells of Hydrilla leaf animal cell. with human cheek cells. • draw and label a Study electron micrographs of plant cell animal cells and plant cells to • identify the cellular identify cellular c ...
Chapter 3: Cell
... • a barrier allows some substances to pass through it while excluding others. • Thus, it allows nutrients to enter the cell but keeps many undesirable substances out. At the same time, valuable cell proteins and other substances are kept within the cell, and wastes are allowed to pass out of it. • M ...
... • a barrier allows some substances to pass through it while excluding others. • Thus, it allows nutrients to enter the cell but keeps many undesirable substances out. At the same time, valuable cell proteins and other substances are kept within the cell, and wastes are allowed to pass out of it. • M ...
THE LIVING ENVIRONMENT VOCABULARY
... down large food particles into smaller ones. The ability to make things look larger than they are. Rod-shaped cell structures that produce most of the energy needed to carry out the cell’s function. The stage of the cell cycle during which the cell’s nucleus divides into two new nuclei and one copy ...
... down large food particles into smaller ones. The ability to make things look larger than they are. Rod-shaped cell structures that produce most of the energy needed to carry out the cell’s function. The stage of the cell cycle during which the cell’s nucleus divides into two new nuclei and one copy ...
Cell - St. Pius X High School
... The Discovery of Cells • Robert Hooke - 1st person to see cells, he was looking at cork and called them "a great many boxes.” (1665) ...
... The Discovery of Cells • Robert Hooke - 1st person to see cells, he was looking at cork and called them "a great many boxes.” (1665) ...
cells?
... Cell Theory= explanation of how cells & life are related Cell Theory states: all living things are composed of cells, cells are the basic unit of structure & fxn-smallest unit of life, cells come from other cells Schleiden, Schwann, Virchow made the Cell Theory in mid-1800’s Hx OF MICROBIOLOGY ...
... Cell Theory= explanation of how cells & life are related Cell Theory states: all living things are composed of cells, cells are the basic unit of structure & fxn-smallest unit of life, cells come from other cells Schleiden, Schwann, Virchow made the Cell Theory in mid-1800’s Hx OF MICROBIOLOGY ...
Cell theory

In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory which describes the properties of cells. These cells are the basic unit of structure in all organisms and also the basic unit of reproduction. With continual improvements made to microscopes over time, magnification technology advanced enough to discover cells in the 17th century. This discovery is largely attributed to Robert Hooke, and began the scientific study of cells, also known as cell biology. Over a century later, many debates about cells began amongst scientists. Most of these debates involved the nature of cellular regeneration, and the idea of cells as a fundamental unit of life. Cell theory was eventually formulated in 1838. This is usually credited to Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, many other scientists like Rudolf Virchow contributed to the theory. Cell theory has become the foundation of biology and is the most widely accepted explanation of the function of cells.The three tenets to the cell theory are as described below: All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells arise from pre-existing, living cells, by biogenesis.