* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Animal Systems and Specialized Cells Scavenger Hunt
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Stem-cell therapy wikipedia , lookup
Induced pluripotent stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
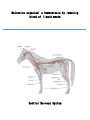
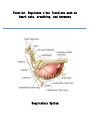
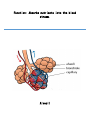
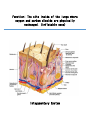
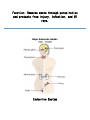
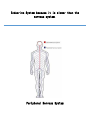
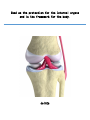
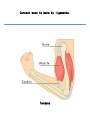
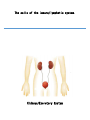
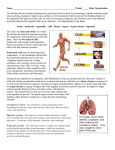
Maintains organism’s homeostasis by removing blood of liquid waste Central Nervous System Function: Regulates vital functions such as heart rate, breathing, and hormones Respiratory System Function: Used to exchange carbon dioxide for oxygen. Circulatory System Function: Transports oxygen to the cells and carries carbon dioxide away from the cells Digestive System Function: Absorbs nutrients into the blood stream. Alveoli Function: The site inside of the lungs where oxygen and carbon dioxide are physically exchanged. (inflatable sacs) Integumentary System Function: Removes waste through perspiration and protects from injury, infection, and UV rays. Endocrine System Function: releases chemicals into your bloodstream that control body growth, reproduction, and metabolism. Second Messenger System Endocrine System because it is slower than the nervous system. Peripheral Nervous System Carries information toward the central nervous system and carries impulses away from the CNS. Skeletal System Used as the protection for the internal organs and is the framework for the body. Joints Connect bone to bone by ligaments. Tendons Connect bone to muscle. Muscular System Actin and myosin contract to move your muscles. Voluntary Muscles Muscles that you can control such as the arms, legs, hands, and face. Involuntary Muscles Muscles that you cannot control including the stomach, heart, and intestines. Reproductive System Used to produce gametes. Immune/Lymphatic Fights off diseases caused by pathogens. Hemoglobin A red protein on the red blood cell that carries oxygen. Red Blood Cell Carries oxygen from the lungs to the cells in the body. Also carries the carbon dioxide back to the lungs to exhale. Palisade Cells Contains a high concentration of chloroplasts to maximize photosynthesis. Xylem Transports water/ minerals up the stem from the soil. Root Hair Cell Increases the amount of surface area the roots have to absorb water and minerals. Phloem Transports food up and down the plant. Epithelial Cells The cells of the integumentary system. Neurons The cells of the nervous system. Muscle Cells The cells of the muscular system. White blood cells The cells of the immune/lymphatic system. Kidneys/Excretory System Central Nervous System Respiratory System Circulatory System Digestive System Alveoli Integumentary System Endocrine System Second Messenger System Peripheral Nervous System Skeletal System Joints Tendons Muscular System Voluntary Muscles Involuntary Muscles Reproductive System Immune/Lymphatic System Hemoglobin Red Blood Cells Palisade Cells Xylem Root Hair Cells Phloem Epithelial Cells Neurons Nerve Cells Muscle Cells White Blood Cells Kidneys/Excretory System