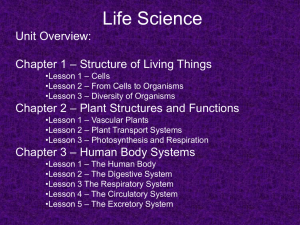
2017 Year 8 Term3 Programme
... Cells are the basic units of living things; they have specialised structures and functions (ACSSU149) ...
... Cells are the basic units of living things; they have specialised structures and functions (ACSSU149) ...
What elements am I made of?
... • Amylase - breaks down sugar • Proteases - break down proteins • Lipases - break down lipids • Catalase - breaks down hydrogen peroxide ...
... • Amylase - breaks down sugar • Proteases - break down proteins • Lipases - break down lipids • Catalase - breaks down hydrogen peroxide ...
Spring Semester Exam Review
... Q9. Why do turtles lay more eggs than can survive? (hint: think about what happens to a lot of them as they travel to the ocean after they hatch) OVERPRODUCTION is necessary because natural selection requires that some organisms will be less fit and die off. If there were not more offspring than can ...
... Q9. Why do turtles lay more eggs than can survive? (hint: think about what happens to a lot of them as they travel to the ocean after they hatch) OVERPRODUCTION is necessary because natural selection requires that some organisms will be less fit and die off. If there were not more offspring than can ...
Study guide packet part 1
... muscles get sore. Bacteria also make lactic acid. Alcohol Fermentation- this is the type of fermentation that is done by yeast. It makes alcohol and can make it from apple juice. If we put apple juice or glucose and yeast into a test tube, the ...
... muscles get sore. Bacteria also make lactic acid. Alcohol Fermentation- this is the type of fermentation that is done by yeast. It makes alcohol and can make it from apple juice. If we put apple juice or glucose and yeast into a test tube, the ...
AP Biology Unit 1- The Chemistry of Life
... Biology Unit 3—Cell Biology—Packet Life’s little compartments: Types of cells and how they work After the last unit, this one may be a little refreshing, since almost all you need to know about this unit can be summarized in a few tables and figures. This unit is about cells Define cell:____________ ...
... Biology Unit 3—Cell Biology—Packet Life’s little compartments: Types of cells and how they work After the last unit, this one may be a little refreshing, since almost all you need to know about this unit can be summarized in a few tables and figures. This unit is about cells Define cell:____________ ...
ANSWERS Performance Final Study
... Part of the experiment not being tested -- used for comparison. (normal, typical) 4. What is an experimental group? Part of the experiment that is being tested 5. A student is studying the effects of radiation on the growth of plants. She exposed four plants of the same species to different amounts ...
... Part of the experiment not being tested -- used for comparison. (normal, typical) 4. What is an experimental group? Part of the experiment that is being tested 5. A student is studying the effects of radiation on the growth of plants. She exposed four plants of the same species to different amounts ...
Revision Sheet Quarter 1 2014-2015 Department:
... a process called cellular respiration where oxygen is used to breakdown sugar molecules and release energy stored in it. Mitochondria then transfer the energy released and store it in ATP molecules. B- Ribosomes: responsible for making proteins by putting aminoacid chains together using instructions ...
... a process called cellular respiration where oxygen is used to breakdown sugar molecules and release energy stored in it. Mitochondria then transfer the energy released and store it in ATP molecules. B- Ribosomes: responsible for making proteins by putting aminoacid chains together using instructions ...
Final Exam Review Part 1
... inside the plasma membrane, not including the nucleus 16. Smooth E and rough ER are different because a. smooth ER has ribosomes attached and rough ER does not smooth ER has no ribosomes attached and rough ER does smoother ER has mitochondria attached and rough ER does not smooth ER has no mitochond ...
... inside the plasma membrane, not including the nucleus 16. Smooth E and rough ER are different because a. smooth ER has ribosomes attached and rough ER does not smooth ER has no ribosomes attached and rough ER does smoother ER has mitochondria attached and rough ER does not smooth ER has no mitochond ...
Name: John D. Ransom Institution: Oklahoma State University
... Death -------------------¥~~Hses-~e~e~----------------------Life Fig. 2 Line Between Life and Death ...
... Death -------------------¥~~Hses-~e~e~----------------------Life Fig. 2 Line Between Life and Death ...
Bio 101 Cumulative FINAL Homework Prof. Fournier
... B) Mitochondria and chloroplasts contain genetic material and can replicate. C) All cells arise from preexisting cells. D) The cell is the basic functional unit of all living things. ...
... B) Mitochondria and chloroplasts contain genetic material and can replicate. C) All cells arise from preexisting cells. D) The cell is the basic functional unit of all living things. ...
Diversity in Living Organisms
... 3. Mode of Nutrition- Autotrophic/ Heterotrophic. This could dictate the body design of ornanisms which need to look for food need to have locomotory organs (animals), while those who can make their food don’t(plants). 4. Body development and organisation into parts, Presence of specialised parts de ...
... 3. Mode of Nutrition- Autotrophic/ Heterotrophic. This could dictate the body design of ornanisms which need to look for food need to have locomotory organs (animals), while those who can make their food don’t(plants). 4. Body development and organisation into parts, Presence of specialised parts de ...
Prokaryotes
... b) DNA/RNA surrounded by capsid (a protein coat) c) Retroviruses – contain RNA as genetic info i) Ex: AIDS d) Considered non-living because they are not made up of cells and cannot live or reproduce on their own e) Some diseases are caused by viruses i) Cannot be treated with antibiotics because the ...
... b) DNA/RNA surrounded by capsid (a protein coat) c) Retroviruses – contain RNA as genetic info i) Ex: AIDS d) Considered non-living because they are not made up of cells and cannot live or reproduce on their own e) Some diseases are caused by viruses i) Cannot be treated with antibiotics because the ...
Topic 1 – Measurement and graphing
... Cells – all living things are made of cells Homeostasis – living things maintain a constant internal environment Respond to environment – living things are able to move and respond to conditions like temperature, sunlight, water etc. Obtain and use energy Grow – get bigger, develop into ma ...
... Cells – all living things are made of cells Homeostasis – living things maintain a constant internal environment Respond to environment – living things are able to move and respond to conditions like temperature, sunlight, water etc. Obtain and use energy Grow – get bigger, develop into ma ...
Sickle Cell Anemia - Woodcliff Lake School
... This recessive genetic disease (ss) illustrates the point that a change in DNA can have major consequences. In this mutation, one base that is part of a gene on chromosomes 11 is changed. People with 2 copies of this mutation (ss) have a disease called sickle cell anemia. Their bodies, because of th ...
... This recessive genetic disease (ss) illustrates the point that a change in DNA can have major consequences. In this mutation, one base that is part of a gene on chromosomes 11 is changed. People with 2 copies of this mutation (ss) have a disease called sickle cell anemia. Their bodies, because of th ...
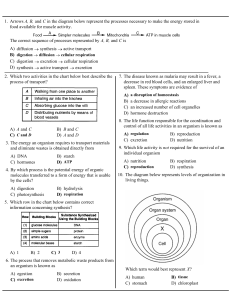
1. Arrows A, B, and C in the diagram below represent the processes
... 26. Base your answer to the following question on the information below and on your knowledge of biology. A solution of an enzyme normally found in the human body was added to a flask containing a solution of proteins in distilled water, and then the flask was stoppered. This mixture was then mainta ...
... 26. Base your answer to the following question on the information below and on your knowledge of biology. A solution of an enzyme normally found in the human body was added to a flask containing a solution of proteins in distilled water, and then the flask was stoppered. This mixture was then mainta ...
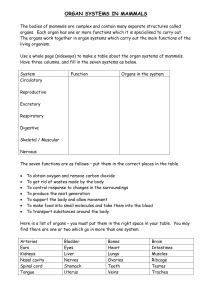
doc Organ systems table Table to fill in which will
... Nervous The seven functions are as follows – put them in the correct places in the table. ...
... Nervous The seven functions are as follows – put them in the correct places in the table. ...
Name: :___________Date
... Name:_________________________Period:___________Date:______________ Google: “biology interactive” and choose: “life organization” and view animation. List the steps of organization in order from smallest to largest and an example of each. CELLS ALIVE ...
... Name:_________________________Period:___________Date:______________ Google: “biology interactive” and choose: “life organization” and view animation. List the steps of organization in order from smallest to largest and an example of each. CELLS ALIVE ...
Cells and Cellular Organization
... II. Cell Theory Robert Hooke: described the units that make up plants as “cells” (cork cells) Mattias Schleiden: cells make up every part of plants Theordar Schwann: animal tissues were also made of cells Robert Brown: discovers the nucleus Schleiden: nucleus plays a role in cell division A. All li ...
... II. Cell Theory Robert Hooke: described the units that make up plants as “cells” (cork cells) Mattias Schleiden: cells make up every part of plants Theordar Schwann: animal tissues were also made of cells Robert Brown: discovers the nucleus Schleiden: nucleus plays a role in cell division A. All li ...
Semester I exam study guide
... useful but mostly they are harmful as changes in DNA can change the way a cell behaves. As genes are a set of hereditary materials that contain instructions necessary for a cell to work so if some of these instructions go wrong the cell may not know how to function. Mutations can be inherited which ...
... useful but mostly they are harmful as changes in DNA can change the way a cell behaves. As genes are a set of hereditary materials that contain instructions necessary for a cell to work so if some of these instructions go wrong the cell may not know how to function. Mutations can be inherited which ...
Biotechnology Notes - Mrs. Kievit Science
... › The use of a patient’s ______ to select treatment that is suited to a patient’s individual genes › The goal is to develop medicine unique to an individual. Biotechnology in Microbiology Microbiology › Field of science that studies ____________________ Microbes can work for and against humans › ...
... › The use of a patient’s ______ to select treatment that is suited to a patient’s individual genes › The goal is to develop medicine unique to an individual. Biotechnology in Microbiology Microbiology › Field of science that studies ____________________ Microbes can work for and against humans › ...
Unit 2 - Cells and Body Systems 1.0 Characteristics of Living Things
... 2.0 Cells play a vital role ...
... 2.0 Cells play a vital role ...
File - G. Scott`s Bio Page
... adhesion (think of adhesive band aid) – Allows water to dissolve most substances = universal solvent – Water is less dense when it freezes, so ponds do not freeze from the bottom up; only the top freezes ...
... adhesion (think of adhesive band aid) – Allows water to dissolve most substances = universal solvent – Water is less dense when it freezes, so ponds do not freeze from the bottom up; only the top freezes ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.