Glossary - The Teacher-Friendly Guide™ to Evolution Using
... and other structures that function to permanently unite the two valves. The study of cells and tissues at the microscopic level. Living as plankton through all stages of a life cycle. Having the same structure and origin, although current function might differ. An “educated guess,” based on evidence ...
... and other structures that function to permanently unite the two valves. The study of cells and tissues at the microscopic level. Living as plankton through all stages of a life cycle. Having the same structure and origin, although current function might differ. An “educated guess,” based on evidence ...
Presentations : Cells
... needed for reproduction and deoxyribonucleic through living cell organism to acid (DNA) • the Controls activities • Serves as a boundary survive including repair of • Presence of genes between the cell and • The animal cell worn-out parts which contain the external contains many tiny hereditary mate ...
... needed for reproduction and deoxyribonucleic through living cell organism to acid (DNA) • the Controls activities • Serves as a boundary survive including repair of • Presence of genes between the cell and • The animal cell worn-out parts which contain the external contains many tiny hereditary mate ...
Science NIOS - WordPress.com
... Class:Related orders make a class. Phylum:A phylum is the largest category with related classes g Kingdom:Kingdom is the largest group of organisms differentiated on very general The bacteria have cell walls (as found in all plant cells) but they have no chlorophyll. (bacteria) It includes bacteria ...
... Class:Related orders make a class. Phylum:A phylum is the largest category with related classes g Kingdom:Kingdom is the largest group of organisms differentiated on very general The bacteria have cell walls (as found in all plant cells) but they have no chlorophyll. (bacteria) It includes bacteria ...
2nd Semester Final Exam Review 2016
... 9. How do prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells differ? The DNA in a prokaryotic cell is not inside a membrane bound nucleus. The DNA in a eukaryotic cell in is a membrane bound nucleus. 10. Name 3 differences between plant and animal cells including the shape. Plant – more rectangular: animal – circular ...
... 9. How do prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells differ? The DNA in a prokaryotic cell is not inside a membrane bound nucleus. The DNA in a eukaryotic cell in is a membrane bound nucleus. 10. Name 3 differences between plant and animal cells including the shape. Plant – more rectangular: animal – circular ...
Body Organization
... » It covers all the inner and outer surfaces of your body » Each internal organ is covered with a layer of this tissue – Nerve tissue » Functions as a messaging system » Carries electrical impulses between your brain and various parts of your body in response to changing conditions – Muscle tissue » ...
... » It covers all the inner and outer surfaces of your body » Each internal organ is covered with a layer of this tissue – Nerve tissue » Functions as a messaging system » Carries electrical impulses between your brain and various parts of your body in response to changing conditions – Muscle tissue » ...
List and tell the function of the parts of a cell
... b. Sexual • Benefits genetic diversity higher rate of survival 2 parents • Disadvantages requires more energy takes a long time Must search for a mate because it requires fertilization 28. List and explain the 4 types of asexual reproduction. a. Budding – exact replica, but smaller at first b. Binar ...
... b. Sexual • Benefits genetic diversity higher rate of survival 2 parents • Disadvantages requires more energy takes a long time Must search for a mate because it requires fertilization 28. List and explain the 4 types of asexual reproduction. a. Budding – exact replica, but smaller at first b. Binar ...
Biology 1 End-of-Course Assessment Practice Test For Multiple
... Which of the following best describes how the process of crossing over during meiosis leads to an increase in genetic diversity? A. During prophase I, DNA replication takes place, and homologous chromosome ...
... Which of the following best describes how the process of crossing over during meiosis leads to an increase in genetic diversity? A. During prophase I, DNA replication takes place, and homologous chromosome ...
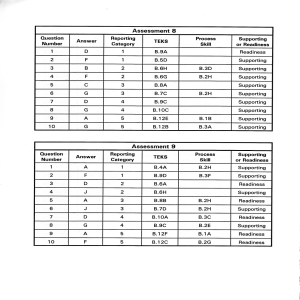
Assessment 8 Assessment I
... Organic compounds found in living organisms are called biomolecules. Study the incomplete table comparing the structures of the four groups of biomolecules found in living organisms. ...
... Organic compounds found in living organisms are called biomolecules. Study the incomplete table comparing the structures of the four groups of biomolecules found in living organisms. ...
Review Guide for Body Systems and Cells Test
... Key Concept 3: The skeletal system holds organs in place, provides a structural support for the body and its muscles, stores minerals and contains materials to make new blood cells. Key Concept 4: The muscular system allows the body to move when attached to bone, and allows movement in internal orga ...
... Key Concept 3: The skeletal system holds organs in place, provides a structural support for the body and its muscles, stores minerals and contains materials to make new blood cells. Key Concept 4: The muscular system allows the body to move when attached to bone, and allows movement in internal orga ...
What You Need to Know for the
... a. All carbohydrates are made from simple sugars (like glucose) and they supply energy. b. Enzymes may break down starches and complex sugars into simple sugars. ...
... a. All carbohydrates are made from simple sugars (like glucose) and they supply energy. b. Enzymes may break down starches and complex sugars into simple sugars. ...
EOC Review Answer Key- Friday
... 6. Why would it be a bad idea to do this? Death of fish 1.03 Formulate and revise scientific explanations and models of biological phenomena using logic and evidence to: explain observations, make inferences and predictions, explain the relationship between evidence and explanation. Bromothymol blue ...
... 6. Why would it be a bad idea to do this? Death of fish 1.03 Formulate and revise scientific explanations and models of biological phenomena using logic and evidence to: explain observations, make inferences and predictions, explain the relationship between evidence and explanation. Bromothymol blue ...
Slide 1
... •Reproduction - formation of another organism. Since viruses cannot reproduce on their own without being inside a host cell, they are not regarded as living organisms. ...
... •Reproduction - formation of another organism. Since viruses cannot reproduce on their own without being inside a host cell, they are not regarded as living organisms. ...
Biology Review PPT
... •Reproduction - formation of another organism. Since viruses cannot reproduce on their own without being inside a host cell, they are not regarded as living organisms. ...
... •Reproduction - formation of another organism. Since viruses cannot reproduce on their own without being inside a host cell, they are not regarded as living organisms. ...
Module 1 (Practice Test)
... It forms short, simple carbon chains. It forms large, complex, diverse molecules. It forms covalent bonds with other carbon atoms It forms covalent bonds than can exist in a single plane ...
... It forms short, simple carbon chains. It forms large, complex, diverse molecules. It forms covalent bonds with other carbon atoms It forms covalent bonds than can exist in a single plane ...
1 - Cloudfront.net
... Frogs and Toads tend to lay many many eggs because there are many hazards between fertalization and full grown frogness! Those eggs that die tend to turn white or opaque. The lucky ones that actually manage to hatch still start out on a journey of many perils. Life starts right as the central yolk s ...
... Frogs and Toads tend to lay many many eggs because there are many hazards between fertalization and full grown frogness! Those eggs that die tend to turn white or opaque. The lucky ones that actually manage to hatch still start out on a journey of many perils. Life starts right as the central yolk s ...
Bio_principles of biology
... • Concept 1.1: Biologists explore life from the microscopic to the global scale • The study of life • Extends from the microscope scale of molecules and cells to the global scale of the entire living planet ...
... • Concept 1.1: Biologists explore life from the microscopic to the global scale • The study of life • Extends from the microscope scale of molecules and cells to the global scale of the entire living planet ...
Strand A - Life Processes and Living Things
... All living things are made up of cells Structure of cells (both plant and animal) Cell membrane: selectively allows substances in and out Nucleus: surrounded by nuclear membrane, contains genetic material, divides for reproduction Cytoplasm contains organelles, small structure that carry out t ...
... All living things are made up of cells Structure of cells (both plant and animal) Cell membrane: selectively allows substances in and out Nucleus: surrounded by nuclear membrane, contains genetic material, divides for reproduction Cytoplasm contains organelles, small structure that carry out t ...
Cells
... The Four Types of Organic Compounds (The Molecules of Life) made from the 6 elements: Carbohydrates: Sugars used for short term energy – major source of energy Lipids: Fats and oils used for long term energy Proteins: Made up of amino acids; used for construction materials and chemical reactio ...
... The Four Types of Organic Compounds (The Molecules of Life) made from the 6 elements: Carbohydrates: Sugars used for short term energy – major source of energy Lipids: Fats and oils used for long term energy Proteins: Made up of amino acids; used for construction materials and chemical reactio ...
Bacteria , Viruses, Protists , and Prions
... molecules and a supply of carbon • Photoheterotrophs: are photosynthetic but also need to take in organic molecules for carbon source ...
... molecules and a supply of carbon • Photoheterotrophs: are photosynthetic but also need to take in organic molecules for carbon source ...
Bacteria, Viruses, Protists, and Prions
... molecules and a supply of carbon • Photoheterotrophs: are photosynthetic but also need to take in organic molecules for carbon source ...
... molecules and a supply of carbon • Photoheterotrophs: are photosynthetic but also need to take in organic molecules for carbon source ...
Biology Midterm Study Guide Ch 1-9 spring 11
... 6. Label the following as science/not science: a. experimenting c. guessing b. observing d. hypothesizing 7. Label the following variables present in Redi’s experiment on spontaneous generation as controlled variable/NOT a controlled variable: a. gauze covering that keeps flies away from meat b. typ ...
... 6. Label the following as science/not science: a. experimenting c. guessing b. observing d. hypothesizing 7. Label the following variables present in Redi’s experiment on spontaneous generation as controlled variable/NOT a controlled variable: a. gauze covering that keeps flies away from meat b. typ ...
Chapter 15: The Cell - Heritage Christian School
... • All living things are made up of one or more cells. • The cell is the functional unit of life. • All living things come from pre-existing cells (Living from living vs. Spontaneous Generation) What does “The Functional Unit of Life” mean? It is the smallest entity that can carry out life functions. ...
... • All living things are made up of one or more cells. • The cell is the functional unit of life. • All living things come from pre-existing cells (Living from living vs. Spontaneous Generation) What does “The Functional Unit of Life” mean? It is the smallest entity that can carry out life functions. ...
Sustainability of Ecosystems Science 10 Test Review Ecologist
... 1. ___________Sunlight_________________ is the ultimate source of energy. 2. Organic soil nutrients contain _________Carbon________________ which is essential for life. ...
... 1. ___________Sunlight_________________ is the ultimate source of energy. 2. Organic soil nutrients contain _________Carbon________________ which is essential for life. ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.