Question Bank Five Kingdom Classification
... 12. Why Euglena has been classified as a plant as well as an animal? Ans. Euglena as a plant shows following features : (i) The body is surrounded by a cell wall. (ii) Chloroplast is present due to which in the presence of sunlight Euglena synthesizes its food. (iii) The pigments of Euglena are ide ...
... 12. Why Euglena has been classified as a plant as well as an animal? Ans. Euglena as a plant shows following features : (i) The body is surrounded by a cell wall. (ii) Chloroplast is present due to which in the presence of sunlight Euglena synthesizes its food. (iii) The pigments of Euglena are ide ...
Course Outline - Roper Mountain Science Center!
... that correlate to the South Carolina Science Academic Standards for seventh grade life science. Course topics are designed to enhance the middle school teacher’s life science knowledge base and provide appropriate lessons for the 7th grade science classroom. Activities are aimed at developing awaren ...
... that correlate to the South Carolina Science Academic Standards for seventh grade life science. Course topics are designed to enhance the middle school teacher’s life science knowledge base and provide appropriate lessons for the 7th grade science classroom. Activities are aimed at developing awaren ...
Chapter 1 (Sections 1-3) Study Guide: Cell Structure and Function
... Cytokinesis: cytoplasm divides List four reasons why mitosis and cell division are important? Growth of many-celled organisms Replacing old cells Reproduction in some organisms Replacing damaged or lost cells How is plant cell cytokines different from animal cell cytokinesis? In animal cells, the ce ...
... Cytokinesis: cytoplasm divides List four reasons why mitosis and cell division are important? Growth of many-celled organisms Replacing old cells Reproduction in some organisms Replacing damaged or lost cells How is plant cell cytokines different from animal cell cytokinesis? In animal cells, the ce ...
Chapter 1 (Sections 1-3) Study Guide: Cell Structure and Function
... Cytokinesis: cytoplasm divides List four reasons why mitosis and cell division are important? Growth of many-celled organisms Replacing old cells Reproduction in some organisms Replacing damaged or lost cells How is plant cell cytokines different from animal cell cytokinesis? In animal cells, the ce ...
... Cytokinesis: cytoplasm divides List four reasons why mitosis and cell division are important? Growth of many-celled organisms Replacing old cells Reproduction in some organisms Replacing damaged or lost cells How is plant cell cytokines different from animal cell cytokinesis? In animal cells, the ce ...
Biology 102 Exam II
... Which phylum includes the largest number of species? All animals are made up of cells considered to be what type of cell? What are the basic stages in a typical animal life cycle? There are two types of development in embryos. What is the type where the embryo resembles the adult form? What is the t ...
... Which phylum includes the largest number of species? All animals are made up of cells considered to be what type of cell? What are the basic stages in a typical animal life cycle? There are two types of development in embryos. What is the type where the embryo resembles the adult form? What is the t ...
Unit One
... things could survive freezing temperatures, but only for a little while; and no living thing could survive boiling temperatures. Life could exist in salt water, but not water that was TOO salty. And life could not exist in highly acid environments (below pH 6) or highly alkaline environments (above ...
... things could survive freezing temperatures, but only for a little while; and no living thing could survive boiling temperatures. Life could exist in salt water, but not water that was TOO salty. And life could not exist in highly acid environments (below pH 6) or highly alkaline environments (above ...
UNIT B Powerpoint-student copy
... Waste removal in the body is done through the organs of the excretory system. (The respiratory and circulatory systems also assist in the process) Ammonia is a chemical waste that the body produces when cells break down protein. The liver converts the ammonia to a less harmful substance called urea. ...
... Waste removal in the body is done through the organs of the excretory system. (The respiratory and circulatory systems also assist in the process) Ammonia is a chemical waste that the body produces when cells break down protein. The liver converts the ammonia to a less harmful substance called urea. ...
Work Booklet Workstations Answers
... of dead or decaying matter. Release digestive enzymes into their environment on dead organic matter to break it down Fungi then absorb the digested food through their cell wall ...
... of dead or decaying matter. Release digestive enzymes into their environment on dead organic matter to break it down Fungi then absorb the digested food through their cell wall ...
MCAS Biology - Fall River Public Schools
... 2 Types of Connective Tissue & How They Attach Muscle to Bone and Bone to Bone ...
... 2 Types of Connective Tissue & How They Attach Muscle to Bone and Bone to Bone ...
Biology EOC review
... - Passive Transport – movement of substances across the plasma membrane without the use of the cell’s energy (with the concentration gradient) 1. DIFFUSION – movement of substances across the plasma membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration 2. OSMOSIS – diffusion of ...
... - Passive Transport – movement of substances across the plasma membrane without the use of the cell’s energy (with the concentration gradient) 1. DIFFUSION – movement of substances across the plasma membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration 2. OSMOSIS – diffusion of ...
1.8_Evolution
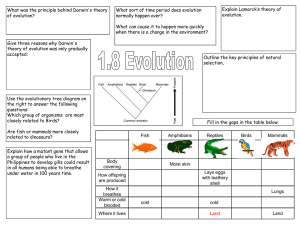
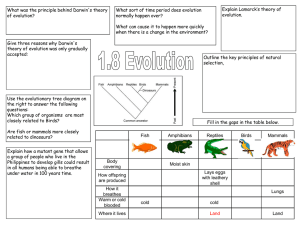
... of evolution? All species evolved from simpler life forms that first developed more than 3 billion years ago Give three reasons why Darwin's theory of evolution was only gradually accepted: •Challenged religion – idea that god made all living organisms •Insufficient evidence at time •Mechanism of in ...
... of evolution? All species evolved from simpler life forms that first developed more than 3 billion years ago Give three reasons why Darwin's theory of evolution was only gradually accepted: •Challenged religion – idea that god made all living organisms •Insufficient evidence at time •Mechanism of in ...
File
... of evolution? All species evolved from simpler life forms that first developed more than 3 billion years ago Give three reasons why Darwin's theory of evolution was only gradually accepted: •Challenged religion – idea that god made all living organisms •Insufficient evidence at time •Mechanism of in ...
... of evolution? All species evolved from simpler life forms that first developed more than 3 billion years ago Give three reasons why Darwin's theory of evolution was only gradually accepted: •Challenged religion – idea that god made all living organisms •Insufficient evidence at time •Mechanism of in ...
HS Life Science Alignment
... externally by environments in which cells exist, including local environments that lead to cell differentiation during the development of multicellular organisms. During the development of complex multicellular organisms, cell differentiation is regulated through the expression of different genes. B ...
... externally by environments in which cells exist, including local environments that lead to cell differentiation during the development of multicellular organisms. During the development of complex multicellular organisms, cell differentiation is regulated through the expression of different genes. B ...
Levels of Organization Notes
... through your small and large intestines before your body rids itself of solid waste. As the food passes through your body, it is digested, and you get important nutrients from the food. Which of the following is the correct term used to describe a group of body parts working together to perform a sp ...
... through your small and large intestines before your body rids itself of solid waste. As the food passes through your body, it is digested, and you get important nutrients from the food. Which of the following is the correct term used to describe a group of body parts working together to perform a sp ...
Objective 2 Taxonomy
... Binomial nomenclature – “2 name system” uses the genus and the species to identify an organism. (homo sapien) Modern taxonomists now classify organisms according to their phylogeny, or evolutionary history. This has become a branch of biology called systematics and uses the following information 1. ...
... Binomial nomenclature – “2 name system” uses the genus and the species to identify an organism. (homo sapien) Modern taxonomists now classify organisms according to their phylogeny, or evolutionary history. This has become a branch of biology called systematics and uses the following information 1. ...
Biology Review
... 6. All organic molecules contain the element ______________. 7. Eukaryotes reproduce asexually by ____________. 8. Eukaryotes reproduce sexually by ____________. 9. Prokaryotes reproduce asexually by ___________ __________. 10. ___________ occurs when a cell loses its ability to control the cell cyc ...
... 6. All organic molecules contain the element ______________. 7. Eukaryotes reproduce asexually by ____________. 8. Eukaryotes reproduce sexually by ____________. 9. Prokaryotes reproduce asexually by ___________ __________. 10. ___________ occurs when a cell loses its ability to control the cell cyc ...
Topic One: Chemistry of Living Things
... A) Water ( _____) : Most common substance in all living things (about 60% of body mass) Needed for chemical reactions (won’t happen in “dry” conditions) Dissolves other molecules into solution, allowing them to be transported through the body. B) Oxygen (______): Needed by most (not all) organis ...
... A) Water ( _____) : Most common substance in all living things (about 60% of body mass) Needed for chemical reactions (won’t happen in “dry” conditions) Dissolves other molecules into solution, allowing them to be transported through the body. B) Oxygen (______): Needed by most (not all) organis ...
Biology End-of-Course Test: Heritage High School 2013
... 2. Provides structural support in plant cells cell wall 3. Store water; are especially large in plants vacule/central vacuole 4. Where photosynthesis takes place chloroplast/chlorophyll 5. Contains chlorophyll (responsible for trapping light energy; green in color) chloroplast 6. Where sugar is made ...
... 2. Provides structural support in plant cells cell wall 3. Store water; are especially large in plants vacule/central vacuole 4. Where photosynthesis takes place chloroplast/chlorophyll 5. Contains chlorophyll (responsible for trapping light energy; green in color) chloroplast 6. Where sugar is made ...
FREE Sample Here - We can offer most test bank and
... Write an essay in PHYSIOLOGICAL terms agreeing with or disagreeing with the following statement from your text: “Reproductive systems are not essential for homeostasis and therefore are not essential for survival of the individual.” ...
... Write an essay in PHYSIOLOGICAL terms agreeing with or disagreeing with the following statement from your text: “Reproductive systems are not essential for homeostasis and therefore are not essential for survival of the individual.” ...
CHAPTER 2: CELL FUNCTION 2.1.
... CHAPTER 2: CELL FUNCTION 2.1. (p. 45) 1. Explain how just a few elements can make up all living things. The most common elements making up all living things are Carbon, Oxygen, Hydrogen, Nitrogen and Phosphorus. These few elements are combined as atoms into molecules that form different compounds. T ...
... CHAPTER 2: CELL FUNCTION 2.1. (p. 45) 1. Explain how just a few elements can make up all living things. The most common elements making up all living things are Carbon, Oxygen, Hydrogen, Nitrogen and Phosphorus. These few elements are combined as atoms into molecules that form different compounds. T ...
Chapter 3 review
... 19.What is an enzymatic protein? In the plasma membrane, it can carry out metabolic reactions directly; some reactions occur as a result of them (like final steps in the electron transport chain) 20.What cellular process is associated with ribosomes? Protein synthesis 21.What is the function of the ...
... 19.What is an enzymatic protein? In the plasma membrane, it can carry out metabolic reactions directly; some reactions occur as a result of them (like final steps in the electron transport chain) 20.What cellular process is associated with ribosomes? Protein synthesis 21.What is the function of the ...
Cells to Body Systems
... • Goal: My goal is to show students through a Powerpoint presentation how cells work together to form body systems. • The text will be used as the main source with the presentation being supplemental. • Web sites used : www.harcourtschool.com and http://trackstar.hprtec.org/main/display.php3?track i ...
... • Goal: My goal is to show students through a Powerpoint presentation how cells work together to form body systems. • The text will be used as the main source with the presentation being supplemental. • Web sites used : www.harcourtschool.com and http://trackstar.hprtec.org/main/display.php3?track i ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.