topic 1 ppt
... moisture, suitable habitat, and exchange of gases Analyze an ecosystem to identify biotic and abiotic components, and describe interactions among these components Describe examples of interaction and interdependency within an ecosystem (identify examples of dependency between species, and ...
... moisture, suitable habitat, and exchange of gases Analyze an ecosystem to identify biotic and abiotic components, and describe interactions among these components Describe examples of interaction and interdependency within an ecosystem (identify examples of dependency between species, and ...
2008 Academic Challenge BIOLOGY TEST
... d. Carbon dioxide fixation takes place during the evening in CAM plants. e. The endoplasmic reticulum may be associated with lipid synthesis, protein synthesis, transport, and detoxification. 38. Match the terms in Column A with the definition that best describes them in Column B. ...
... d. Carbon dioxide fixation takes place during the evening in CAM plants. e. The endoplasmic reticulum may be associated with lipid synthesis, protein synthesis, transport, and detoxification. 38. Match the terms in Column A with the definition that best describes them in Column B. ...
Biology Review
... 6. All organic molecules contain the element ______________. 7. Eukaryotes reproduce asexually by ____________. 8. Eukaryotes reproduce sexually by ____________. 9. Prokaryotes reproduce asexually by ___________ __________. 10. ___________ occurs when a cell loses its ability to control the cell cyc ...
... 6. All organic molecules contain the element ______________. 7. Eukaryotes reproduce asexually by ____________. 8. Eukaryotes reproduce sexually by ____________. 9. Prokaryotes reproduce asexually by ___________ __________. 10. ___________ occurs when a cell loses its ability to control the cell cyc ...
Cells Unit Study Guide
... 19. What is the cell theory? It explains the relationship between cells and living things and states that (1) all living things are composed of cells; (2) Cells are the basic units of structure and function in all living things; (3) all cells are produced from other cells (mitosis and meiosis). 20. ...
... 19. What is the cell theory? It explains the relationship between cells and living things and states that (1) all living things are composed of cells; (2) Cells are the basic units of structure and function in all living things; (3) all cells are produced from other cells (mitosis and meiosis). 20. ...
Macromolecules are very large biomolecules formed by a process of
... Carnivores – eat consumers (meat) Omnivores – eat meat and plants ...
... Carnivores – eat consumers (meat) Omnivores – eat meat and plants ...
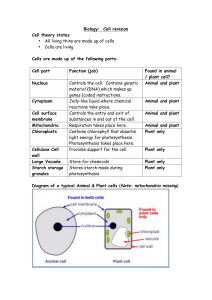
Biology Cell revision
... Biology: Cell revision Cell theory states • All living thins are made up of cells • Cells are living Cells are made up of the following parts: Cell part ...
... Biology: Cell revision Cell theory states • All living thins are made up of cells • Cells are living Cells are made up of the following parts: Cell part ...
1999 AP Biology Exam - Speedway High School
... 46. A number of different phylogenies (evolutionary trees) have been proposed by scientists. These phylogenies are useful because they can be used to (A) determine when two similar populations of a species evolved into two separate species (B) evaluate which groups of organisms may be most closely r ...
... 46. A number of different phylogenies (evolutionary trees) have been proposed by scientists. These phylogenies are useful because they can be used to (A) determine when two similar populations of a species evolved into two separate species (B) evaluate which groups of organisms may be most closely r ...
Goal 6: Cell Theory Review Guide
... and animal cells. Similarities – basically the same size, cell membrane, cytoplasm contains same basic organelles Differences – plant has cell wall, chloroplasts, and a large central vacuole, carries out photosynthesis; animal cell has centrioles obviously there are more, this is just a sample of th ...
... and animal cells. Similarities – basically the same size, cell membrane, cytoplasm contains same basic organelles Differences – plant has cell wall, chloroplasts, and a large central vacuole, carries out photosynthesis; animal cell has centrioles obviously there are more, this is just a sample of th ...
Document
... • Dominant traits always are visible, and are represented by capital letters. • Recessive traits are hidden unless both alleles are the recessive one ...
... • Dominant traits always are visible, and are represented by capital letters. • Recessive traits are hidden unless both alleles are the recessive one ...
Genetic Engineering of Biological Machines
... What other technologies can be used/have been used to address this area? ...
... What other technologies can be used/have been used to address this area? ...
LT #4 I can describe that cells differentiate to form
... differentiate to form specialized cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms. ...
... differentiate to form specialized cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms. ...
Human Body Systems Review answers
... Human Body Systems Review 1. Put the following in order starting with the smallest: organs, organisms, organ systems, cells, tissues ...
... Human Body Systems Review 1. Put the following in order starting with the smallest: organs, organisms, organ systems, cells, tissues ...
Biology model examination for grade 12
... B. NADPH D. A&B 54. Which of the following cannot be recycled in ecosystem? A. Sulphur C. Energy B. H2O D. carbon 55. In a food chain organisms that are found in first trophic level are A. Producers C. Secondary consumers B. primary consumers D. Decomposers 56. A theoretical maximum birth rate of an ...
... B. NADPH D. A&B 54. Which of the following cannot be recycled in ecosystem? A. Sulphur C. Energy B. H2O D. carbon 55. In a food chain organisms that are found in first trophic level are A. Producers C. Secondary consumers B. primary consumers D. Decomposers 56. A theoretical maximum birth rate of an ...
Cells_and_Chemical_Changes_Background_Info_
... Because atoms in compounds occur in definite ratios, scientists can write chemical formulas for substances, such as 1120 for water. Chemists can also classify substances into two broad groups: organic and inorganic. With few exceptions, organic substances contain the element carbon. Inorganic subst ...
... Because atoms in compounds occur in definite ratios, scientists can write chemical formulas for substances, such as 1120 for water. Chemists can also classify substances into two broad groups: organic and inorganic. With few exceptions, organic substances contain the element carbon. Inorganic subst ...
Biological Context
... Note qualifiers: likely, on average, possibly, decreased odds ... Outcomes may not be black-andwhite since one trait can be affected by many genes or variants (polygenic or quantitative trait) ...
... Note qualifiers: likely, on average, possibly, decreased odds ... Outcomes may not be black-andwhite since one trait can be affected by many genes or variants (polygenic or quantitative trait) ...
Fertilization and Development
... – Lungs and other organs undergo changes to prepare for life outside the uterus – Fetus can regulate its body temp. – Central nervous system and lungs complete development ...
... – Lungs and other organs undergo changes to prepare for life outside the uterus – Fetus can regulate its body temp. – Central nervous system and lungs complete development ...
Unit 6
... c) Possess a single “naked” chromosome consisting of a single DNA molecule without the proteins found in eukaryotes. d) Most of prokaryotes contain on the cell wall peptidoglycans. e) Another feature important in describing prokaryotes is their ability to survive in the presence or absence of oxygen ...
... c) Possess a single “naked” chromosome consisting of a single DNA molecule without the proteins found in eukaryotes. d) Most of prokaryotes contain on the cell wall peptidoglycans. e) Another feature important in describing prokaryotes is their ability to survive in the presence or absence of oxygen ...
What You Absolutely Need to Know To Pass the NYS Living
... 9. Cells! All living this are of one or more cells! Reproduction is the only life process that does NOT have to occur for the organism to remain ...
... 9. Cells! All living this are of one or more cells! Reproduction is the only life process that does NOT have to occur for the organism to remain ...
Cellular Energy Unit Vocabulary California Standard
... California Standard Set 1. Cell Biology 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism’s cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: f. f. Students know usable energy is captured from sunlight by ...
... California Standard Set 1. Cell Biology 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism’s cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: f. f. Students know usable energy is captured from sunlight by ...
Human Bio 11 – Dalesandro
... 2) What blood cell contains histamine and controls allergic reactions? Describe this cell’s appearance. 3) What blood cell controls clotting and stops you from bleeding? Describe this cell’s appearance. 4) What blood cell produces antibodies to fight off invading organisms like bacteria and viruses? ...
... 2) What blood cell contains histamine and controls allergic reactions? Describe this cell’s appearance. 3) What blood cell controls clotting and stops you from bleeding? Describe this cell’s appearance. 4) What blood cell produces antibodies to fight off invading organisms like bacteria and viruses? ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.