Cells - Livingstone High School
... • Goal: My goal is to show students through a Powerpoint presentation how cells work together to form body systems. • The text will be used as the main source with the presentation being supplemental. • Web sites used : www.harcourtschool.com and http://trackstar.hprtec.org/main/display.php3?track i ...
... • Goal: My goal is to show students through a Powerpoint presentation how cells work together to form body systems. • The text will be used as the main source with the presentation being supplemental. • Web sites used : www.harcourtschool.com and http://trackstar.hprtec.org/main/display.php3?track i ...
Diversity of Life Notes
... 2. Sac fungi produce spores in a small, saclike structure called an ascus; yeasts can also reproduce by budding. 3. A zygospore fungus produces spores in a round case called a sporangium. 4. Some fungi, like penicillin, are called imperfect because they have never been observed reproducing sexually ...
... 2. Sac fungi produce spores in a small, saclike structure called an ascus; yeasts can also reproduce by budding. 3. A zygospore fungus produces spores in a round case called a sporangium. 4. Some fungi, like penicillin, are called imperfect because they have never been observed reproducing sexually ...
4 Types Biological Molecules in plants and animals
... catalysts for chemical reactions in living things. Thousands of chemical reactions are going on in your body EACH SECOND. Sugar does not turn into water and carbon dioxide by itself. Outside the body, this reaction would need a flame. How does the body do this at a lower temperature? Enzymes allow y ...
... catalysts for chemical reactions in living things. Thousands of chemical reactions are going on in your body EACH SECOND. Sugar does not turn into water and carbon dioxide by itself. Outside the body, this reaction would need a flame. How does the body do this at a lower temperature? Enzymes allow y ...
Chapter 11
... Enzymes allow your body to initiate chemical reactions at low temperature and to control the rate of reactions. Catalyst – a chemical that allows a reaction to have a much lower activation energy than it normally would The body controls the rate of reactions by regulating the amount of enzymes produ ...
... Enzymes allow your body to initiate chemical reactions at low temperature and to control the rate of reactions. Catalyst – a chemical that allows a reaction to have a much lower activation energy than it normally would The body controls the rate of reactions by regulating the amount of enzymes produ ...
Building Macromolecules Notes
... the formation of polymers, Water (H2O), is released or is the by-product of the reaction. c. The breakdown of some complex molecules, such as polymers, occurs through a process known as hydrolysis. i. Hydrolysis is the reverse of a condensation reaction. The addition of water, to some polymers can b ...
... the formation of polymers, Water (H2O), is released or is the by-product of the reaction. c. The breakdown of some complex molecules, such as polymers, occurs through a process known as hydrolysis. i. Hydrolysis is the reverse of a condensation reaction. The addition of water, to some polymers can b ...
Cloudfront.net
... 11. The diagram shows a pyramid of energy, with producers at the bottom and higher order consumers occupying successively higher levels. As energy is transferred from producers to first-order, second-order, and higher-order consumers, a large amount of energy is converted to thermal energy and give ...
... 11. The diagram shows a pyramid of energy, with producers at the bottom and higher order consumers occupying successively higher levels. As energy is transferred from producers to first-order, second-order, and higher-order consumers, a large amount of energy is converted to thermal energy and give ...
unit3examstudyguide
... – Hyphae is responsible for releasing enzymes to break down nutrients and then absorbing the nutrients - Sexual reproduction: the hyphae grows above ground and creates a stolon. - Stolons of 2 different fungi connect to make gametangia - Gametangia make gametes and gametes make baby fungi ...
... – Hyphae is responsible for releasing enzymes to break down nutrients and then absorbing the nutrients - Sexual reproduction: the hyphae grows above ground and creates a stolon. - Stolons of 2 different fungi connect to make gametangia - Gametangia make gametes and gametes make baby fungi ...
Cells and Systems Notes
... TOPIC 1 : LIVING ORGANISMS Characteristics of Living Things Scientists agree that living organisms have some of the following characteristics: ...
... TOPIC 1 : LIVING ORGANISMS Characteristics of Living Things Scientists agree that living organisms have some of the following characteristics: ...
Chemical reactions take place inside cells.
... and hydrogen. Inside cells, sugar molecules are broken down. This process provides usable energy for the cell. Simple sugar molecules can also be linked into long chains to form more complex carbohydrates, such as starch, cellulose, and glycogen. Starch and cellulose are complex carbohydrates made b ...
... and hydrogen. Inside cells, sugar molecules are broken down. This process provides usable energy for the cell. Simple sugar molecules can also be linked into long chains to form more complex carbohydrates, such as starch, cellulose, and glycogen. Starch and cellulose are complex carbohydrates made b ...
The Tiny Living World Around Us
... • Most cells can be seen with microscopes • Basic microscopes have magnifying lenses that can let us see microscopic cells/organisms • Really powerful microscopes let us see the small details of cells • Special microscopes or microscope slides can let us see things while they are still alive ...
... • Most cells can be seen with microscopes • Basic microscopes have magnifying lenses that can let us see microscopic cells/organisms • Really powerful microscopes let us see the small details of cells • Special microscopes or microscope slides can let us see things while they are still alive ...
Science Cumulative Review 1 Unicellular and Multicellular
... c. Human d. Grass How are the cells of a multicellular organism most different from the cells of a unicellular organism? a. Cells in a multicellular organism are specialized while cells in a unicellular organism are generalized. b. Cells in a unicellular organism are specialized while cells in a mul ...
... c. Human d. Grass How are the cells of a multicellular organism most different from the cells of a unicellular organism? a. Cells in a multicellular organism are specialized while cells in a unicellular organism are generalized. b. Cells in a unicellular organism are specialized while cells in a mul ...
Name Date ______ Hour ______ Living Things Study Guide 1
... Physical digestion = biting and chewing , chemical digestion = saliva 31. What type or types of digestion occur in the stomach? Give example(s) mechanical digestion = squeezing and churning of food into smaller pieces by muscles of stomach Chemical digestion = acids and enzymes in the stomach break ...
... Physical digestion = biting and chewing , chemical digestion = saliva 31. What type or types of digestion occur in the stomach? Give example(s) mechanical digestion = squeezing and churning of food into smaller pieces by muscles of stomach Chemical digestion = acids and enzymes in the stomach break ...
REVIEW QUESTIONS- Structure and Function of
... muscular-skeletal system but would not operate without the _____________ system providing the impulses (signals) that cause the muscles to act. A. respiratory B. reproductive C. nervous D. cardiovascular ...
... muscular-skeletal system but would not operate without the _____________ system providing the impulses (signals) that cause the muscles to act. A. respiratory B. reproductive C. nervous D. cardiovascular ...
Chabot College
... its bioethical impact in our modern world. Designed for non-majors in biology or the biomedical sciences. 3 hours lecture, 3 hours laboratory. Prerequisite Skills: None Expected Outcomes for Students: Upon completion of the course, the student should be able to: ...
... its bioethical impact in our modern world. Designed for non-majors in biology or the biomedical sciences. 3 hours lecture, 3 hours laboratory. Prerequisite Skills: None Expected Outcomes for Students: Upon completion of the course, the student should be able to: ...
Chapter Review
... lung.The lungs are made of several kinds of tissue, such as the bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli. Sample answer: The main reason that multicellular organisms can be more complex than unicellular organisms is that multicellular organisms have cell specialization. Specialization allows some cells to ...
... lung.The lungs are made of several kinds of tissue, such as the bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli. Sample answer: The main reason that multicellular organisms can be more complex than unicellular organisms is that multicellular organisms have cell specialization. Specialization allows some cells to ...
Chapter 1 Lesson 1~ Cells cells split or divide to form new cells 1 ½
... 1 ½ million organisms have been identified (over 1 billion have not been named) ...
... 1 ½ million organisms have been identified (over 1 billion have not been named) ...
EOC_STUDY_GUIDE_adapted_from_Gaston_County
... - Unicellular – organism that exists as a singular, independent cell - Multicellular – organism that exists as specialized groups of cells; cells are organized into tissues that perform the same function; tissues form organs and organs make up an organ system - Prokaryote – has nuclear material in t ...
... - Unicellular – organism that exists as a singular, independent cell - Multicellular – organism that exists as specialized groups of cells; cells are organized into tissues that perform the same function; tissues form organs and organs make up an organ system - Prokaryote – has nuclear material in t ...
Test Review Sheet: Biology Final – 09 Know the steps of the
... A sample of digestive juice was removed from the stomach of a pig. The juice was placed in a test tube along with some grains of wheat. A second test tube was set up containing an equal number of wheat grains, with distilled water rather than digestive juice. The test tubes were kept for 8 hours at ...
... A sample of digestive juice was removed from the stomach of a pig. The juice was placed in a test tube along with some grains of wheat. A second test tube was set up containing an equal number of wheat grains, with distilled water rather than digestive juice. The test tubes were kept for 8 hours at ...
Unit 3 Review Sheet
... o How do cell receptors play a role in this example? Why does insulin only bind to insulin cell receptors? - Guard Cells (Plants) *You should be able to describe (in detail) at least one of the feedback mechanism. Dynamic Equilibrium - What happens if an organism cannot maintain homeostasis through ...
... o How do cell receptors play a role in this example? Why does insulin only bind to insulin cell receptors? - Guard Cells (Plants) *You should be able to describe (in detail) at least one of the feedback mechanism. Dynamic Equilibrium - What happens if an organism cannot maintain homeostasis through ...
Cells - WordPress.com
... The combination of the two genes decides the baby’s features. If you have 2 different genes for a characteristic like hair or eye colour, one colour is usually dominant over the other, and that colour will feature. ...
... The combination of the two genes decides the baby’s features. If you have 2 different genes for a characteristic like hair or eye colour, one colour is usually dominant over the other, and that colour will feature. ...
Parent Curriculum Night Handout
... • Biology S and Biology G • E-mail is best way to contact me • Also work as Athletic Trainer ...
... • Biology S and Biology G • E-mail is best way to contact me • Also work as Athletic Trainer ...
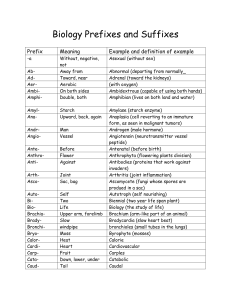
Biology Prefixes and Suffixes
... that forms the epidermis of roots and shoots) pseudoscience (practice that resembles science but is considered to be without scientific foundation) psychology (science that deals with mental processes and behavior) pteridology (the study of ferns) puberty (stage of adolescence marked by the function ...
... that forms the epidermis of roots and shoots) pseudoscience (practice that resembles science but is considered to be without scientific foundation) psychology (science that deals with mental processes and behavior) pteridology (the study of ferns) puberty (stage of adolescence marked by the function ...
EOC Review 2011 #5
... Jean Baptiste Lamarck: Created the Theory of Use and Disuse and Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics. He stated the more an organism uses a structure, the more developed it will become. If they are not using the structure, it will eventually disappear. He then stated that any trait/characterist ...
... Jean Baptiste Lamarck: Created the Theory of Use and Disuse and Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics. He stated the more an organism uses a structure, the more developed it will become. If they are not using the structure, it will eventually disappear. He then stated that any trait/characterist ...
Slide 1
... • What are the four macromolecules found in living organisms? • What are the structure (subunits) and function of these 4 macromolecules? • How are proteins organized and how is their shape important to their function? • How are DNA similar and how are they different? ...
... • What are the four macromolecules found in living organisms? • What are the structure (subunits) and function of these 4 macromolecules? • How are proteins organized and how is their shape important to their function? • How are DNA similar and how are they different? ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.